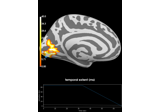
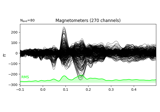
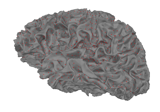
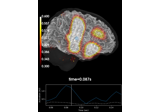
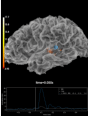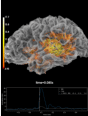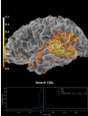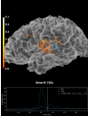
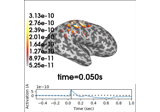
mne.viz.Brain¶
- class mne.viz.Brain(subject_id, hemi='both', surf='pial', title=None, cortex='classic', alpha=1.0, size=800, background='black', foreground=None, figure=None, subjects_dir=None, views='auto', offset='auto', show_toolbar=False, offscreen=False, interaction='trackball', units='mm', view_layout='vertical', silhouette=False, theme='auto', show=True)[source]¶
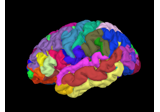
Class for visualizing a brain.
Warning
The API for this class is not currently complete. We suggest using
mne.viz.plot_source_estimates()with the PyVista backend enabled to obtain aBraininstance.- Parameters
- subject_id
str Subject name in Freesurfer subjects dir.
- hemi
str Hemisphere id (ie ‘lh’, ‘rh’, ‘both’, or ‘split’). In the case of ‘both’, both hemispheres are shown in the same window. In the case of ‘split’ hemispheres are displayed side-by-side in different viewing panes.
- surf
str FreeSurfer surface mesh name (ie ‘white’, ‘inflated’, etc.).
- title
str Title for the window.
- cortex
str,list,dict Specifies how the cortical surface is rendered. Options:
The name of one of the preset cortex styles:
'classic'(default),'high_contrast','low_contrast', or'bone'.A single color-like argument to render the cortex as a single color, e.g.
'red'or(0.1, 0.4, 1.).A list of two color-like used to render binarized curvature values for gyral (first) and sulcal (second). regions, e.g.,
['red', 'blue']or[(1, 0, 0), (0, 0, 1)].A dict containing keys
'vmin', 'vmax', 'colormap'with values used to render the binarized curvature (where 0 is gyral, 1 is sulcal).
Changed in version 0.24: Add support for non-string arguments.
- alpha
floatin [0, 1] Alpha level to control opacity of the cortical surface.
- size
int| array_like, shape (2,) The size of the window, in pixels. can be one number to specify a square window, or a length-2 sequence to specify (width, height).
- background
tuple(int,int,int) The color definition of the background: (red, green, blue).
- foregroundmatplotlib color
Color of the foreground (will be used for colorbars and text). None (default) will use black or white depending on the value of
background.- figure
listofFigure|None|int If None (default), a new window will be created with the appropriate views. For single view plots, the figure can be specified as int to retrieve the corresponding Mayavi window.
- subjects_dir
str|None If not None, this directory will be used as the subjects directory instead of the value set using the SUBJECTS_DIR environment variable.
- views
list|str The views to use.
- offsetbool |
str If True, shifts the right- or left-most x coordinate of the left and right surfaces, respectively, to be at zero. This is useful for viewing inflated surface where hemispheres typically overlap. Can be “auto” (default) use True with inflated surfaces and False otherwise (Default: ‘auto’). Only used when
hemi='both'.Changed in version 0.23: Default changed to “auto”.
- show_toolbarbool
If True, toolbars will be shown for each view.
- offscreenbool
If True, rendering will be done offscreen (not shown). Useful mostly for generating images or screenshots, but can be buggy. Use at your own risk.
- interaction
str Can be “trackball” (default) or “terrain”, i.e. a turntable-style camera.
- units
str Can be ‘m’ or ‘mm’ (default).
- view_layout
str Can be “vertical” (default) or “horizontal”. When using “horizontal” mode, the PyVista backend must be used and hemi cannot be “split”.
- silhouette
dict| bool As a dict, it contains the
color,linewidth,alphaopacity anddecimate(level of decimation between 0 and 1 or None) of the brain’s silhouette to display. If True, the default values are used and if False, no silhouette will be displayed. Defaults to False.- theme
str| path-like Can be “auto” (default), “light”, or “dark” or a path-like to a custom stylesheet. For Dark-Mode and automatic Dark-Mode-Detection,
qdarkstylerespectively and darkdetect is required.- showbool
Display the window as soon as it is ready. Defaults to True.
