Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Morph surface source estimate#
This example demonstrates how to morph an individual subject’s
mne.SourceEstimate to a common reference space. We achieve this using
mne.SourceMorph. Pre-computed data will be morphed based on
a spherical representation of the cortex computed using the spherical
registration of FreeSurfer
(https://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/SurfaceRegAndTemplates)
1. This
transform will be used to morph the surface vertices of the subject towards the
reference vertices. Here we will use ‘fsaverage’ as a reference space (see
https://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/FsAverage).
The transformation will be applied to the surface source estimate. A plot
depicting the successful morph will be created for the spherical and inflated
surface representation of 'fsaverage', overlaid with the morphed surface
source estimate.
Note
For background information about morphing see Morphing and averaging source estimates.
# Author: Tommy Clausner <tommy.clausner@gmail.com>
#
# License: BSD-3-Clause
import mne
from mne.datasets import sample
print(__doc__)
Setup paths
data_path = sample.data_path()
sample_dir = data_path / "MEG" / "sample"
subjects_dir = data_path / "subjects"
fname_src = subjects_dir / "sample" / "bem" / "sample-oct-6-src.fif"
fname_fwd = sample_dir / "sample_audvis-meg-oct-6-fwd.fif"
fname_fsaverage_src = subjects_dir / "fsaverage" / "bem" / "fsaverage-ico-5-src.fif"
fname_stc = sample_dir / "sample_audvis-meg"
Load example data
# Read stc from file
stc = mne.read_source_estimate(fname_stc, subject="sample")
Setting up SourceMorph for SourceEstimate#
In MNE, surface source estimates represent the source space simply as
lists of vertices (see The SourceEstimate data structure).
This list can either be obtained from mne.SourceSpaces (src) or from
the stc itself. If you use the source space, be sure to use the
source space from the forward or inverse operator, because vertices
can be excluded during forward computation due to proximity to the BEM
inner skull surface:
src_orig = mne.read_source_spaces(fname_src)
print(src_orig) # n_used=4098, 4098
fwd = mne.read_forward_solution(fname_fwd)
print(fwd["src"]) # n_used=3732, 3766
print([len(v) for v in stc.vertices])
Reading a source space...
Computing patch statistics...
Patch information added...
Distance information added...
[done]
Reading a source space...
Computing patch statistics...
Patch information added...
Distance information added...
[done]
2 source spaces read
<SourceSpaces: [<surface (lh), n_vertices=155407, n_used=4098>, <surface (rh), n_vertices=156866, n_used=4098>] MRI (surface RAS) coords, subject 'sample', ~27.5 MB>
Reading forward solution from /home/circleci/mne_data/MNE-sample-data/MEG/sample/sample_audvis-meg-oct-6-fwd.fif...
Reading a source space...
Computing patch statistics...
Patch information added...
Distance information added...
[done]
Reading a source space...
Computing patch statistics...
Patch information added...
Distance information added...
[done]
2 source spaces read
Desired named matrix (kind = 3523) not available
Read MEG forward solution (7498 sources, 306 channels, free orientations)
Source spaces transformed to the forward solution coordinate frame
<SourceSpaces: [<surface (lh), n_vertices=155407, n_used=3732>, <surface (rh), n_vertices=156866, n_used=3766>] head coords, subject 'sample', ~31.0 MB>
[3732, 3766]
We also need to specify the set of vertices to morph to. This can be done
using the spacing parameter, but for consistency it’s better to pass the
src_to parameter.
Note
Since the default values of mne.compute_source_morph() are
spacing=5, subject_to='fsaverage', in this example
we could actually omit the src_to and subject_to arguments
below. The ico-5 fsaverage source space contains the
special values [np.arange(10242)] * 2, but in general this will
not be true for other spacings or other subjects. Thus it is recommended
to always pass the destination src for consistency.
Initialize SourceMorph for SourceEstimate
src_to = mne.read_source_spaces(fname_fsaverage_src)
print(src_to[0]["vertno"]) # special, np.arange(10242)
morph = mne.compute_source_morph(
stc,
subject_from="sample",
subject_to="fsaverage",
src_to=src_to,
subjects_dir=subjects_dir,
)
Reading a source space...
