Note
Click here to download the full example code
Plotting topographic maps of evoked data¶
Load evoked data and plot topomaps for selected time points using multiple additional options.
# Authors: Christian Brodbeck <christianbrodbeck@nyu.edu>
# Tal Linzen <linzen@nyu.edu>
# Denis A. Engeman <denis.engemann@gmail.com>
# Mikołaj Magnuski <mmagnuski@swps.edu.pl>
# Eric Larson <larson.eric.d@gmail.com>
#
# License: BSD (3-clause)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mne.datasets import sample
from mne import read_evokeds
print(__doc__)
path = sample.data_path()
fname = path + '/MEG/sample/sample_audvis-ave.fif'
# load evoked corresponding to a specific condition
# from the fif file and subtract baseline
condition = 'Left Auditory'
evoked = read_evokeds(fname, condition=condition, baseline=(None, 0))
Out:
Reading /home/circleci/mne_data/MNE-sample-data/MEG/sample/sample_audvis-ave.fif ...
Read a total of 4 projection items:
PCA-v1 (1 x 102) active
PCA-v2 (1 x 102) active
PCA-v3 (1 x 102) active
Average EEG reference (1 x 60) active
Found the data of interest:
t = -199.80 ... 499.49 ms (Left Auditory)
0 CTF compensation matrices available
nave = 55 - aspect type = 100
Projections have already been applied. Setting proj attribute to True.
Applying baseline correction (mode: mean)
Basic plot_topomap() options¶
We plot evoked topographies using mne.Evoked.plot_topomap(). The first
argument, times allows to specify time instants (in seconds!) for which
topographies will be shown. We select timepoints from 50 to 150 ms with a
step of 20ms and plot magnetometer data:
times = np.arange(0.05, 0.151, 0.02)
evoked.plot_topomap(times, ch_type='mag', time_unit='s')
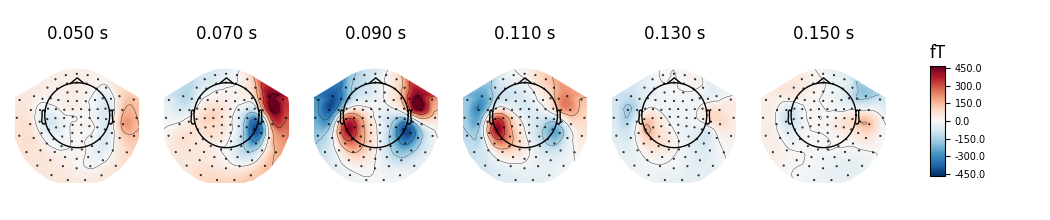
Out:
Removing projector <Projection | Average EEG reference, active : True, n_channels : 60>
If times is set to None at most 10 regularly spaced topographies will be shown:
evoked.plot_topomap(ch_type='mag', time_unit='s')
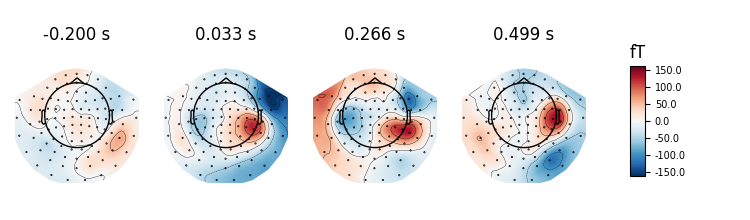
Out:
Removing projector <Projection | Average EEG reference, active : True, n_channels : 60>
We can use nrows and ncols parameter to create multiline plots
with more timepoints.
