Note
Click here to download the full example code
Corrupt known signal with point spread¶
The aim of this tutorial is to demonstrate how to put a known signal at a
desired location(s) in a mne.SourceEstimate and then corrupt the
signal with point-spread by applying a forward and inverse solution.
import os.path as op
import numpy as np
import mne
from mne.datasets import sample
from mne.minimum_norm import read_inverse_operator, apply_inverse
from mne.simulation import simulate_stc, simulate_evoked
First, we set some parameters.
seed = 42
# parameters for inverse method
method = 'sLORETA'
snr = 3.
lambda2 = 1.0 / snr ** 2
# signal simulation parameters
# do not add extra noise to the known signals
nave = np.inf
T = 100
times = np.linspace(0, 1, T)
dt = times[1] - times[0]
# Paths to MEG data
data_path = sample.data_path()
subjects_dir = op.join(data_path, 'subjects')
fname_fwd = op.join(data_path, 'MEG', 'sample',
'sample_audvis-meg-oct-6-fwd.fif')
fname_inv = op.join(data_path, 'MEG', 'sample',
'sample_audvis-meg-oct-6-meg-fixed-inv.fif')
fname_evoked = op.join(data_path, 'MEG', 'sample',
'sample_audvis-ave.fif')
Load the MEG data¶
fwd = mne.read_forward_solution(fname_fwd)
fwd = mne.convert_forward_solution(fwd, force_fixed=True, surf_ori=True,
use_cps=False)
fwd['info']['bads'] = []
inv_op = read_inverse_operator(fname_inv)
raw = mne.io.read_raw_fif(op.join(data_path, 'MEG', 'sample',
'sample_audvis_raw.fif'))
raw.set_eeg_reference(projection=True)
events = mne.find_events(raw)
event_id = {'Auditory/Left': 1, 'Auditory/Right': 2}
epochs = mne.Epochs(raw, events, event_id, baseline=(None, 0), preload=True)
epochs.info['bads'] = []
evoked = epochs.average()
labels = mne.read_labels_from_annot('sample', subjects_dir=subjects_dir)
label_names = [label.name for label in labels]
n_labels = len(labels)
Out:
Reading forward solution from /home/circleci/mne_data/MNE-sample-data/MEG/sample/sample_audvis-meg-oct-6-fwd.fif...
Reading a source space...
Computing patch statistics...
Patch information added...
Distance information added...
[done]
Reading a source space...
Computing patch statistics...
Patch information added...
Distance information added...
[done]
2 source spaces read
Desired named matrix (kind = 3523) not available
Read MEG forward solution (7498 sources, 306 channels, free orientations)
Source spaces transformed to the forward solution coordinate frame
Changing to fixed-orientation forward solution with surface-based source orientations...
[done]
Reading inverse operator decomposition from /home/circleci/mne_data/MNE-sample-data/MEG/sample/sample_audvis-meg-oct-6-meg-fixed-inv.fif...
Reading inverse operator info...
[done]
Reading inverse operator decomposition...
[done]
305 x 305 full covariance (kind = 1) found.
Read a total of 4 projection items:
PCA-v1 (1 x 102) active
PCA-v2 (1 x 102) active
PCA-v3 (1 x 102) active
Average EEG reference (1 x 60) active
Noise covariance matrix read.
7498 x 7498 diagonal covariance (kind = 2) found.
Source covariance matrix read.
Did not find the desired covariance matrix (kind = 6)
7498 x 7498 diagonal covariance (kind = 5) found.
Depth priors read.
Did not find the desired covariance matrix (kind = 3)
Reading a source space...
Computing patch statistics...
Patch information added...
Distance information added...
[done]
Reading a source space...
Computing patch statistics...
Patch information added...
Distance information added...
[done]
2 source spaces read
Read a total of 4 projection items:
PCA-v1 (1 x 102) active
PCA-v2 (1 x 102) active
PCA-v3 (1 x 102) active
Average EEG reference (1 x 60) active
Source spaces transformed to the inverse solution coordinate frame
Opening raw data file /home/circleci/mne_data/MNE-sample-data/MEG/sample/sample_audvis_raw.fif...
Read a total of 3 projection items:
PCA-v1 (1 x 102) idle
PCA-v2 (1 x 102) idle
PCA-v3 (1 x 102) idle
Range : 25800 ... 192599 = 42.956 ... 320.670 secs
Ready.
Adding average EEG reference projection.
