Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
HF-SEF dataset#
This example looks at high-frequency SEF responses.
# Author: Jussi Nurminen (jnu@iki.fi)
#
# License: BSD-3-Clause
import mne
import os
from mne.datasets import hf_sef
fname_evoked = os.path.join(hf_sef.data_path(), "MEG/subject_b/hf_sef_15min-ave.fif")
print(__doc__)
Read evoked data
Found the data of interest:
t = -50.00 ... 250.00 ms (SEF)
0 CTF compensation matrices available
nave = 2790 - aspect type = 100
No projector specified for this dataset. Please consider the method self.add_proj.
Create a highpass filtered version
evoked_hp = evoked.copy()
evoked_hp.filter(l_freq=300, h_freq=None)
Setting up high-pass filter at 3e+02 Hz
FIR filter parameters
---------------------
Designing a one-pass, zero-phase, non-causal highpass filter:
- Windowed time-domain design (firwin) method
- Hamming window with 0.0194 passband ripple and 53 dB stopband attenuation
- Lower passband edge: 300.00
- Lower transition bandwidth: 75.00 Hz (-6 dB cutoff frequency: 262.50 Hz)
- Filter length: 133 samples (0.044 s)
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 17 tasks | elapsed: 0.0s
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 71 tasks | elapsed: 0.0s
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 161 tasks | elapsed: 0.1s
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 287 tasks | elapsed: 0.1s
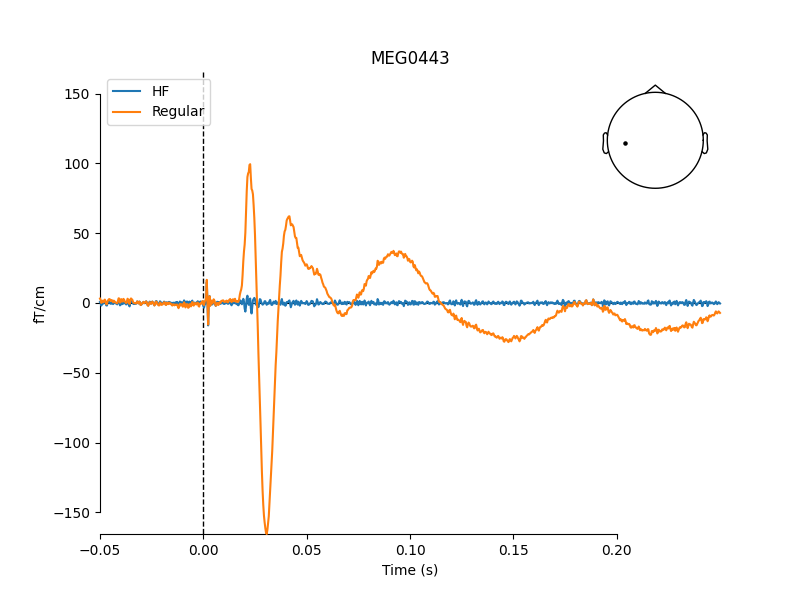
Compare high-pass filtered and unfiltered data on a single channel
ch = "MEG0443"
pick = evoked.ch_names.index(ch)
edi = {"HF": evoked_hp, "Regular": evoked}
mne.viz.plot_compare_evokeds(edi, picks=pick)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 5.340 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 10 MB