Note
Click here to download the full example code
Display sensitivity maps for EEG and MEG sensors¶
Sensitivity maps can be produced from forward operators that indicate how well different sensor types will be able to detect neural currents from different regions of the brain.
To get started with forward modeling see Head model and forward computation.
# Author: Eric Larson <larson.eric.d@gmail.com>
#
# License: BSD (3-clause)
import numpy as np
import mne
from mne.datasets import sample
from mne.source_space import compute_distance_to_sensors
from mne.source_estimate import SourceEstimate
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
print(__doc__)
data_path = sample.data_path()
fwd_fname = data_path + '/MEG/sample/sample_audvis-meg-eeg-oct-6-fwd.fif'
subjects_dir = data_path + '/subjects'
# Read the forward solutions with surface orientation
fwd = mne.read_forward_solution(fwd_fname)
mne.convert_forward_solution(fwd, surf_ori=True, copy=False)
leadfield = fwd['sol']['data']
print("Leadfield size : %d x %d" % leadfield.shape)
Out:
Reading forward solution from /home/circleci/mne_data/MNE-sample-data/MEG/sample/sample_audvis-meg-eeg-oct-6-fwd.fif...
Reading a source space...
Computing patch statistics...
Patch information added...
Distance information added...
[done]
Reading a source space...
Computing patch statistics...
Patch information added...
Distance information added...
[done]
2 source spaces read
Desired named matrix (kind = 3523) not available
Read MEG forward solution (7498 sources, 306 channels, free orientations)
Desired named matrix (kind = 3523) not available
Read EEG forward solution (7498 sources, 60 channels, free orientations)