1 projection items deactivated
320 events found
Event IDs: [ 1 2 3 4 5 32]
Not setting metadata
Not setting metadata
145 matching events found
Setting baseline interval to [-0.19979521315838786, 0.0] sec
Applying baseline correction (mode: mean)
Created an SSP operator (subspace dimension = 4)
4 projection items activated
Loading data for 145 events and 421 original time points ...
0 bad epochs dropped
Reading labels from parcellation...
read 34 labels from /home/circleci/mne_data/MNE-sample-data/subjects/sample/label/lh.aparc.annot
read 34 labels from /home/circleci/mne_data/MNE-sample-data/subjects/sample/label/rh.aparc.annot
Estimate the background noise covariance from the baseline period¶
cov = mne.compute_covariance(epochs, tmin=None, tmax=0.)
Out:
Computing rank from data with rank=None
Using tolerance 1.4e-08 (2.2e-16 eps * 306 dim * 2.1e+05 max singular value)
Estimated rank (mag + grad): 303
MEG: rank 303 computed from 306 data channels with 3 projectors
Using tolerance 4.9e-11 (2.2e-16 eps * 60 dim * 3.7e+03 max singular value)
Estimated rank (eeg): 59
EEG: rank 59 computed from 60 data channels with 1 projector
Created an SSP operator (subspace dimension = 4)
Setting small MEG eigenvalues to zero (without PCA)
Setting small EEG eigenvalues to zero (without PCA)
Reducing data rank from 366 -> 362
Estimating covariance using EMPIRICAL
Done.
Number of samples used : 17545
[done]
Generate sinusoids in two spatially distant labels¶
# The known signal is all zero-s off of the two labels of interest
signal = np.zeros((n_labels, T))
idx = label_names.index('inferiorparietal-lh')
signal[idx, :] = 1e-7 * np.sin(5 * 2 * np.pi * times)
idx = label_names.index('rostralmiddlefrontal-rh')
signal[idx, :] = 1e-7 * np.sin(7 * 2 * np.pi * times)
Find the center vertices in source space of each label¶
We want the known signal in each label to only be active at the center. We create a mask for each label that is 1 at the center vertex and 0 at all other vertices in the label. This mask is then used when simulating source-space data.
hemi_to_ind = {'lh': 0, 'rh': 1}
for i, label in enumerate(labels):
# The `center_of_mass` function needs labels to have values.
labels[i].values.fill(1.)
# Restrict the eligible vertices to be those on the surface under
# consideration and within the label.
surf_vertices = fwd['src'][hemi_to_ind[label.hemi]]['vertno']
restrict_verts = np.intersect1d(surf_vertices, label.vertices)
com = labels[i].center_of_mass(subject='sample',
subjects_dir=subjects_dir,
restrict_vertices=restrict_verts,
surf='white')
# Convert the center of vertex index from surface vertex list to Label's
# vertex list.
cent_idx = np.where(label.vertices == com)[0][0]
# Create a mask with 1 at center vertex and zeros elsewhere.
labels[i].values.fill(0.)
labels[i].values[cent_idx] = 1.
Create source-space data with known signals¶
Put known signals onto surface vertices using the array of signals and the label masks (stored in labels[i].values).
