Note
Click here to download the full example code
Time-frequency beamforming using DICS¶
Compute DICS source power 1 in a grid of time-frequency windows.
# Author: Roman Goj <roman.goj@gmail.com>
#
# License: BSD (3-clause)
import mne
from mne.event import make_fixed_length_events
from mne.datasets import sample
from mne.time_frequency import csd_fourier
from mne.beamformer import tf_dics
from mne.viz import plot_source_spectrogram
print(__doc__)
data_path = sample.data_path()
raw_fname = data_path + '/MEG/sample/sample_audvis_raw.fif'
noise_fname = data_path + '/MEG/sample/ernoise_raw.fif'
event_fname = data_path + '/MEG/sample/sample_audvis_raw-eve.fif'
fname_fwd = data_path + '/MEG/sample/sample_audvis-meg-eeg-oct-6-fwd.fif'
subjects_dir = data_path + '/subjects'
label_name = 'Aud-lh'
fname_label = data_path + '/MEG/sample/labels/%s.label' % label_name
Read raw data
raw = mne.io.read_raw_fif(raw_fname, preload=True)
raw.info['bads'] = ['MEG 2443'] # 1 bad MEG channel
# Pick a selection of magnetometer channels. A subset of all channels was used
# to speed up the example. For a solution based on all MEG channels use
# meg=True, selection=None and add mag=4e-12 to the reject dictionary.
left_temporal_channels = mne.read_selection('Left-temporal')
picks = mne.pick_types(raw.info, meg='mag', eeg=False, eog=False,
stim=False, exclude='bads',
selection=left_temporal_channels)
raw.pick_channels([raw.ch_names[pick] for pick in picks])
reject = dict(mag=4e-12)
# Re-normalize our empty-room projectors, which should be fine after
# subselection
raw.info.normalize_proj()
# Setting time windows. Note that tmin and tmax are set so that time-frequency
# beamforming will be performed for a wider range of time points than will
# later be displayed on the final spectrogram. This ensures that all time bins
# displayed represent an average of an equal number of time windows.
tmin, tmax, tstep = -0.5, 0.75, 0.05 # s
tmin_plot, tmax_plot = -0.3, 0.5 # s
# Read epochs
event_id = 1
events = mne.read_events(event_fname)
epochs = mne.Epochs(raw, events, event_id, tmin, tmax,
baseline=None, preload=True, proj=True, reject=reject)
# Read empty room noise raw data
raw_noise = mne.io.read_raw_fif(noise_fname, preload=True)
raw_noise.info['bads'] = ['MEG 2443'] # 1 bad MEG channel
raw_noise.pick_channels([raw_noise.ch_names[pick] for pick in picks])
raw_noise.info.normalize_proj()
# Create noise epochs and make sure the number of noise epochs corresponds to
# the number of data epochs
events_noise = make_fixed_length_events(raw_noise, event_id)
epochs_noise = mne.Epochs(raw_noise, events_noise, event_id, tmin_plot,
tmax_plot, baseline=None, preload=True, proj=True,
reject=reject)
epochs_noise.info.normalize_proj()
epochs_noise.apply_proj()
# then make sure the number of epochs is the same
epochs_noise = epochs_noise[:len(epochs.events)]
# Read forward operator
forward = mne.read_forward_solution(fname_fwd)
# Read label
label = mne.read_label(fname_label)
Out:
Opening raw data file /home/circleci/mne_data/MNE-sample-data/MEG/sample/sample_audvis_raw.fif...
Read a total of 3 projection items:
PCA-v1 (1 x 102) idle
PCA-v2 (1 x 102) idle
PCA-v3 (1 x 102) idle
Range : 25800 ... 192599 = 42.956 ... 320.670 secs
Ready.
Reading 0 ... 166799 = 0.000 ... 277.714 secs...
Not setting metadata
Not setting metadata
72 matching events found
No baseline correction applied
Created an SSP operator (subspace dimension = 3)
3 projection items activated
Loading data for 72 events and 751 original time points ...
0 bad epochs dropped
Opening raw data file /home/circleci/mne_data/MNE-sample-data/MEG/sample/ernoise_raw.fif...
Isotrak not found
Read a total of 3 projection items:
PCA-v1 (1 x 102) idle
PCA-v2 (1 x 102) idle
PCA-v3 (1 x 102) idle
Range : 19800 ... 85867 = 32.966 ... 142.965 secs
Ready.
Reading 0 ... 66067 = 0.000 ... 109.999 secs...
Not setting metadata
Not setting metadata
110 matching events found
No baseline correction applied
Created an SSP operator (subspace dimension = 3)
3 projection items activated
Loading data for 110 events and 481 original time points ...
1 bad epochs dropped
Projections have already been applied. Setting proj attribute to True.
Reading forward solution from /home/circleci/mne_data/MNE-sample-data/MEG/sample/sample_audvis-meg-eeg-oct-6-fwd.fif...
Reading a source space...
Computing patch statistics...
Patch information added...
Distance information added...
[done]
Reading a source space...
