Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
KIT phantom dataset tutorial#
Here we read KIT data obtained from a phantom with 49 dipoles sequentially activated with 2-cycle 11 Hz sinusoidal bursts to verify source localization accuracy.
# Authors: Eric Larson <larson.eric.d@gmail.com>
#
# License: BSD-3-Clause
# Copyright the MNE-Python contributors.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from scipy.signal import find_peaks
import mne
data_path = mne.datasets.phantom_kit.data_path()
actual_pos, actual_ori = mne.dipole.get_phantom_dipoles("oyama")
actual_pos, actual_ori = actual_pos[:49], actual_ori[:49] # only 49 of 50 dipoles
raw = mne.io.read_raw_kit(data_path / "002_phantom_11Hz_100uA.con")
# cut from ~800 to ~300s for speed, and also at convenient dip stim boundaries
# chosen by examining MISC 017 by eye.
raw.crop(11.5, 302.9).load_data()
raw.filter(None, 40) # 11 Hz stimulation, no need to keep higher freqs
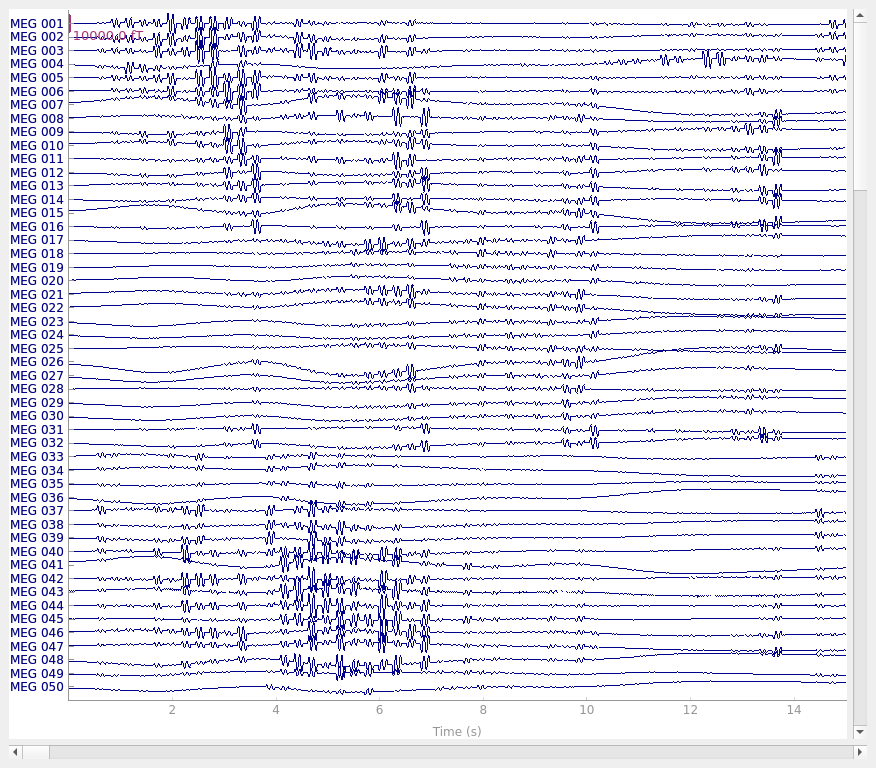
plot_scalings = dict(mag=5e-12) # large-amplitude sinusoids
raw_plot_kwargs = dict(duration=15, n_channels=50, scalings=plot_scalings)
raw.plot(**raw_plot_kwargs)
Extracting SQD Parameters from /home/circleci/mne_data/MNE-phantom-KIT-data/002_phantom_11Hz_100uA.con...
Creating Raw.info structure...
Setting channel info structure...
Creating Info structure...
Ready.
Reading 0 ... 582800 = 0.000 ... 291.400 secs...
