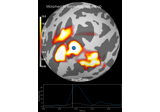
mne.read_source_estimate#
- mne.read_source_estimate(fname, subject=None)[source]#
Read a source estimate object.
- Parameters:
- fnamepath-like
Path to (a) source-estimate file(s).
- subject
str|None Name of the subject the source estimate(s) is (are) from. It is good practice to set this attribute to avoid combining incompatible labels and SourceEstimates (e.g., ones from other subjects). Note that due to file specification limitations, the subject name isn’t saved to or loaded from files written to disk.
- Returns:
- stc
SourceEstimate|VectorSourceEstimate|VolSourceEstimate|MixedSourceEstimate The source estimate object loaded from file.
- stc
Notes
for volume source estimates,
fnameshould provide the path to a single file named'*-vl.stc`or'*-vol.stc'for surface source estimates,
fnameshould either provide the path to the file corresponding to a single hemisphere ('*-lh.stc','*-rh.stc') or only specify the asterisk part in these patterns. In any case, the function expects files for both hemisphere with names following this pattern.for vector surface source estimates, only HDF5 files are supported.
for mixed source estimates, only HDF5 files are supported.
for single time point
.wfiles,fnameshould follow the same pattern as for surface estimates, except that files are named'*-lh.w'and'*-rh.w'.
Examples using mne.read_source_estimate#
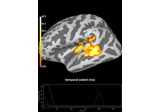
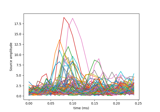
2 samples permutation test on source data with spatio-temporal clustering

Extracting time course from source_estimate object