Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Player with annotations🔗
Annotations from a Raw object can be streamed as an event
stream by PlayerLSL. The stream will be irregularly sampled,
numerical, and of type 'annotations'.
A Annotations contain 3 information:
the onset of the annotation
the duration of the annotation
the description of the annotation
To stream all 3 information, it’s duration-hod encoded along the channels. For instance,
consider a Raw object with 3 different Annotations
description: 'event1', 'event2', and 'event3'. The event stream will have 3
channels, each corresponding to one of the 3 descriptions. When an annotation is
streamed, it’s duration is encoded as the value on its channel while the other channels
remain to zero.
Note
Annotation with a duration equal to zero are special cased and yield an encoded
value of -1.
import uuid
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from mne import Annotations, create_info
from mne.io import RawArray
from mne.viz import set_browser_backend
from mne_lsl.player import PlayerLSL
from mne_lsl.stream import StreamLSL
annotations = Annotations(
onset=[1, 2, 3],
duration=[0.1, 0.2, 0.3],
description=["event1", "event2", "event3"],
)
annotations
<Annotations | 3 segments: event1 (1), event2 (1), event3 (1)>
With the 3 annotations above, the event stream will stream the following samples:
at time
1, the annotation'event1'is pushed. The sample push isarray([[0.1, 0, 0]]), of shape (1, 3).at time
2, the annotation'event2'is pushed. The sample push isarray([[0, 0.2, 0]]), of shape (1, 3).at time
3, the annotation'event3'is pushed. The sample push isarray([[0, 0, 0.3]]), of shape (1, 3).
If more than one annotations are present in the chunk currently pushed, then a chunk
is pushed. For instance, if the annotations at time 2 and 3 are pushed at the
same time, then the chunk push is array([[0., 0.2., 0.], [0., 0., 0.3]]), of shape
(2, 3).
Example on mock signal🔗
Let’s create a mock Raw object with annotations and stream both the
signal and the annotations.
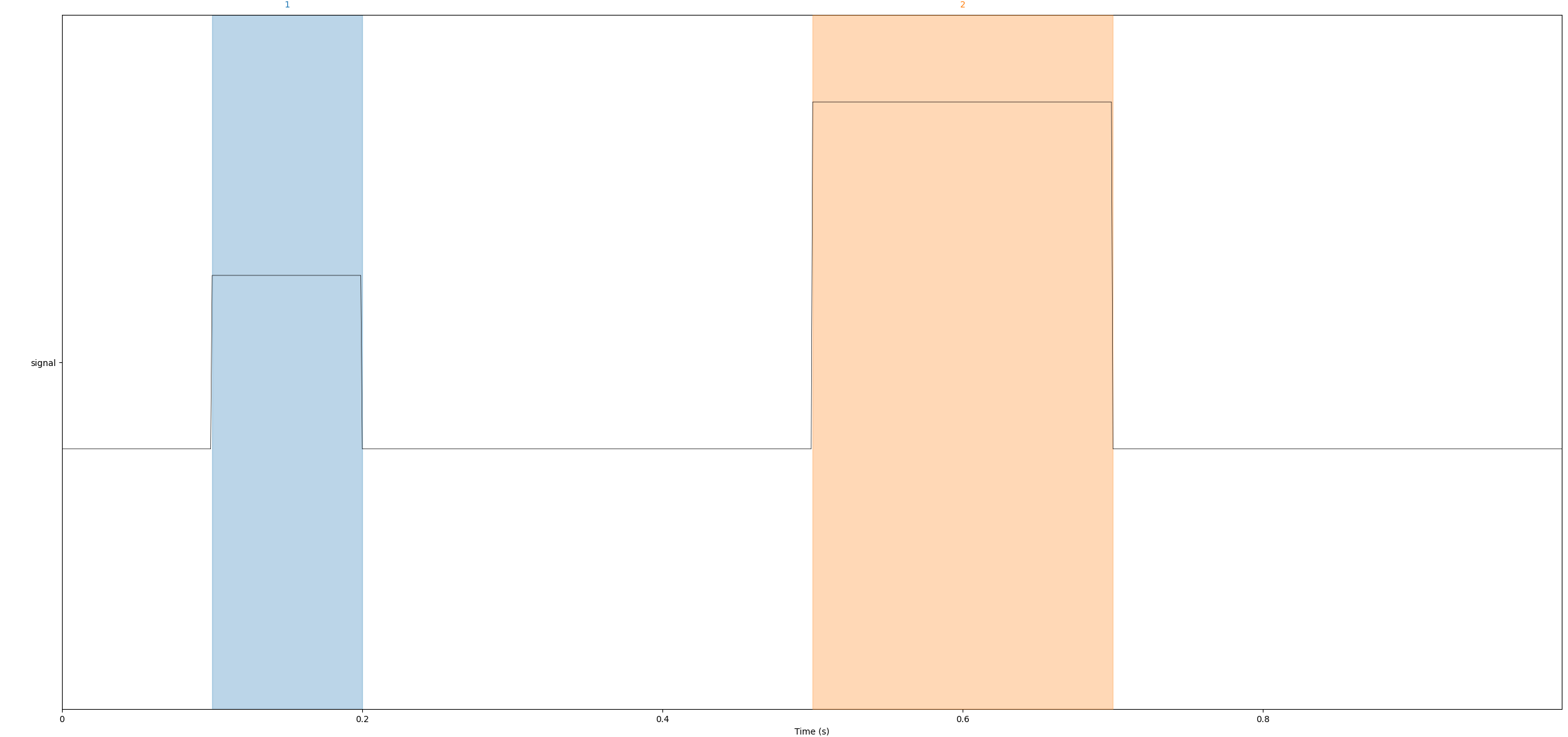
data = np.zeros((1, 1000)) # 1 channel, 1000 samples
data[0, 100:200] = 1
data[0, 500:700] = 2
info = create_info(["signal"], 1000, "misc")
raw = RawArray(data, info)
annotations = Annotations(onset=[0.1, 0.5], duration=[0.1, 0.2], description=["1", "2"])
raw.set_annotations(annotations)
set_browser_backend("matplotlib") # easier to plot with matplotlib in a documentation
raw.plot(scalings=dict(misc=2), show_scrollbars=False, show_scalebars=False)
plt.show()
Now that we have the Raw object, we can stream it with a
PlayerLSL object.