Filtering raw data in 1 contiguous segment
Setting up low-pass filter at 40 Hz
FIR filter parameters
---------------------
Designing a one-pass, zero-phase, non-causal lowpass filter:
- Windowed time-domain design (firwin) method
- Hamming window with 0.0194 passband ripple and 53 dB stopband attenuation
- Upper passband edge: 40.00 Hz
- Upper transition bandwidth: 10.00 Hz (-6 dB cutoff frequency: 45.00 Hz)
- Filter length: 661 samples (0.331 s)
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 17 tasks | elapsed: 0.3s
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 71 tasks | elapsed: 1.4s
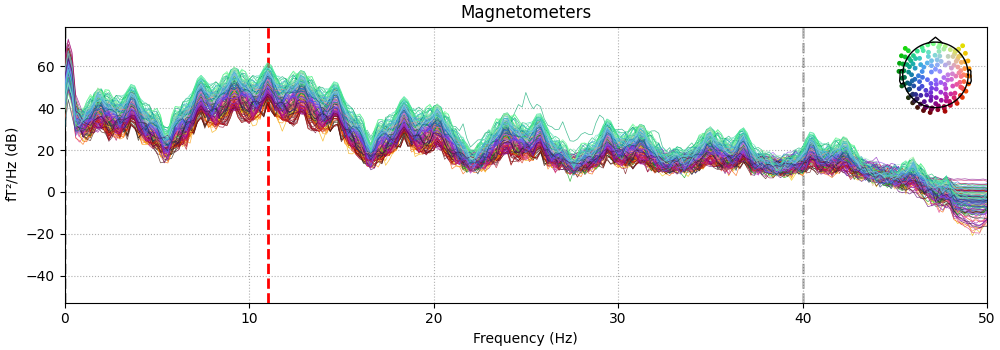
We can also look at the power spectral density to see the phantom oscillations at 11 Hz plus the expected frequency-domain sinc-like oscillations due to the time-domain boxcar windowing of the 11 Hz sinusoid.
spectrum = raw.copy().crop(0, 60).compute_psd(n_fft=10000)
fig = spectrum.plot()
fig.axes[0].set_xlim(0, 50)
dip_freq = 11.0
fig.axes[0].axvline(dip_freq, color="r", ls="--", lw=2, zorder=4)
Effective window size : 5.000 (s)
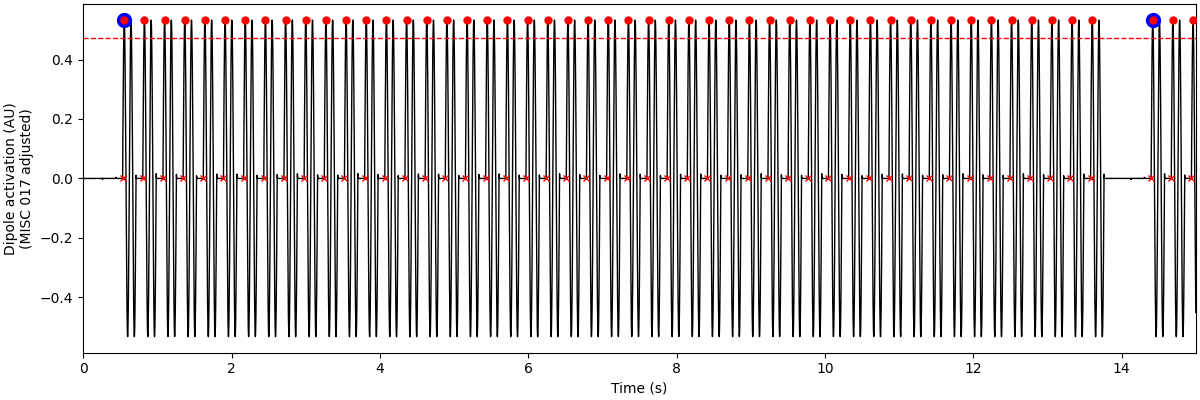
To find the events, we can look at the MISC channel that recorded the activations.