all_times = np.arange(-0.2, 0.5, 0.03)
evoked.plot_topomap(all_times, ch_type='mag', time_unit='s',
ncols=8, nrows='auto')
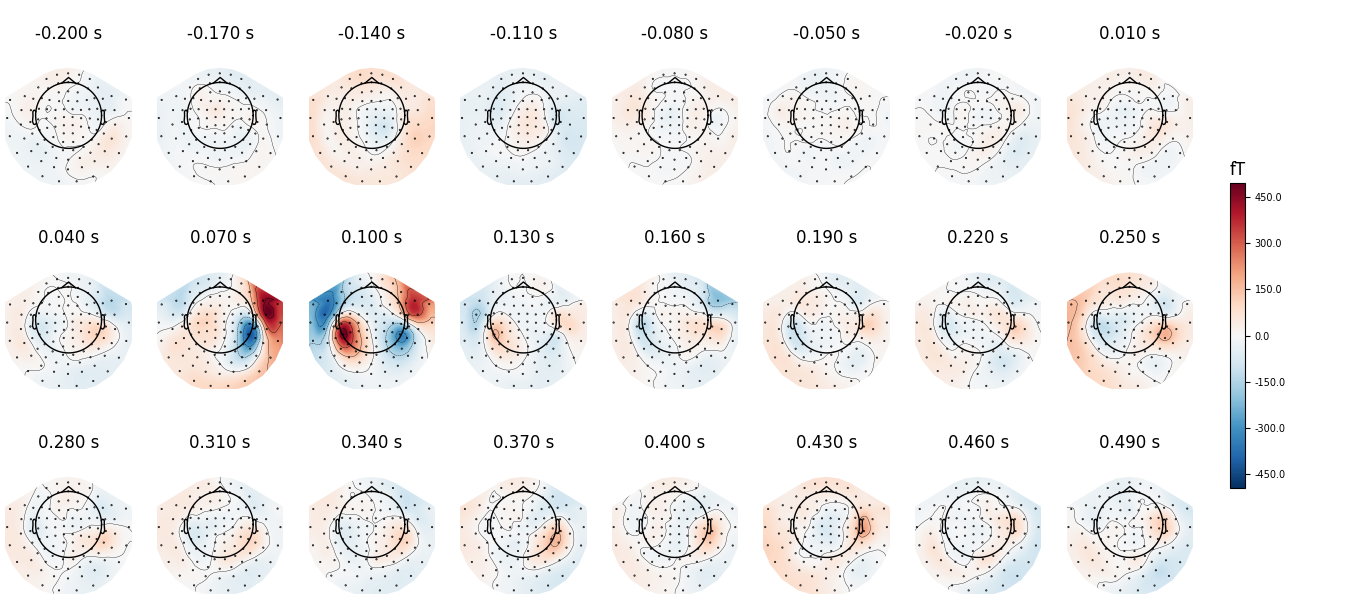
Out:
Removing projector <Projection | Average EEG reference, active : True, n_channels : 60>
Instead of showing topographies at specific time points we can compute averages of 50 ms bins centered on these time points to reduce the noise in the topographies:
evoked.plot_topomap(times, ch_type='mag', average=0.05, time_unit='s')
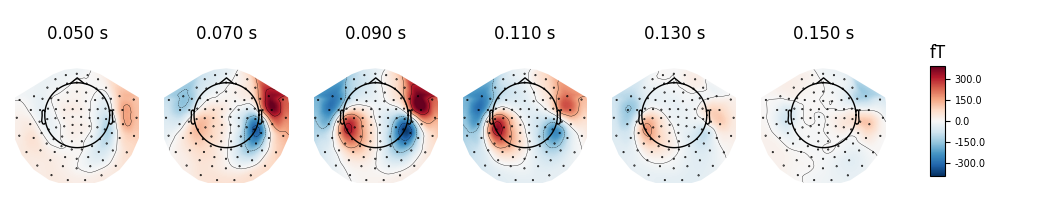
Out:
Removing projector <Projection | Average EEG reference, active : True, n_channels : 60>
We can plot gradiometer data (plots the RMS for each pair of gradiometers)
evoked.plot_topomap(times, ch_type='grad', time_unit='s')
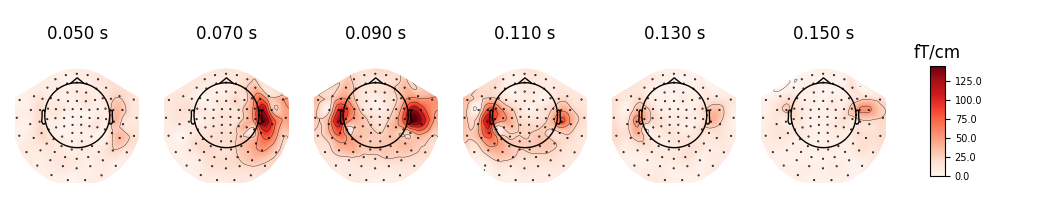
Out:
Removing projector <Projection | PCA-v1, active : True, n_channels : 102>
Removing projector <Projection | PCA-v2, active : True, n_channels : 102>
Removing projector <Projection | PCA-v3, active : True, n_channels : 102>
Removing projector <Projection | Average EEG reference, active : True, n_channels : 60>
