Note
Click here to download the full example code
Linear classifier on sensor data with plot patterns and filters¶
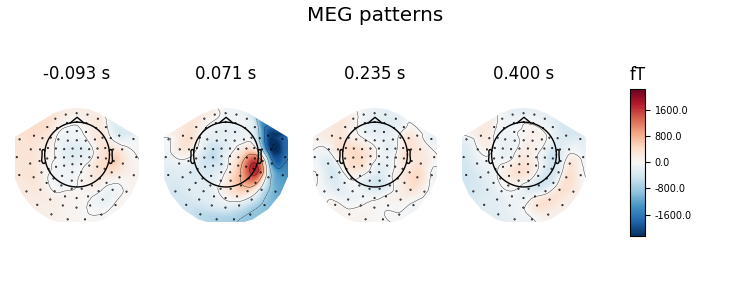
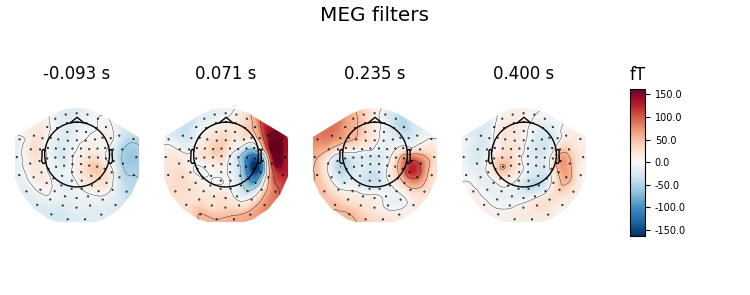
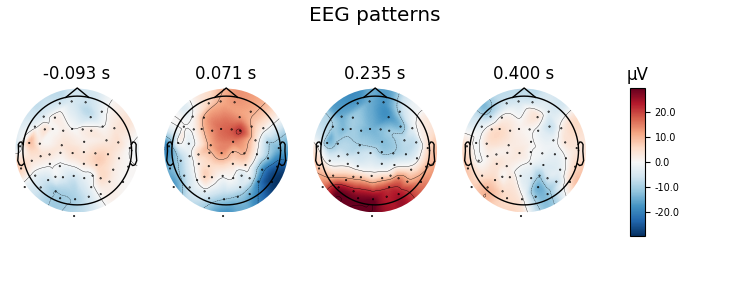
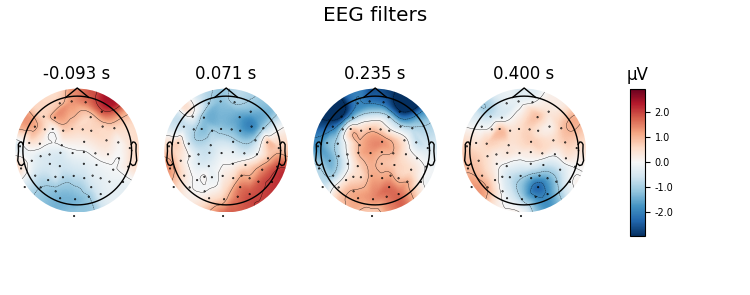
Here decoding, a.k.a MVPA or supervised machine learning, is applied to M/EEG data in sensor space. Fit a linear classifier with the LinearModel object providing topographical patterns which are more neurophysiologically interpretable 1 than the classifier filters (weight vectors). The patterns explain how the MEG and EEG data were generated from the discriminant neural sources which are extracted by the filters. Note patterns/filters in MEG data are more similar than EEG data because the noise is less spatially correlated in MEG than EEG.
# Authors: Alexandre Gramfort <alexandre.gramfort@inria.fr>
# Romain Trachel <trachelr@gmail.com>
# Jean-Remi King <jeanremi.king@gmail.com>
#
# License: BSD (3-clause)
import mne
from mne import io, EvokedArray
from mne.datasets import sample
from mne.decoding import Vectorizer, get_coef
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
# import a linear classifier from mne.decoding
from mne.decoding import LinearModel
print(__doc__)
data_path = sample.data_path()
sample_path = data_path + '/MEG/sample'
Set parameters
raw_fname = sample_path + '/sample_audvis_filt-0-40_raw.fif'
event_fname = sample_path + '/sample_audvis_filt-0-40_raw-eve.fif'
tmin, tmax = -0.1, 0.4
event_id = dict(aud_l=1, vis_l=3)
# Setup for reading the raw data
raw = io.read_raw_fif(raw_fname, preload=True)
raw.filter(.5, 25, fir_design='firwin')
events = mne.read_events(event_fname)
# Read epochs
epochs = mne.Epochs(raw, events, event_id, tmin, tmax, proj=True,
decim=2, baseline=None, preload=True)
del raw
labels = epochs.events[:, -1]
# get MEG and EEG data
meg_epochs = epochs.copy().pick_types(meg=True, eeg=False)
meg_data = meg_epochs.get_data().reshape(len(labels), -1)
Out:
Opening raw data file /home/circleci/mne_data/MNE-sample-data/MEG/sample/sample_audvis_filt-0-40_raw.fif...