Here we use a very simple thresholding approach to find the events.
The MISC 017 channel holds the dipole activations, which are 2-cycle 11 Hz sinusoidal
bursts with the initial sinusoidal deflection downward, so we do a little bit of
signal manipulation to help find_peaks().
# Figure out events
dip_act, dip_t = raw["MISC 017"]
dip_act = dip_act[0] # 2D to 1D array
dip_act -= dip_act.mean() # remove DC offset
dip_act *= -1 # invert so first deflection is positive
thresh = np.percentile(dip_act, 90)
min_dist = raw.info["sfreq"] / dip_freq * 0.9 # 90% of period, to be safe
peaks = find_peaks(dip_act, height=thresh, distance=min_dist)[0]
assert len(peaks) % 2 == 0 # 2-cycle modulations
peaks = peaks[::2] # take only first peaks of each 2-cycle burst
fig, ax = plt.subplots(layout="constrained", figsize=(12, 4))
stop = int(15 * raw.info["sfreq"]) # 15 sec
ax.plot(dip_t[:stop], dip_act[:stop], color="k", lw=1)
ax.axhline(thresh, color="r", ls="--", lw=1)
peak_idx = peaks[peaks < stop]
ax.plot(dip_t[peak_idx], dip_act[peak_idx], "ro", zorder=5, ms=5)
ax.set(xlabel="Time (s)", ylabel="Dipole activation (AU)\n(MISC 017 adjusted)")
ax.set(xlim=dip_t[[0, stop - 1]])
# We know that there are 32 dipoles, so mark the first ones as well
n_dip = 49
assert len(peaks) % n_dip == 0 # we found them all (hopefully)
ax.plot(dip_t[peak_idx[::n_dip]], dip_act[peak_idx[::n_dip]], "bo", zorder=4, ms=10)
# Knowing we've caught the top of the first cycle of a 11 Hz sinusoid, plot onsets
# with red X's.
onsets = peaks - np.round(raw.info["sfreq"] / dip_freq / 4.0).astype(
int
) # shift to start
onset_idx = onsets[onsets < stop]
ax.plot(dip_t[onset_idx], dip_act[onset_idx], "rx", zorder=5, ms=5)
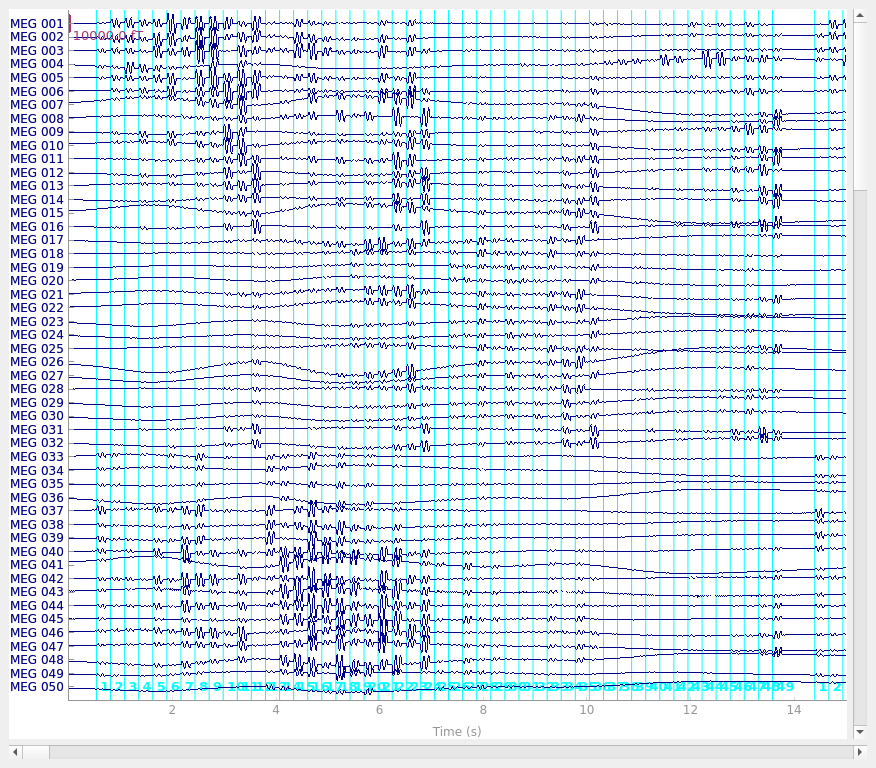
Given the onsets are now stored in peaks, we can create our events array and plot
on our raw data.