Additional plot_topomap() options¶
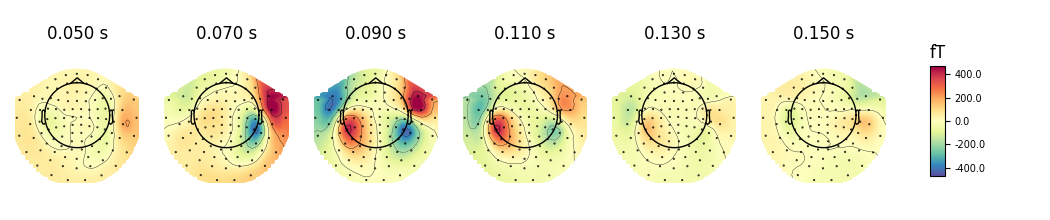
We can also use a range of various mne.viz.plot_topomap() arguments
that control how the topography is drawn. For example:
cmap- to specify the color mapres- to control the resolution of the topographies (lower resolution means faster plotting)outlines='skirt'to see the topography stretched beyond the head circlecontoursto define how many contour lines should be plotted
evoked.plot_topomap(times, ch_type='mag', cmap='Spectral_r', res=32,
outlines='skirt', contours=4, time_unit='s')
Out:
Removing projector <Projection | Average EEG reference, active : True, n_channels : 60>
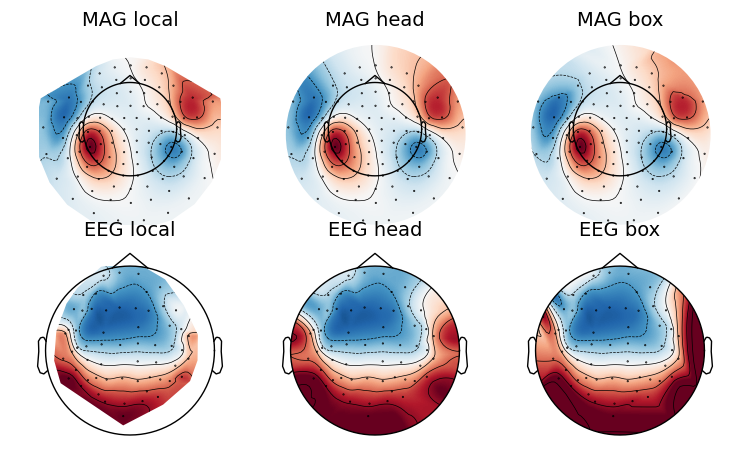
If you look at the edges of the head circle of a single topomap you’ll see the effect of extrapolation. There are three extrapolation modes:
extrapolate='local'extrapolates only to points close to the sensors.extrapolate='head'extrapolates out to the head head circle.extrapolate='box'extrapolates to a large box stretching beyond the head circle.