- subject_id
Notes
This table shows the capabilities of each Brain backend (”✓” for full support, and “-” for partial support):
3D function:
surfer.Brain
mne.viz.Brain
add_annotation
✓
✓
add_data
✓
✓
add_foci
✓
✓
add_head
✓
add_label
✓
✓
add_sensors
✓
add_skull
✓
add_text
✓
✓
add_volume_labels
✓
close
✓
✓
data
✓
✓
foci
✓
labels
✓
✓
remove_data
✓
remove_foci
✓
remove_head
✓
remove_labels
✓
✓
remove_annotations
✓
remove_sensors
✓
remove_skull
✓
remove_text
✓
remove_volume_labels
✓
scale_data_colormap
✓
save_image
✓
✓
save_movie
✓
✓
screenshot
✓
✓
show_view
✓
✓
TimeViewer
✓
✓
enable_depth_peeling
✓
get_picked_points
✓
add_data(volume)
✓
view_layout
✓
flatmaps
✓
vertex picking
✓
label picking
✓
- Attributes
Methods
__hash__()Hash the object.
add_annotation(annot[, borders, alpha, ...])Add an annotation file.
add_data(array[, fmin, fmid, fmax, thresh, ...])Display data from a numpy array on the surface or volume.
add_foci(coords[, coords_as_verts, ...])Add spherical foci, possibly mapping to displayed surf.
add_head([dense, color, alpha])Add a mesh to render the outer head surface.
add_label(label[, color, alpha, ...])Add an ROI label to the image.
add_sensors(info, trans[, meg, eeg, fnirs, ...])Add mesh objects to represent sensor positions.
add_skull([outer, color, alpha])Add a mesh to render the skull surface.
add_text(x, y, text[, name, color, opacity, ...])Add a text to the visualization.
add_volume_labels([aseg, labels, colors, ...])Add labels to the rendering from an anatomical segmentation.
Detect automatically fitting scaling parameters.
Clear the picking glyphs.
close()Close all figures and cleanup data structure.
Enable depth peeling.
Return the vertices of the picked points.
help()Display the help window.
plot_time_course(hemi, vertex_id, color[, ...])Plot the vertex time course.
plot_time_line([update])Add the time line to the MPL widget.
Remove all annotations from the image.
Remove rendered data from the mesh.
Remove head objects from the rendered scene.
Remove all the ROI labels from the image.
remove_sensors([kind])Remove sensors from the rendered scene.
Remove skull objects from the rendered scene.
remove_text([name])Remove text from the rendered scene.
Remove the volume labels from the rendered scene.
reset()Reset view and time step.
Reset the camera.
Restore original scaling parameters.
save_image([filename, mode])Save view from all panels to disk.
save_movie([filename, time_dilation, tmin, ...])Save a movie (for data with a time axis).
screenshot([mode, time_viewer])Generate a screenshot of current view.
set_data_smoothing(n_steps)Set the number of smoothing steps.
set_playback_speed(speed)Set the time playback speed.
set_time(time)Set the time to display (in seconds).
set_time_interpolation(interpolation)Set the interpolation mode.
set_time_point(time_idx)Set the time point shown (can be a float to interpolate).
setup_time_viewer([time_viewer, show_traces])Configure the time viewer parameters.
show()Display the window.
show_view([view, roll, distance, row, col, ...])Orient camera to display view.
toggle_interface([value])Toggle the interface.
toggle_playback([value])Toggle time playback.
update_lut([fmin, fmid, fmax, alpha])Update color map.
- add_annotation(annot, borders=True, alpha=1, hemi=None, remove_existing=True, color=None, **kwargs)[source]¶
Add an annotation file.
- Parameters
- annot
str|tuple Either path to annotation file or annotation name. Alternatively, the annotation can be specified as a
(labels, ctab)tuple per hemisphere, i.e.annot=(labels, ctab)for a single hemisphere orannot=((lh_labels, lh_ctab), (rh_labels, rh_ctab))for both hemispheres.labelsandctabshould be arrays as returned bynibabel.freesurfer.io.read_annot().- bordersbool |
int Show only label borders. If int, specify the number of steps (away from the true border) along the cortical mesh to include as part of the border definition.
- alpha
float Opacity of the head surface. Must be between 0 and 1 (inclusive). Default is 0.5.
- hemi
str|None If None, it is assumed to belong to the hemipshere being shown. If two hemispheres are being shown, data must exist for both hemispheres.
- remove_existingbool
If True (default), remove old annotations.
- colormatplotlib-style color
code If used, show all annotations in the same (specified) color. Probably useful only when showing annotation borders.
- **kwargs
dict These are passed to the underlying
mayavi.mlab.pipeline.surfacecall.
- annot
Examples using
add_annotation:
- add_data(array, fmin=None, fmid=None, fmax=None, thresh=None, center=None, transparent=False, colormap='auto', alpha=1, vertices=None, smoothing_steps=None, time=None, time_label='auto', colorbar=True, hemi=None, remove_existing=None, time_label_size=None, initial_time=None, scale_factor=None, vector_alpha=None, clim=None, src=None, volume_options=0.4, colorbar_kwargs=None, verbose=None)[source]¶
Display data from a numpy array on the surface or volume.