Now we can figure out our epoching parameters and epoch the data, sanity checking some values along the way knowing how the stimulation was done.
# Sanity check and determine epoching params
deltas = np.diff(events[:, 0], axis=0)
group_deltas = deltas[n_dip - 1 :: n_dip] / raw.info["sfreq"] # gap between 49 and 1
assert (group_deltas > 0.8).all()
assert (group_deltas < 0.9).all()
others = np.delete(deltas, np.arange(n_dip - 1, len(deltas), n_dip)) # remove 49->1
others = others / raw.info["sfreq"]
assert (others > 0.25).all()
assert (others < 0.3).all()
tmax = 1 / dip_freq * 2.0 # 2 cycles
tmin = tmax - others.min()
assert tmin < 0
epochs = mne.Epochs(
raw,
events,
tmin=tmin,
tmax=tmax,
baseline=(None, 0),
decim=10,
picks="data",
preload=True,
)
del raw
epochs.plot(scalings=plot_scalings)
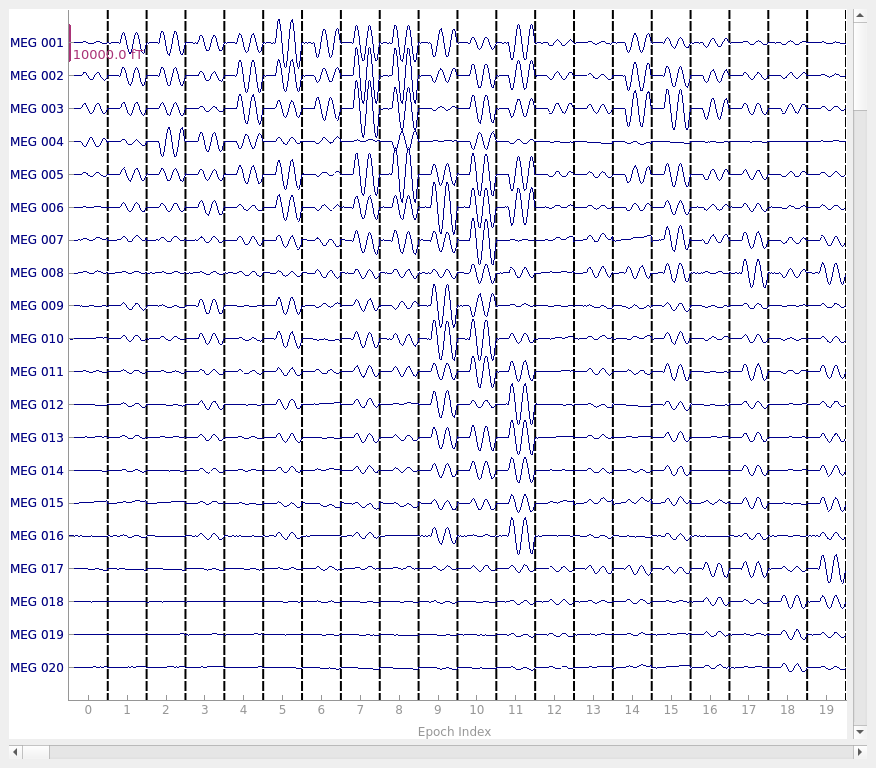
Not setting metadata
1029 matching events found
Setting baseline interval to [-0.085, 0.0] s
Applying baseline correction (mode: mean)
0 projection items activated
Using data from preloaded Raw for 1029 events and 544 original time points (prior to decimation) ...