Computing patch statistics...
Patch information added...
Distance information added...
[done]
2 source spaces read
Desired named matrix (kind = 3523) not available
Read MEG forward solution (7498 sources, 306 channels, free orientations)
Desired named matrix (kind = 3523) not available
Read EEG forward solution (7498 sources, 60 channels, free orientations)
MEG and EEG forward solutions combined
Source spaces transformed to the forward solution coordinate frame
Time-frequency beamforming based on DICS
# Setting frequency bins as in Dalal et al. 2008
freq_bins = [(4, 12), (12, 30), (30, 55), (65, 300)] # Hz
win_lengths = [0.3, 0.2, 0.15, 0.1] # s
# Then set FFTs length for each frequency range.
# Should be a power of 2 to be faster.
n_ffts = [256, 128, 128, 128]
# Subtract evoked response prior to computation?
subtract_evoked = False
# Calculating noise cross-spectral density from empty room noise for each
# frequency bin and the corresponding time window length. To calculate noise
# from the baseline period in the data, change epochs_noise to epochs
noise_csds = []
for freq_bin, win_length, n_fft in zip(freq_bins, win_lengths, n_ffts):
noise_csd = csd_fourier(epochs_noise, fmin=freq_bin[0], fmax=freq_bin[1],
tmin=-win_length, tmax=0, n_fft=n_fft)
noise_csds.append(noise_csd.sum())
# Computing DICS solutions for time-frequency windows in a label in source
# space for faster computation, use label=None for full solution
stcs = tf_dics(epochs, forward, noise_csds, tmin, tmax, tstep, win_lengths,
freq_bins=freq_bins, subtract_evoked=subtract_evoked,
n_ffts=n_ffts, reg=0.05, label=label, inversion='matrix')
# Plotting source spectrogram for source with maximum activity
# Note that tmin and tmax are set to display a time range that is smaller than
# the one for which beamforming estimates were calculated. This ensures that
# all time bins shown are a result of smoothing across an identical number of
# time windows.
plot_source_spectrogram(stcs, freq_bins, tmin=tmin_plot, tmax=tmax_plot,
source_index=None, colorbar=True)
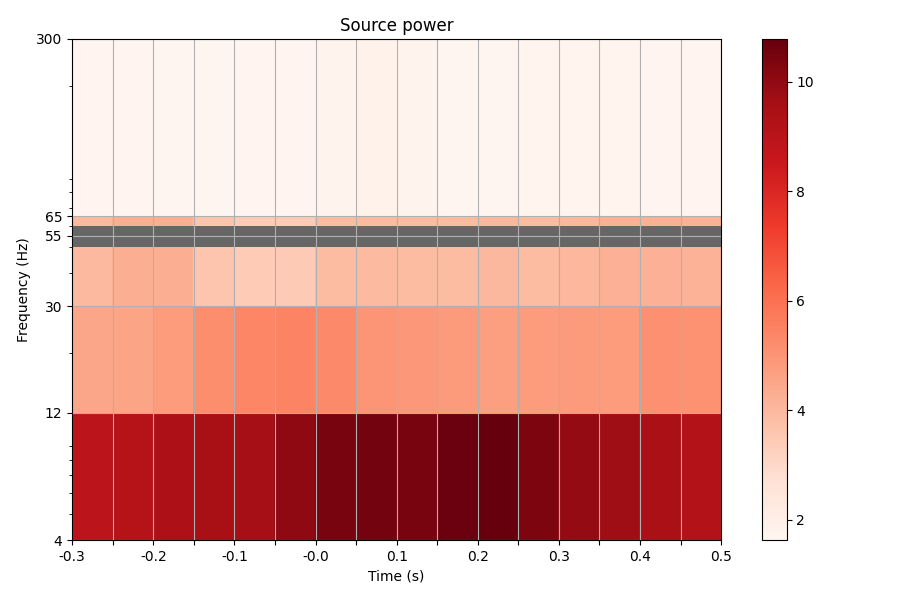
Out:
Computing cross-spectral density from epochs...
0%| | CSD epoch blocks : 0/72 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
36%|###6 | CSD epoch blocks : 26/72 [00:00<00:00, 1621.83it/s]
83%|########3 | CSD epoch blocks : 60/72 [00:00<00:00, 1862.08it/s]
100%|##########| CSD epoch blocks : 72/72 [00:00<00:00, 1881.66it/s]
[done]
Computing cross-spectral density from epochs...
0%| | CSD epoch blocks : 0/72 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
43%|####3 | CSD epoch blocks : 31/72 [00:00<00:00, 1873.21it/s]
69%|######9 | CSD epoch blocks : 50/72 [00:00<00:00, 1506.03it/s]
100%|##########| CSD epoch blocks : 72/72 [00:00<00:00, 1636.63it/s]
[done]
Computing cross-spectral density from epochs...
