Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Decoding real-time data🔗
This example demonstrates how to decode real-time data using MNE-Python
and Scikit-learn. We will stream the sample_audvis_raw.fif
file from MNE’s sample dataset with a PlayerLSL, process the
signal through a StreamLSL, and decode the epochs created with
EpochsStream.
import time
import uuid
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from mne.decoding import Vectorizer
from mne.io import read_raw_fif
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import ShuffleSplit, cross_val_score
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from mne_lsl.datasets import sample
from mne_lsl.player import PlayerLSL
from mne_lsl.stream import EpochsStream, StreamLSL
fname = sample.data_path() / "mne-sample" / "sample_audvis_raw.fif"
raw = read_raw_fif(fname, preload=False).pick(("meg", "stim")).load_data()
source_id = uuid.uuid4().hex
player = PlayerLSL(raw, chunk_size=200, name="real-time-decoding", source_id=source_id)
player.start()
player.info
Signal processing🔗
We will apply minimal signal processing to the data. First, only the gradiometers will be used for decoding, thus other channels are removed. Then we mark bad channels and applying a low-pass filter at 40 Hz.
stream = StreamLSL(bufsize=5, name="real-time-decoding", source_id=source_id)
stream.connect(acquisition_delay=0.1, processing_flags="all")
stream.info["bads"] = ["MEG 2443"]
stream.pick(("grad", "stim")).filter(None, 40, picks="grad")
stream.info
Epoch the signal🔗
Next, we will create epochs around the event 1 (audio left) and 3 (visual
left).
epochs = EpochsStream(
stream,
bufsize=10,
event_id=dict(audio_left=1, visual_left=3),
event_channels="STI 014",
tmin=-0.2,
tmax=0.5,
baseline=(None, 0),
reject=dict(grad=4000e-13), # unit: T / m (gradiometers)
).connect(acquisition_delay=0.1)
epochs.info
Define the classifier🔗
We will use a LogisticRegression classifier to decode
the epochs.
Note
The object Vectorizer is used to transform the epochs in a
2D array of shape (n_epochs, n_features). It’s simply reshapes the epochs data
with:
data = epochs.get_data()
data = data.reshape(data.shape[0], -1)
vectorizer = Vectorizer()
scaler = StandardScaler()
clf = LogisticRegression()
classifier = Pipeline([("vector", vectorizer), ("scaler", scaler), ("svm", clf)])
Decode🔗
First, we will wait for a minimum number of epochs to be available. Then, the classifier will be trained for the first time and future epochs will be used to retrain the classifier every 5 epochs.
min_epochs = 10
while epochs.n_new_epochs < min_epochs:
time.sleep(0.5)
# prepare figure to plot classifiation score
if not plt.isinteractive():
plt.ion()
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set_xlabel("Epochsn n°")
ax.set_ylabel("Classification score (% correct)")
ax.set_title("Real-time decoding")
ax.set_xlim([min_epochs, 50])
ax.set_ylim([30, 105])
ax.axhline(50, color="k", linestyle="--", label="Chance level")
plt.show()
# decoding loop
scores_x, scores, std_scores = [], [], []
while True:
if len(scores_x) != 0 and 50 <= scores_x[-1]:
break
n_epochs = epochs.n_new_epochs
if n_epochs == 0 or n_epochs % 5 != 0:
time.sleep(0.5) # give time to the streaming and acquisition threads
continue
if len(scores_x) == 0: # first training
X = epochs.get_data(n_epochs=n_epochs)
y = epochs.events[-n_epochs:]
else:
X = np.concatenate((X, epochs.get_data(n_epochs=n_epochs)), axis=0)
y = np.concatenate((y, epochs.events[-n_epochs:]))
cv = ShuffleSplit(5, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
scores_t = cross_val_score(classifier, X, y, cv=cv, n_jobs=1) * 100
std_scores.append(scores_t.std())
scores.append(scores_t.mean())
scores_x.append(scores_x[-1] + n_epochs if len(scores_x) != 0 else n_epochs)
# update figure
ax.plot(scores_x[-2:], scores[-2:], "-x", color="b")
hyp_limits = (
np.asarray(scores[-2:]) - np.asarray(std_scores[-2:]),
np.asarray(scores[-2:]) + np.asarray(std_scores[-2:]),
)
fill = ax.fill_between(
scores_x[-2:], y1=hyp_limits[0], y2=hyp_limits[1], color="b", alpha=0.5
)
plt.pause(0.1)
plt.draw()
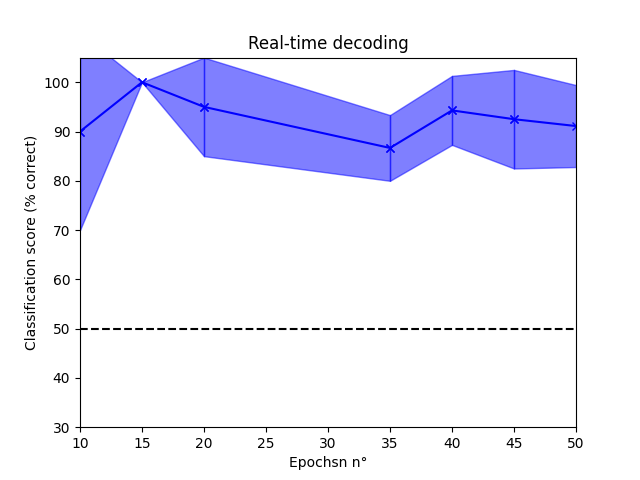
Free resources🔗
When you are done with a PlayerLSL,
StreamLSL or EpochsStream, don’t
forget to free the resources they use to continuously mock an LSL stream or receive
new data from an LSL stream.
<EpochsStream OFF (n: 10 between (-0.2, 0.5 seconds)> connected to:
<Stream: ON | real-time-decoding (source: 486db2e816be49baa59e1c5d75eb3396)>
<Stream: OFF | real-time-decoding (source: 486db2e816be49baa59e1c5d75eb3396)>
<Player: real-time-decoding | OFF | /home/runner/mne_data/MNE-LSL-data/sample/mne-sample/sample_audvis_raw.fif>
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 15.098 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 637 MB