0 bad epochs dropped
Now we can average the epochs for each dipole, get the activation at the peak time,
and create an mne.EvokedArray from the result.
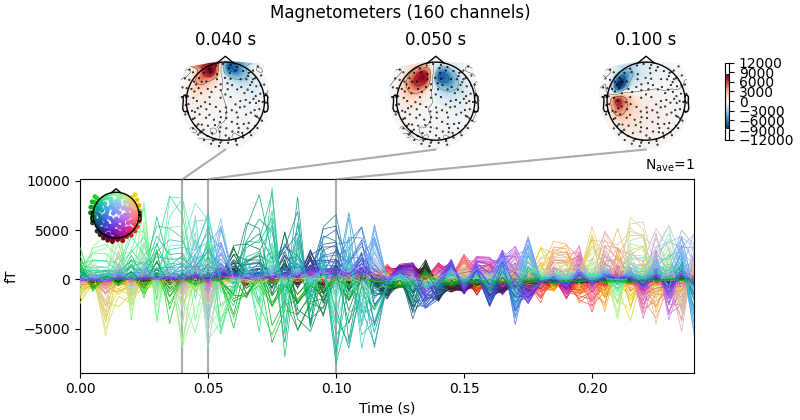
No projector specified for this dataset. Please consider the method self.add_proj.
Let’s fit dipoles at each dipole’s peak activation time.
trans = mne.transforms.Transform("head", "mri", np.eye(4))
sphere = mne.make_sphere_model(r0=(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), head_radius=0.08)
cov = mne.compute_covariance(epochs, tmax=0, method="empirical")
# We need to correct the ``dev_head_t`` because it's incorrect for these data!
# relative to the helmet: hleft, forward, up
translation = mne.transforms.translation(x=0.01, y=-0.015, z=-0.088)
# pitch down (rot about x/R), roll left (rot about y/A), yaw left (rot about z/S)
rotation = mne.transforms.rotation(
x=np.deg2rad(5),
y=np.deg2rad(-1),
z=np.deg2rad(-3),
)
evoked.info["dev_head_t"]["trans"][:] = translation @ rotation
dip, residual = mne.fit_dipole(evoked, cov, sphere, n_jobs=None)
Equiv. model fitting -> RV = 0.00364477 %
mu1 = 0.944121 lambda1 = 0.138646
mu2 = 0.665982 lambda2 = 0.684475
mu3 = -0.140083 lambda3 = -0.0127517
Set up EEG sphere model with scalp radius 80.0 mm
Computing rank from data with rank=None
Using tolerance 2.4e-09 (2.2e-16 eps * 160 dim * 6.6e+04 max singular value)
Estimated rank (mag): 160
MAG: rank 160 computed from 160 data channels with 0 projectors
Reducing data rank from 160 -> 160
Estimating covariance using EMPIRICAL
Done.
Number of samples used : 18522
[done]
BEM : <ConductorModel | Sphere (3 layers): r0=[0.0, 0.0, 0.0] R=80 mm>
MRI transform : identity
Sphere model : origin at ( 0.00 0.00 0.00) mm, rad = 0.1 mm
Guess grid : 20.0 mm
Guess mindist : 5.0 mm
Guess exclude : 20.0 mm
Using normal MEG coil definitions.