0%| | CSD epoch blocks : 0/72 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
44%|####4 | CSD epoch blocks : 32/72 [00:00<00:00, 1989.88it/s]
90%|######### | CSD epoch blocks : 65/72 [00:00<00:00, 2002.41it/s]
100%|##########| CSD epoch blocks : 72/72 [00:00<00:00, 1983.06it/s]
[done]
Computing cross-spectral density from epochs...
0%| | CSD epoch blocks : 0/72 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
18%|#8 | CSD epoch blocks : 13/72 [00:00<00:00, 776.84it/s]
33%|###3 | CSD epoch blocks : 24/72 [00:00<00:00, 698.40it/s]
46%|####5 | CSD epoch blocks : 33/72 [00:00<00:00, 639.33it/s]
64%|######3 | CSD epoch blocks : 46/72 [00:00<00:00, 679.41it/s]
82%|########1 | CSD epoch blocks : 59/72 [00:00<00:00, 706.46it/s]
100%|##########| CSD epoch blocks : 72/72 [00:00<00:00, 725.22it/s]
100%|##########| CSD epoch blocks : 72/72 [00:00<00:00, 719.48it/s]
[done]
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -500 to -200 ms, in frequency range 4 to 12 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -450 to -150 ms, in frequency range 4 to 12 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -400 to -100 ms, in frequency range 4 to 12 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -350 to -49 ms, in frequency range 4 to 12 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -300 to 0 ms, in frequency range 4 to 12 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -250 to 49 ms, in frequency range 4 to 12 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -199 to 100 ms, in frequency range 4 to 12 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -149 to 150 ms, in frequency range 4 to 12 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -99 to 200 ms, in frequency range 4 to 12 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -49 to 250 ms, in frequency range 4 to 12 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 0 to 300 ms, in frequency range 4 to 12 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 50 to 350 ms, in frequency range 4 to 12 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 100 to 400 ms, in frequency range 4 to 12 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 150 to 450 ms, in frequency range 4 to 12 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 200 to 500 ms, in frequency range 4 to 12 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 250 to 550 ms, in frequency range 4 to 12 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 300 to 600 ms, in frequency range 4 to 12 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 350 to 650 ms, in frequency range 4 to 12 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 400 to 700 ms, in frequency range 4 to 12 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 450 to 750 ms, in frequency range 4 to 12 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -500 to -300 ms, in frequency range 12 to 30 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -450 to -250 ms, in frequency range 12 to 30 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -400 to -200 ms, in frequency range 12 to 30 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -350 to -149 ms, in frequency range 12 to 30 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -300 to -99 ms, in frequency range 12 to 30 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -250 to -49 ms, in frequency range 12 to 30 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -199 to 0 ms, in frequency range 12 to 30 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -149 to 50 ms, in frequency range 12 to 30 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -99 to 100 ms, in frequency range 12 to 30 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -49 to 150 ms, in frequency range 12 to 30 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 0 to 200 ms, in frequency range 12 to 30 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 50 to 250 ms, in frequency range 12 to 30 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 100 to 300 ms, in frequency range 12 to 30 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 150 to 350 ms, in frequency range 12 to 30 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 200 to 400 ms, in frequency range 12 to 30 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 250 to 450 ms, in frequency range 12 to 30 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 300 to 500 ms, in frequency range 12 to 30 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 350 to 550 ms, in frequency range 12 to 30 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 400 to 600 ms, in frequency range 12 to 30 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 450 to 650 ms, in frequency range 12 to 30 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 500 to 700 ms, in frequency range 12 to 30 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 550 to 750 ms, in frequency range 12 to 30 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -500 to -350 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -450 to -300 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -400 to -250 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -350 to -199 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -300 to -150 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -250 to -100 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -199 to -49 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -149 to 0 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -99 to 50 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -49 to 100 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 0 to 150 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 50 to 200 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 100 to 250 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 150 to 300 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 200 to 350 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 250 to 400 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 300 to 450 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 350 to 500 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 400 to 550 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 450 to 600 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 500 to 650 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 550 to 700 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 600 to 750 ms, in frequency range 30 to 55 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -500 to -400 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -450 to -350 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -400 to -300 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -350 to -249 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -300 to -199 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -250 to -150 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -199 to -99 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -149 to -49 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -99 to 0 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window -49 to 50 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 0 to 100 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 50 to 150 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 100 to 200 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 150 to 250 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 200 to 300 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 250 to 350 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 300 to 400 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 350 to 450 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 400 to 500 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 450 to 550 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 500 to 600 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 550 to 650 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 600 to 700 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
Computing time-frequency DICS beamformer for time window 650 to 750 ms, in frequency range 65 to 300 Hz
References¶
- 1
Sarang S. Dalal, Adrian G. Guggisberg, Erik Edwards, Kensuke Sekihara, Anne M. Findlay, Ryan T. Canolty, Mitchel S. Berger, Robert T. Knight, Nicholas M. Barbaro, Heidi E. Kirsch, and Srikantan S. Nagarajan. Five-dimensional neuroimaging: localization of the time–frequency dynamics of cortical activity. NeuroImage, 40(4):1686–1700, 2008. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.01.023.
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 23.773 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 487 MB