Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Generate simulated source data#
This example illustrates how to use the mne.simulation.SourceSimulator
class to generate source estimates and raw data. It is meant to be a brief
introduction and only highlights the simplest use case.
# Author: Kostiantyn Maksymenko <kostiantyn.maksymenko@gmail.com>
# Samuel Deslauriers-Gauthier <sam.deslauriers@gmail.com>
#
# License: BSD-3-Clause
import numpy as np
import mne
from mne.datasets import sample
print(__doc__)
For this example, we will be using the information of the sample subject. This will download the data if it not already on your machine. We also set the subjects directory so we don’t need to give it to functions.
data_path = sample.data_path()
subjects_dir = data_path / 'subjects'
subject = 'sample'
First, we get an info structure from the test subject.
evoked_fname = data_path / 'MEG' / subject / 'sample_audvis-ave.fif'
info = mne.io.read_info(evoked_fname)
tstep = 1. / info['sfreq']
Read a total of 4 projection items:
PCA-v1 (1 x 102) active
PCA-v2 (1 x 102) active
PCA-v3 (1 x 102) active
Average EEG reference (1 x 60) active
To simulate sources, we also need a source space. It can be obtained from the forward solution of the sample subject.
Reading forward solution from /home/circleci/mne_data/MNE-sample-data/MEG/sample/sample_audvis-meg-eeg-oct-6-fwd.fif...
Reading a source space...
Computing patch statistics...
Patch information added...
Distance information added...
[done]
Reading a source space...
Computing patch statistics...
Patch information added...
Distance information added...
[done]
2 source spaces read
Desired named matrix (kind = 3523) not available
Read MEG forward solution (7498 sources, 306 channels, free orientations)
Desired named matrix (kind = 3523) not available
Read EEG forward solution (7498 sources, 60 channels, free orientations)
Forward solutions combined: MEG, EEG
Source spaces transformed to the forward solution coordinate frame
To select a region to activate, we use the caudal middle frontal to grow a region of interest.
selected_label = mne.read_labels_from_annot(
subject, regexp='caudalmiddlefrontal-lh', subjects_dir=subjects_dir)[0]
location = 'center' # Use the center of the region as a seed.
extent = 10. # Extent in mm of the region.
label = mne.label.select_sources(
subject, selected_label, location=location, extent=extent,
subjects_dir=subjects_dir)
Reading labels from parcellation...
read 1 labels from /home/circleci/mne_data/MNE-sample-data/subjects/sample/label/lh.aparc.annot
read 0 labels from /home/circleci/mne_data/MNE-sample-data/subjects/sample/label/rh.aparc.annot
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Using backend SequentialBackend with 1 concurrent workers.
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 1 out of 1 | elapsed: 0.0s remaining: 0.0s
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 1 out of 1 | elapsed: 0.0s finished
Define the time course of the activity for each source of the region to activate. Here we use a sine wave at 18 Hz with a peak amplitude of 10 nAm.
source_time_series = np.sin(2. * np.pi * 18. * np.arange(100) * tstep) * 10e-9
Define when the activity occurs using events. The first column is the sample of the event, the second is not used, and the third is the event id. Here the events occur every 200 samples.
Create simulated source activity. Here we use a SourceSimulator whose add_data method is key. It specified where (label), what (source_time_series), and when (events) an event type will occur.
Project the source time series to sensor space and add some noise. The source simulator can be given directly to the simulate_raw function.