Noise covariance : <Covariance | kind : full, shape : (160, 160), range : [-1e-26, +2.5e-26], n_samples : 18521>
Coordinate transformation: MRI (surface RAS) -> head
1.000000 0.000000 0.000000 0.00 mm
0.000000 1.000000 0.000000 0.00 mm
0.000000 0.000000 1.000000 0.00 mm
0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 1.00
Coordinate transformation: MEG device -> head
0.998477 0.050618 -0.021924 10.00 mm
-0.052328 0.994909 -0.086126 -15.00 mm
0.017452 0.087142 0.996043 -88.00 mm
0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 1.00
0 bad channels total
Read 160 MEG channels from info
105 coil definitions read
Coordinate transformation: MEG device -> head
0.998477 0.050618 -0.021924 10.00 mm
-0.052328 0.994909 -0.086126 -15.00 mm
0.017452 0.087142 0.996043 -88.00 mm
0.000000 0.000000 0.000000 1.00
MEG coil definitions created in head coordinates.
Decomposing the sensor noise covariance matrix...
Computing rank from covariance with rank=None
Using tolerance 8.5e-15 (2.2e-16 eps * 160 dim * 0.24 max singular value)
Estimated rank (mag): 160
MAG: rank 160 computed from 160 data channels with 0 projectors
Setting small MAG eigenvalues to zero (without PCA)
Created the whitener using a noise covariance matrix with rank 160 (0 small eigenvalues omitted)
---- Computing the forward solution for the guesses...
Making a spherical guess space with radius 72.0 mm...
Filtering (grid = 20 mm)...
Surface CM = ( 0.0 0.0 0.0) mm
Surface fits inside a sphere with radius 72.0 mm
Surface extent:
x = -72.0 ... 72.0 mm
y = -72.0 ... 72.0 mm
z = -72.0 ... 72.0 mm
Grid extent:
x = -80.0 ... 80.0 mm
y = -80.0 ... 80.0 mm
z = -80.0 ... 80.0 mm
729 sources before omitting any.
178 sources after omitting infeasible sources not within 20.0 - 72.0 mm.
170 sources remaining after excluding the sources outside the surface and less than 5.0 mm inside.
Go through all guess source locations...
[done 170 sources]
---- Fitted : 0.0 ms
---- Fitted : 5.0 ms
---- Fitted : 10.0 ms
---- Fitted : 15.0 ms
---- Fitted : 20.0 ms
---- Fitted : 25.0 ms
---- Fitted : 30.0 ms
---- Fitted : 35.0 ms
---- Fitted : 40.0 ms
---- Fitted : 45.0 ms
---- Fitted : 50.0 ms
---- Fitted : 55.0 ms
---- Fitted : 60.0 ms
---- Fitted : 65.0 ms
---- Fitted : 70.0 ms
---- Fitted : 75.0 ms
---- Fitted : 80.0 ms
[Parallel(n_jobs=1)]: Done 17 tasks | elapsed: 0.6s
---- Fitted : 85.0 ms
---- Fitted : 90.0 ms
---- Fitted : 95.0 ms
---- Fitted : 100.0 ms
---- Fitted : 105.0 ms
---- Fitted : 110.0 ms
---- Fitted : 115.0 ms
---- Fitted : 120.0 ms
---- Fitted : 125.0 ms
---- Fitted : 130.0 ms
---- Fitted : 135.0 ms
---- Fitted : 140.0 ms
---- Fitted : 145.0 ms
---- Fitted : 150.0 ms
---- Fitted : 155.0 ms
---- Fitted : 160.0 ms
---- Fitted : 165.0 ms
---- Fitted : 170.0 ms
---- Fitted : 175.0 ms
---- Fitted : 180.0 ms
---- Fitted : 185.0 ms
---- Fitted : 190.0 ms
---- Fitted : 195.0 ms
---- Fitted : 200.0 ms
---- Fitted : 205.0 ms
---- Fitted : 210.0 ms
---- Fitted : 215.0 ms
---- Fitted : 220.0 ms
---- Fitted : 225.0 ms
---- Fitted : 230.0 ms
---- Fitted : 235.0 ms
---- Fitted : 240.0 ms
No projector specified for this dataset. Please consider the method self.add_proj.