MEG and EEG forward solutions combined
Source spaces transformed to the forward solution coordinate frame
Average patch normals will be employed in the rotation to the local surface coordinates....
Converting to surface-based source orientations...
[done]
Leadfield size : 366 x 22494
Compute sensitivity maps
grad_map = mne.sensitivity_map(fwd, ch_type='grad', mode='fixed')
mag_map = mne.sensitivity_map(fwd, ch_type='mag', mode='fixed')
eeg_map = mne.sensitivity_map(fwd, ch_type='eeg', mode='fixed')
Out:
204 out of 366 channels remain after picking
102 out of 366 channels remain after picking
60 out of 366 channels remain after picking
Adding average EEG reference projection.
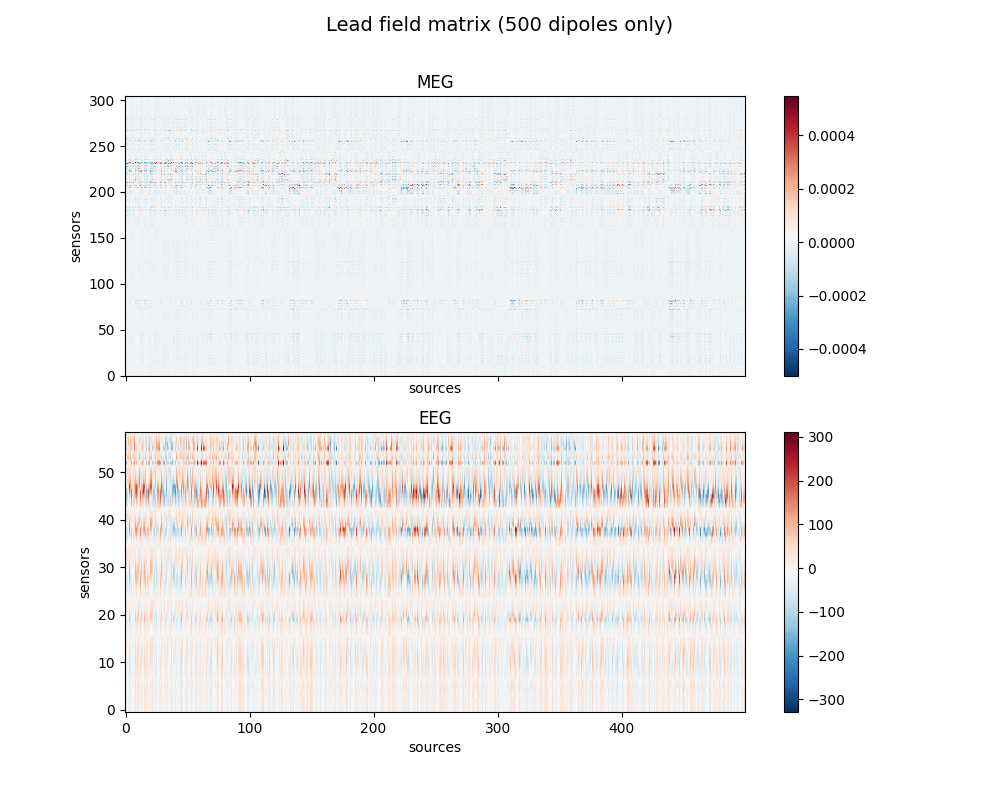
Show gain matrix a.k.a. leadfield matrix with sensitivity map
picks_meg = mne.pick_types(fwd['info'], meg=True, eeg=False)
picks_eeg = mne.pick_types(fwd['info'], meg=False, eeg=True)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(10, 8), sharex=True)
fig.suptitle('Lead field matrix (500 dipoles only)', fontsize=14)
for ax, picks, ch_type in zip(axes, [picks_meg, picks_eeg], ['meg', 'eeg']):
im = ax.imshow(leadfield[picks, :500], origin='lower', aspect='auto',
cmap='RdBu_r')
ax.set_title(ch_type.upper())
ax.set_xlabel('sources')
ax.set_ylabel('sensors')
fig.colorbar(im, ax=ax)
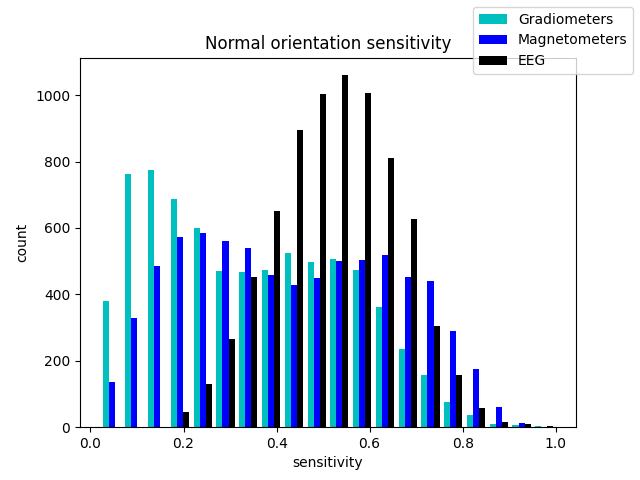
fig_2, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.hist([grad_map.data.ravel(), mag_map.data.ravel(), eeg_map.data.ravel()],
bins=20, label=['Gradiometers', 'Magnetometers', 'EEG'],
color=['c', 'b', 'k'])
fig_2.legend()
ax.set(title='Normal orientation sensitivity',
xlabel='sensitivity', ylabel='count')