Note
Note that forcing annotations=True is not necessary since the
PlayerLSL will automatically stream annotations if they
are present in the Raw object.
Note
A chunk_size of 1 is needed here or the timestamps ts from the signal and
annotations streams are not reliable enough.
source_id = uuid.uuid4().hex
player = PlayerLSL(
raw,
chunk_size=1,
name="tutorial-annots",
source_id=source_id,
annotations=True,
).start()
We can now acquire both streams with 2 StreamLSL objects.
stream = StreamLSL(2, name="tutorial-annots", source_id=source_id)
stream.connect(acquisition_delay=0.1, processing_flags="all")
stream.info
stream_annotations = StreamLSL(2, stype="annotations", source_id=source_id)
stream_annotations.connect(acquisition_delay=0.1, processing_flags="all")
stream_annotations.info
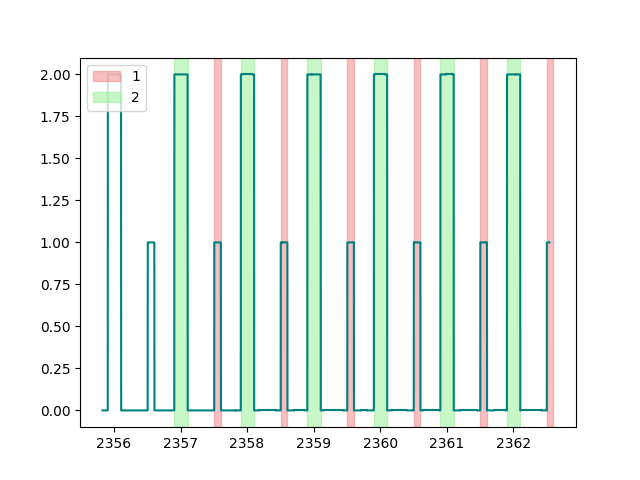
We can now acquire new samples from both streams and create a matplotlib figure to plot the signal and the annotations in real-time.
if not plt.isinteractive():
plt.ion()
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# add legend
colors = ["lightcoral", "lightgreen"]
patches = [
mpatches.Patch(color=colors[k], label=ch, alpha=0.5)
for k, ch in enumerate(stream_annotations.ch_names)
]
ax.legend(handles=patches, loc="upper left")
plt.show()
n = 0 # number of annotations
while n <= 10:
if stream.n_new_samples == 0:
continue
data, ts = stream.get_data(winsize=stream.n_new_samples / stream.info["sfreq"])
ax.plot(ts, data.squeeze(), color="teal")
if stream_annotations.n_new_samples != 0:
data_annotations, ts_annotations = stream_annotations.get_data(
winsize=stream_annotations.n_new_samples
)
for sample, time in zip(data_annotations.T, ts_annotations, strict=True):
k = np.where(sample != 0)[0][0] # find the annotation
ax.axvspan(
time,
time + sample[k],
label=stream_annotations.ch_names[k],
color=colors[k],
alpha=0.5,
)
n += 1
fig.canvas.draw()
fig.canvas.flush_events()
Free resources🔗
When you are done with a PlayerLSL, a
StreamLSL or a EpochsStream don’t
forget to free the resources they use to continuously mock an LSL stream or
receive new data from an LSL stream.
<Stream: OFF | tutorial-annots (source: f3b7992550bc4670bd1722fb566bbb66)>
<Stream: OFF | tutorial-annots-annotations (source: f3b7992550bc4670bd1722fb566bbb66)>
<Player: tutorial-annots | OFF>
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 10.275 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 196 MB