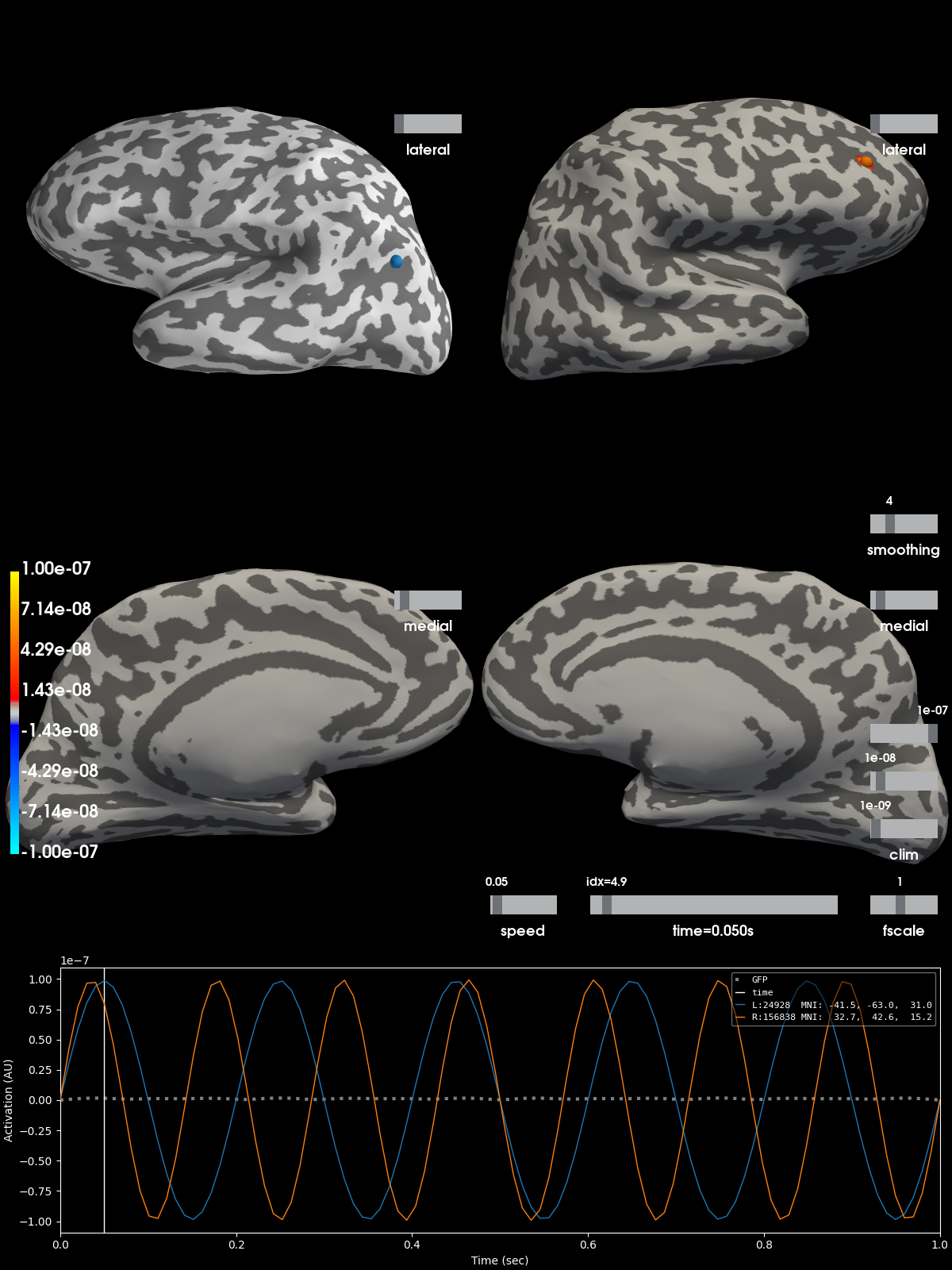
Plot original signals¶
Note that the original signals are highly concentrated (point) sources.
kwargs = dict(subjects_dir=subjects_dir, hemi='split', smoothing_steps=4,
time_unit='s', initial_time=0.05, size=1200,
views=['lat', 'med'])
clim = dict(kind='value', pos_lims=[1e-9, 1e-8, 1e-7])
brain_gen = stc_gen.plot(clim=clim, **kwargs)
Simulate sensor-space signals¶
Use the forward solution and add Gaussian noise to simulate sensor-space
(evoked) data from the known source-space signals. The amount of noise is
controlled by nave (higher values imply less noise).
evoked_gen = simulate_evoked(fwd, stc_gen, evoked.info, cov, nave,
random_state=seed)
# Map the simulated sensor-space data to source-space using the inverse
# operator.
stc_inv = apply_inverse(evoked_gen, inv_op, lambda2, method=method)
Out:
Projecting source estimate to sensor space...
[done]
4 projection items deactivated
Created an SSP operator (subspace dimension = 3)
4 projection items activated
SSP projectors applied...
Preparing the inverse operator for use...
Scaled noise and source covariance from nave = 1 to nave = 1
Created the regularized inverter
Created an SSP operator (subspace dimension = 3)
Created the whitener using a noise covariance matrix with rank 302 (3 small eigenvalues omitted)
Computing noise-normalization factors (sLORETA)...
[done]
Applying inverse operator to ""...
Picked 305 channels from the data
Computing inverse...
Eigenleads need to be weighted ...
Computing residual...
Explained 99.7% variance
sLORETA...