raw = mne.simulation.simulate_raw(info, source_simulator, forward=fwd)
cov = mne.make_ad_hoc_cov(raw.info)
mne.simulation.add_noise(raw, cov, iir_filter=[0.2, -0.2, 0.04])
raw.plot()
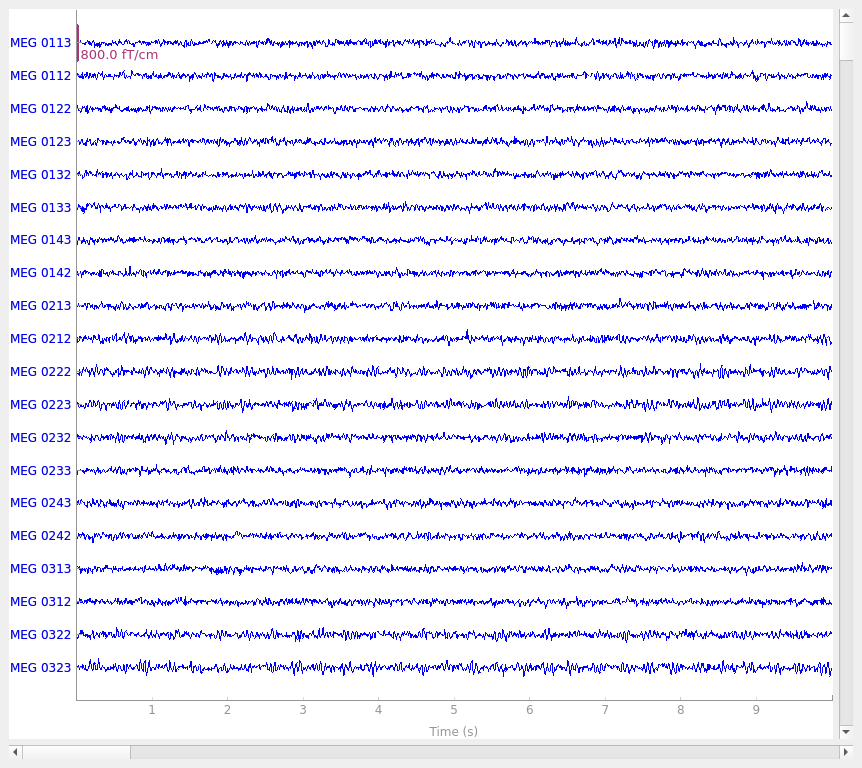
Setting up raw simulation: 1 position, "cos2" interpolation
Event information stored on channel: STI 014
Interval 0.000-1.665 sec
Setting up forward solutions
Computing gain matrix for transform #1/1
Interval 0.000-1.665 sec
Interval 0.000-1.665 sec
Interval 0.000-1.665 sec
Interval 0.000-1.665 sec
Interval 0.000-1.665 sec
Interval 0.000-1.665 sec
Interval 0.000-1.665 sec
Interval 0.000-1.665 sec
Interval 0.000-1.665 sec
10 STC iterations provided
[done]
Adding noise to 366/376 channels (366 channels in cov)
Plot evoked data to get another view of the simulated raw data.
events = mne.find_events(raw)
epochs = mne.Epochs(raw, events, 1, tmin=-0.05, tmax=0.2)
evoked = epochs.average()
evoked.plot()
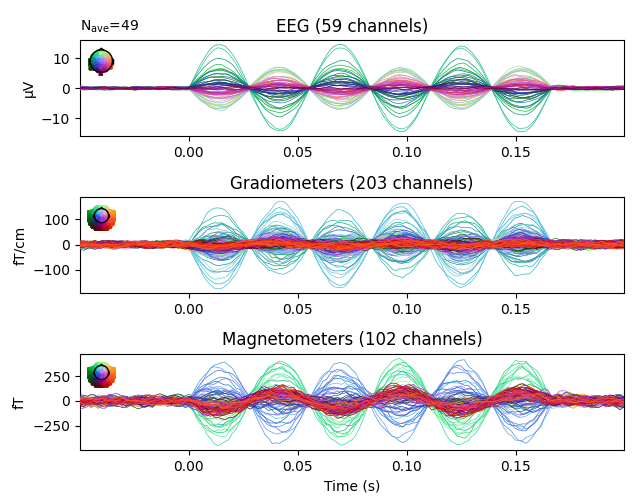
50 events found
Event IDs: [1]
Not setting metadata
50 matching events found
Setting baseline interval to [-0.049948803289596964, 0.0] sec
Applying baseline correction (mode: mean)
Created an SSP operator (subspace dimension = 4)
4 projection items activated
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 13.562 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 129 MB