49 time points fitted
Finally let’s look at the results.
print(f"Average amplitude: {np.mean(dip.amplitude) * 1e9:0.1f} nAm")
print(f"Average GOF: {np.mean(dip.gof):0.1f}%")
diffs = 1000 * np.sqrt(np.sum((dip.pos - actual_pos) ** 2, axis=-1))
print(f"Average loc error: {np.mean(diffs):0.1f} mm")
angles = np.rad2deg(np.arccos(np.abs(np.sum(dip.ori * actual_ori, axis=1))))
print(f"Average ori error: {np.mean(angles):0.1f}°")
fig = mne.viz.plot_alignment(
evoked.info,
trans,
bem=sphere,
coord_frame="head",
meg="helmet",
show_axes=True,
)
fig = mne.viz.plot_dipole_locations(
dipoles=dip, mode="arrow", color=(0.2, 1.0, 0.5), fig=fig
)
actual_amp = np.ones(len(dip)) # misc amp to create Dipole instance
actual_gof = np.ones(len(dip)) # misc GOF to create Dipole instance
dip_true = mne.Dipole(dip.times, actual_pos, actual_amp, actual_ori, actual_gof)
fig = mne.viz.plot_dipole_locations(
dipoles=dip_true, mode="arrow", color=(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), fig=fig
)
mne.viz.set_3d_view(figure=fig, azimuth=90, elevation=90, distance=0.5)
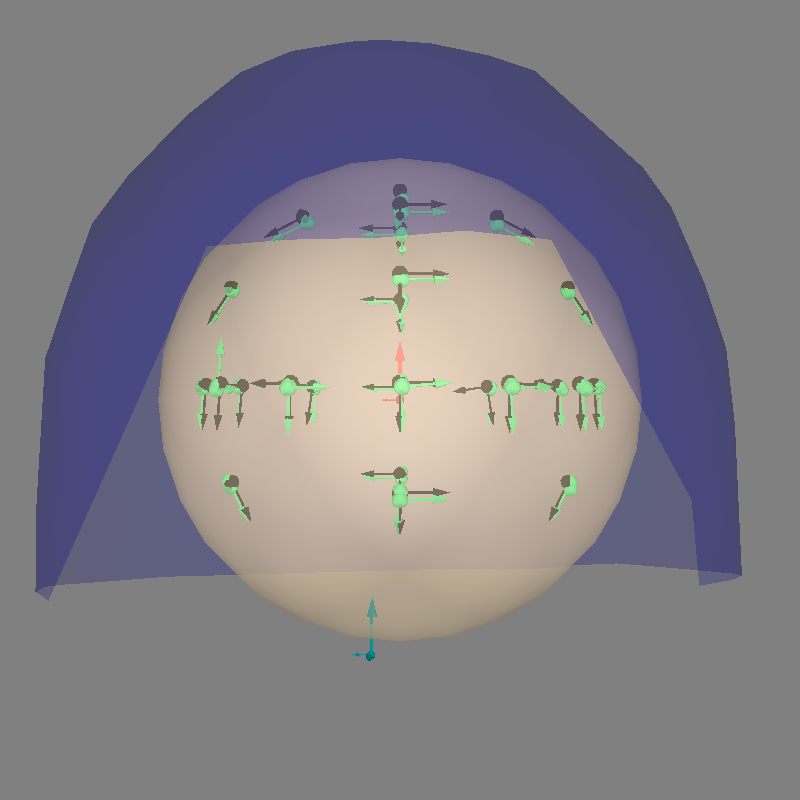
Average amplitude: 578.7 nAm
Average GOF: 99.6%
Average loc error: 1.7 mm
Average ori error: 9.6°
Getting helmet for system KIT (derived from 160 MEG channel locations)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 30.392 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 2057 MB