The default value extrapolate='auto' will use 'local' for MEG sensors
and 'head' otherwise. Here we show each option:
extrapolations = ['local', 'head', 'box']
fig, axes = plt.subplots(figsize=(7.5, 4.5), nrows=2, ncols=3)
# Here we look at EEG channels, and use a custom head sphere to get all the
# sensors to be well within the drawn head surface
for axes_row, ch_type in zip(axes, ('mag', 'eeg')):
for ax, extr in zip(axes_row, extrapolations):
evoked.plot_topomap(0.1, ch_type=ch_type, size=2, extrapolate=extr,
axes=ax, show=False, colorbar=False,
sphere=(0., 0., 0., 0.09))
ax.set_title('%s %s' % (ch_type.upper(), extr), fontsize=14)
fig.tight_layout()
Out:
Removing projector <Projection | Average EEG reference, active : True, n_channels : 60>
Removing projector <Projection | Average EEG reference, active : True, n_channels : 60>
Removing projector <Projection | Average EEG reference, active : True, n_channels : 60>
Removing projector <Projection | PCA-v1, active : True, n_channels : 102>
Removing projector <Projection | PCA-v2, active : True, n_channels : 102>
Removing projector <Projection | PCA-v3, active : True, n_channels : 102>
Removing projector <Projection | PCA-v1, active : True, n_channels : 102>
Removing projector <Projection | PCA-v2, active : True, n_channels : 102>
Removing projector <Projection | PCA-v3, active : True, n_channels : 102>
Removing projector <Projection | PCA-v1, active : True, n_channels : 102>
Removing projector <Projection | PCA-v2, active : True, n_channels : 102>
Removing projector <Projection | PCA-v3, active : True, n_channels : 102>
More advanced usage¶
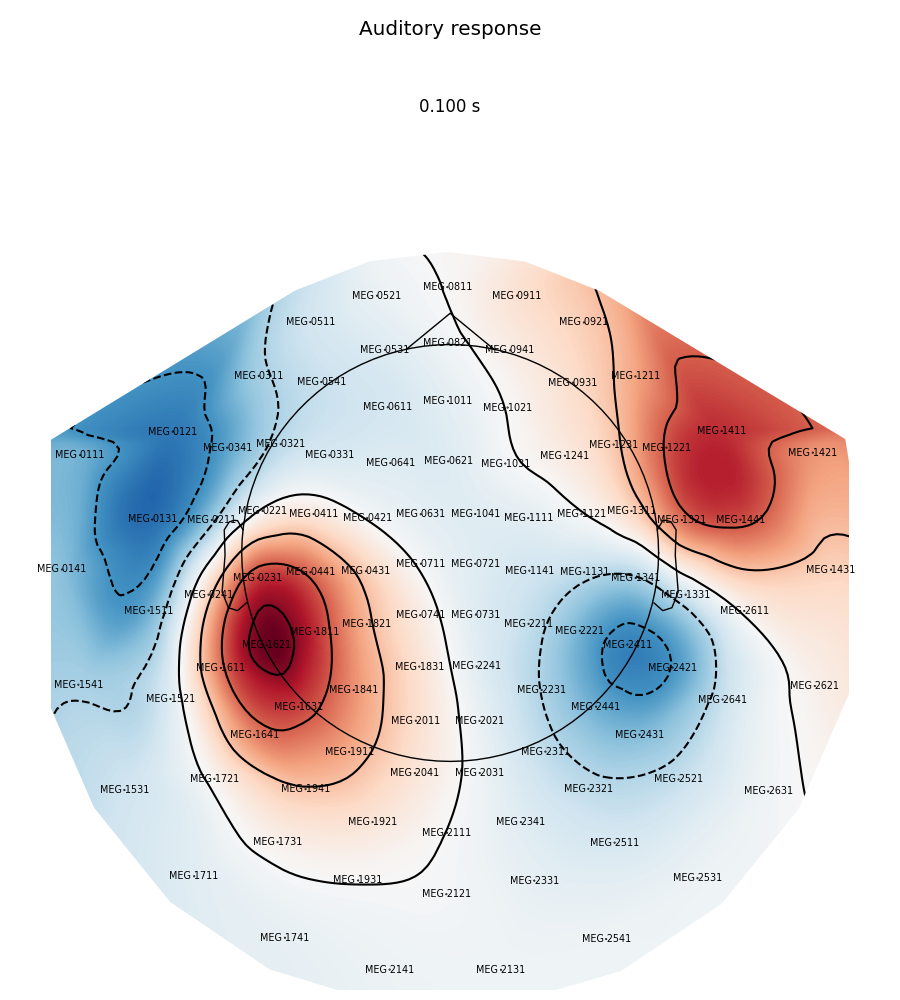
Now we plot magnetometer data as topomap at a single time point: 100 ms post-stimulus, add channel labels, title and adjust plot margins:
evoked.plot_topomap(0.1, ch_type='mag', show_names=True, colorbar=False,
size=6, res=128, title='Auditory response',
time_unit='s')
plt.subplots_adjust(left=0.01, right=0.99, bottom=0.01, top=0.88)
Out:
Removing projector <Projection | Average EEG reference, active : True, n_channels : 60>
Animating the topomap¶
Instead of using a still image we can plot magnetometer data as an animation, which animates properly only in matplotlib interactive mode.
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 22.337 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 8 MB