[done]
Plot the point-spread of corrupted signal¶
Notice that after applying the forward- and inverse-operators to the known point sources that the point sources have spread across the source-space. This spread is due to the minimum norm solution so that the signal leaks to nearby vertices with similar orientations so that signal ends up crossing the sulci and gyri.
brain_inv = stc_inv.plot(**kwargs)
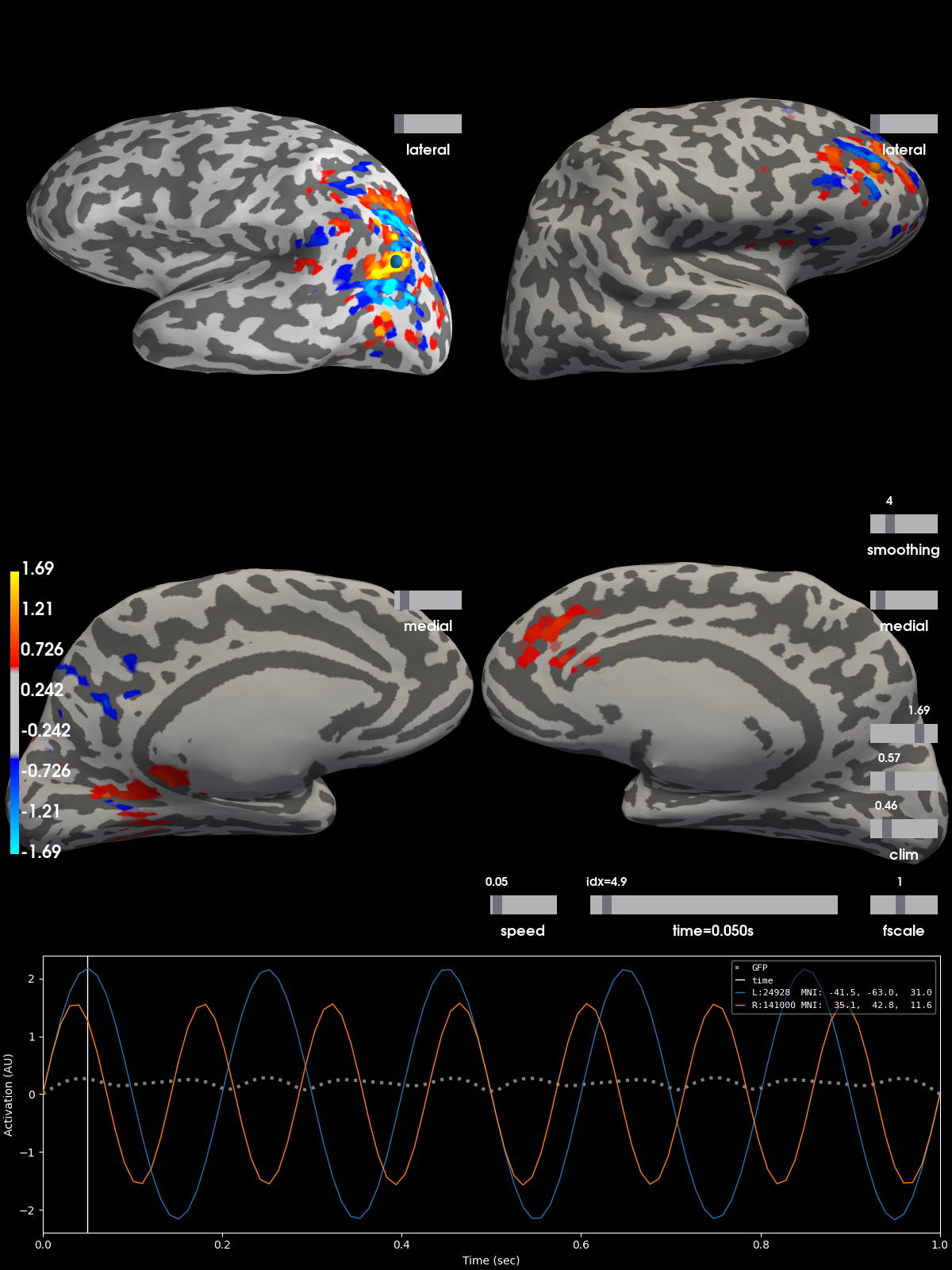
Out:
Using control points [0.45968308 0.57021267 1.69354621]
Exercises¶
Change the
methodparameter to either'dSPM'or'MNE'to explore the effect of the inverse method.Try setting
evoked_snrto a small, finite value, e.g. 3., to see the effect of noise.
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 36.625 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 400 MB