Read a total of 4 projection items:
PCA-v1 (1 x 102) idle
PCA-v2 (1 x 102) idle
PCA-v3 (1 x 102) idle
Average EEG reference (1 x 60) idle
Range : 6450 ... 48149 = 42.956 ... 320.665 secs
Ready.
Reading 0 ... 41699 = 0.000 ... 277.709 secs...
Filtering raw data in 1 contiguous segment
Setting up band-pass filter from 0.5 - 25 Hz
FIR filter parameters
---------------------
Designing a one-pass, zero-phase, non-causal bandpass filter:
- Windowed time-domain design (firwin) method
- Hamming window with 0.0194 passband ripple and 53 dB stopband attenuation
- Lower passband edge: 0.50
- Lower transition bandwidth: 0.50 Hz (-6 dB cutoff frequency: 0.25 Hz)
- Upper passband edge: 25.00 Hz
- Upper transition bandwidth: 6.25 Hz (-6 dB cutoff frequency: 28.12 Hz)
- Filter length: 993 samples (6.613 sec)
Not setting metadata
Not setting metadata
145 matching events found
No baseline correction applied
Created an SSP operator (subspace dimension = 4)
4 projection items activated
Loading data for 145 events and 76 original time points ...
0 bad epochs dropped
Removing projector <Projection | Average EEG reference, active : True, n_channels : 60>
Decoding in sensor space using a LogisticRegression classifier¶
clf = LogisticRegression(solver='lbfgs')
scaler = StandardScaler()
# create a linear model with LogisticRegression
model = LinearModel(clf)
# fit the classifier on MEG data
X = scaler.fit_transform(meg_data)
model.fit(X, labels)
# Extract and plot spatial filters and spatial patterns
for name, coef in (('patterns', model.patterns_), ('filters', model.filters_)):
# We fitted the linear model onto Z-scored data. To make the filters
# interpretable, we must reverse this normalization step
coef = scaler.inverse_transform([coef])[0]
# The data was vectorized to fit a single model across all time points and
# all channels. We thus reshape it:
coef = coef.reshape(len(meg_epochs.ch_names), -1)
# Plot
evoked = EvokedArray(coef, meg_epochs.info, tmin=epochs.tmin)
evoked.plot_topomap(title='MEG %s' % name, time_unit='s')
Let’s do the same on EEG data using a scikit-learn pipeline
X = epochs.pick_types(meg=False, eeg=True)
y = epochs.events[:, 2]
# Define a unique pipeline to sequentially:
clf = make_pipeline(
Vectorizer(), # 1) vectorize across time and channels
StandardScaler(), # 2) normalize features across trials
LinearModel(
LogisticRegression(solver='lbfgs'))) # 3) fits a logistic regression
clf.fit(X, y)
# Extract and plot patterns and filters
for name in ('patterns_', 'filters_'):
# The `inverse_transform` parameter will call this method on any estimator
# contained in the pipeline, in reverse order.
coef = get_coef(clf, name, inverse_transform=True)
evoked = EvokedArray(coef, epochs.info, tmin=epochs.tmin)
evoked.plot_topomap(title='EEG %s' % name[:-1], time_unit='s')
Out:
Removing projector <Projection | PCA-v1, active : True, n_channels : 102>
Removing projector <Projection | PCA-v2, active : True, n_channels : 102>
Removing projector <Projection | PCA-v3, active : True, n_channels : 102>
References¶
- 1
Stefan Haufe, Frank Meinecke, Kai Görgen, Sven Dähne, John-Dylan Haynes, Benjamin Blankertz, and Felix Bießmann. On the interpretation of weight vectors of linear models in multivariate neuroimaging. NeuroImage, 87:96–110, 2014. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.10.067.
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 7.651 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 1033 MB