brain_sens = grad_map.plot(
subjects_dir=subjects_dir, clim=dict(lims=[0, 50, 100]), figure=1)
brain_sens.add_text(0.1, 0.9, 'Gradiometer sensitivity', 'title', font_size=16)
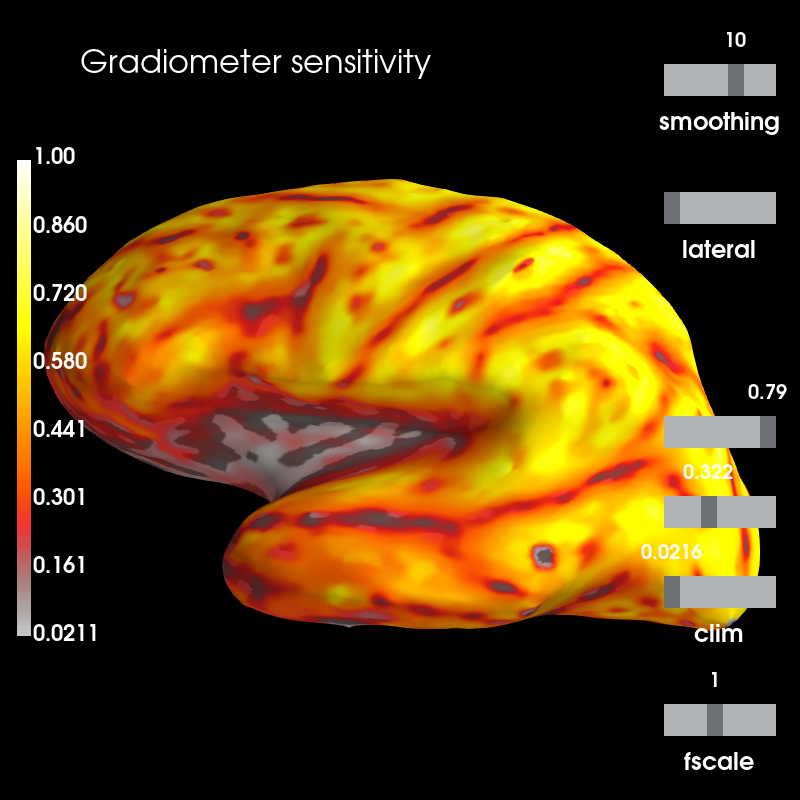
Out:
Using control points [0.02108201 0.32186553 1. ]
Compare sensitivity map with distribution of source depths
# source space with vertices
src = fwd['src']
# Compute minimum Euclidean distances between vertices and MEG sensors
depths = compute_distance_to_sensors(src=src, info=fwd['info'],
picks=picks_meg).min(axis=1)
maxdep = depths.max() # for scaling
vertices = [src[0]['vertno'], src[1]['vertno']]
depths_map = SourceEstimate(data=depths, vertices=vertices, tmin=0.,
tstep=1.)
brain_dep = depths_map.plot(
subject='sample', subjects_dir=subjects_dir,
clim=dict(kind='value', lims=[0, maxdep / 2., maxdep]), figure=2)
brain_dep.add_text(0.1, 0.9, 'Source depth (m)', 'title', font_size=16)
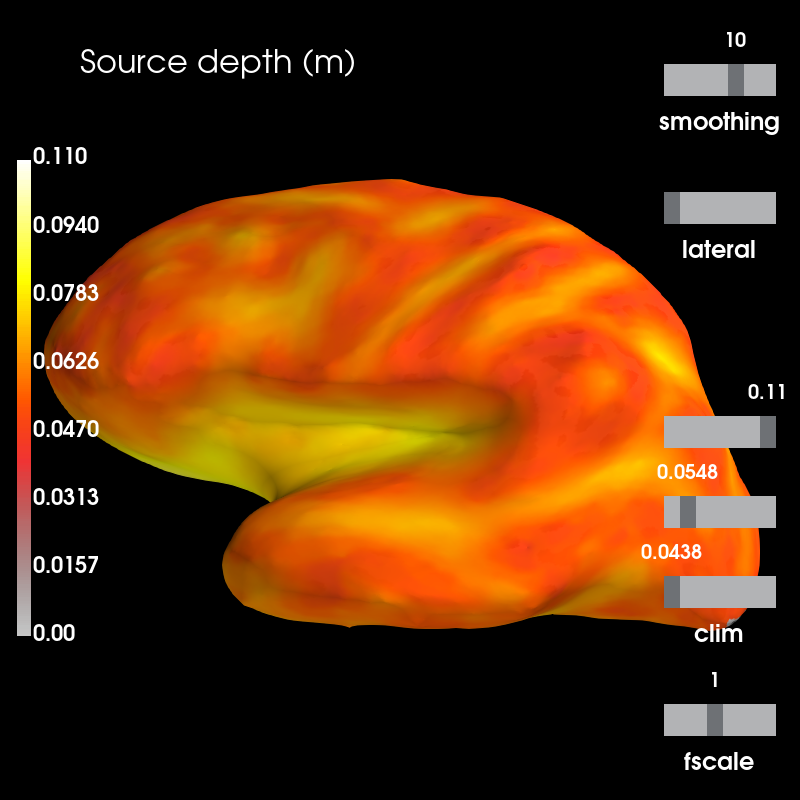
Sensitivity is likely to co-vary with the distance between sources to sensors. To determine the strength of this relationship, we can compute the correlation between source depth and sensitivity values.
corr = np.corrcoef(depths, grad_map.data[:, 0])[0, 1]
print('Correlation between source depth and gradiomter sensitivity values: %f.'
% corr)
Out:
Correlation between source depth and gradiomter sensitivity values: -0.815476.
Gradiometer sensitiviy is highest close to the sensors, and decreases rapidly with inreasing source depth. This is confirmed by the high negative correlation between the two.
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 16.205 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 134 MB