[done]
Reading a source space...
[done]
2 source spaces read
[ 0 1 2 ... 10239 10240 10241]
surface source space present ...
Computing morph matrix...
Left-hemisphere map read.
Right-hemisphere map read.
17 smooth iterations done.
14 smooth iterations done.
[done]
[done]
Apply morph to (Vector) SourceEstimate#
The morph will be applied to the source estimate data, by giving it as the first argument to the morph we computed above.
Plot results#
# Define plotting parameters
surfer_kwargs = dict(
hemi="lh",
subjects_dir=subjects_dir,
clim=dict(kind="value", lims=[8, 12, 15]),
views="lateral",
initial_time=0.09,
time_unit="s",
size=(800, 800),
smoothing_steps=5,
)
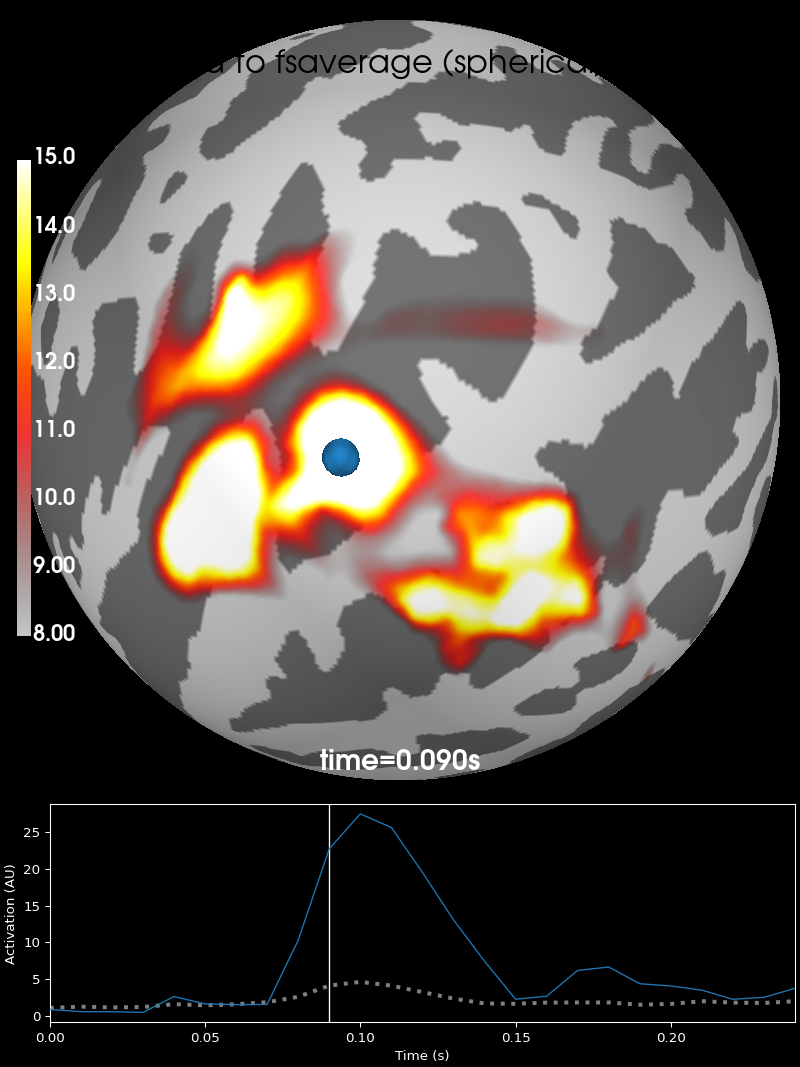
# As spherical surface
brain = stc_fsaverage.plot(surface="sphere", **surfer_kwargs)
# Add title
brain.add_text(0.1, 0.9, "Morphed to fsaverage (spherical)", "title", font_size=16)
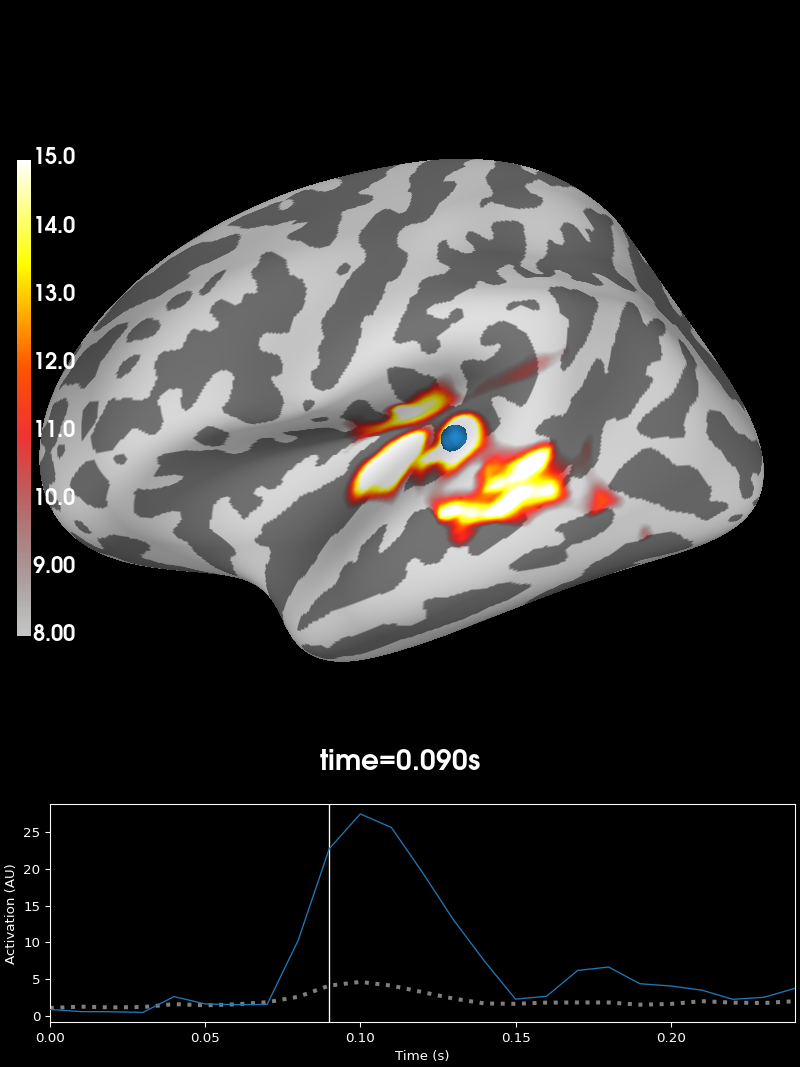
As inflated surface
brain_inf = stc_fsaverage.plot(surface="inflated", **surfer_kwargs)
# Add title
brain_inf.add_text(0.1, 0.9, "Morphed to fsaverage (inflated)", "title", font_size=16)
Reading and writing SourceMorph from and to disk#
An instance of SourceMorph can be saved, by calling
morph.save.
This method allows for specification of a filename under which the morph
will be save in “.h5” format. If no file extension is provided, “-morph.h5”
will be appended to the respective defined filename:
>>> morph.save('my-file-name')
Reading a saved source morph can be achieved by using
mne.read_source_morph():
>>> morph = mne.read_source_morph('my-file-name-morph.h5')
Once the environment is set up correctly, no information such as
subject_from or subjects_dir must be provided, since it can be
inferred from the data and use morph to ‘fsaverage’ by default. SourceMorph
can further be used without creating an instance and assigning it to a
variable. Instead mne.compute_source_morph() and
mne.SourceMorph.apply() can be
easily chained into a handy one-liner. Taking this together the shortest
possible way to morph data directly would be:
surface source space present ...
Computing morph matrix...
Left-hemisphere map read.
Right-hemisphere map read.
17 smooth iterations done.
14 smooth iterations done.
[done]
[done]
For more examples, check out examples using SourceMorph.apply.
References#
- 1
Douglas N. Greve, Lise Van der Haegen, Qing Cai, Steven Stufflebeam, Mert R. Sabuncu, Bruce Fischl, and Marc Brysbaert. A surface-based analysis of language lateralization and cortical asymmetry. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 25(9):1477–1492, 2013. doi:10.1162/jocn_a_00405.
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 16.078 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 28 MB