This provides a similar interface to
surfer.Brain.add_overlay(), but it displays it with a single colormap. It offers more flexibility over the colormap, and provides a way to display four-dimensional data (i.e., a timecourse) or five-dimensional data (i.e., a vector-valued timecourse).Note
fminsets the low end of the colormap, and is separate from thresh (this is a different convention fromsurfer.Brain.add_overlay()).- Parameters
- array
numpyarray, shape (n_vertices[, 3][, n_times]) Data array. For the data to be understood as vector-valued (3 values per vertex corresponding to X/Y/Z surface RAS), then
arraymust be have all 3 dimensions. If vectors with no time dimension are desired, consider using a singleton (e.g.,np.newaxis) to create a “time” dimension and passtime_label=None(vector values are not supported).- fmin
float Minimum value in colormap (uses real fmin if None).
- fmid
float Intermediate value in colormap (fmid between fmin and fmax if None).
- fmax
float Maximum value in colormap (uses real max if None).
- thresh
Noneorfloat Not supported yet. If not None, values below thresh will not be visible.
- center
floatorNone If not None, center of a divergent colormap, changes the meaning of fmin, fmax and fmid.
- transparentbool |
None If True: use a linear transparency between fmin and fmid and make values below fmin fully transparent (symmetrically for divergent colormaps). None will choose automatically based on colormap type.
- colormap
str,listof color, orarray Name of matplotlib colormap to use, a list of matplotlib colors, or a custom look up table (an n x 4 array coded with RBGA values between 0 and 255), the default “auto” chooses a default divergent colormap, if “center” is given (currently “icefire”), otherwise a default sequential colormap (currently “rocket”).
- alpha
floatin [0, 1] Alpha level to control opacity of the overlay.
- vertices
numpyarray Vertices for which the data is defined (needed if
len(data) < nvtx).- smoothing_steps
intorNone Number of smoothing steps (smoothing is used if len(data) < nvtx) The value ‘nearest’ can be used too. None (default) will use as many as necessary to fill the surface.
- time
numpyarray Time points in the data array (if data is 2D or 3D).
- time_label
str|callable()|None Format of the time label (a format string, a function that maps floating point time values to strings, or None for no label). The default is
'auto', which will usetime=%0.2f msif there is more than one time point.- colorbarbool
Whether to add a colorbar to the figure. Can also be a tuple to give the (row, col) index of where to put the colorbar.
- hemi
str|None If None, it is assumed to belong to the hemisphere being shown. If two hemispheres are being shown, an error will be thrown.
- remove_existingbool
Not supported yet. Remove surface added by previous “add_data” call. Useful for conserving memory when displaying different data in a loop.
- time_label_size
int Font size of the time label (default 14).
- initial_time
float|None Time initially shown in the plot.
Noneto use the first time sample (default).- scale_factor
float|None(default) The scale factor to use when displaying glyphs for vector-valued data.
- vector_alpha
float|None Alpha level to control opacity of the arrows. Only used for vector-valued data. If None (default),
alphais used.- clim
dict Original clim arguments.
- srcinstance of
SourceSpaces|None The source space corresponding to the source estimate. Only necessary if the STC is a volume or mixed source estimate.
- volume_options
float|dict|None Options for volumetric source estimate plotting, with key/value pairs:
'resolution'float | NoneResolution (in mm) of volume rendering. Smaller (e.g., 1.) looks better at the cost of speed. None (default) uses the volume source space resolution, which is often something like 7 or 5 mm, without resampling.
'blending'strCan be “mip” (default) for maximum intensity projection or “composite” for composite blending using alpha values.
'alpha'float | NoneAlpha for the volumetric rendering. Defaults are 0.4 for vector source estimates and 1.0 for scalar source estimates.
'surface_alpha'float | NoneAlpha for the surface enclosing the volume(s). None (default) will use half the volume alpha. Set to zero to avoid plotting the surface.
'silhouette_alpha'float | NoneAlpha for a silhouette along the outside of the volume. None (default) will use
0.25 * surface_alpha.
'silhouette_linewidth'floatThe line width to use for the silhouette. Default is 2.
A float input (default 1.) or None will be used for the
'resolution'entry.- colorbar_kwargs
dict|None Options to pass to
pyvista.Plotter.add_scalar_bar()(e.g.,dict(title_font_size=10)).- verbosebool |
str|int|None Control verbosity of the logging output. If
None, use the default verbosity level. See the logging documentation andmne.verbose()for details. Should only be passed as a keyword argument.
- array
Notes
If the data is defined for a subset of vertices (specified by the “vertices” parameter), a smoothing method is used to interpolate the data onto the high resolution surface. If the data is defined for subsampled version of the surface, smoothing_steps can be set to None, in which case only as many smoothing steps are applied until the whole surface is filled with non-zeros.
Due to a Mayavi (or VTK) alpha rendering bug,
vector_alphais clamped to be strictly < 1.Examples using
add_data:
- add_foci(coords, coords_as_verts=False, map_surface=None, scale_factor=1, color='white', alpha=1, name=None, hemi=None, resolution=50)[source]¶
Add spherical foci, possibly mapping to displayed surf.
The foci spheres can be displayed at the coordinates given, or mapped through a surface geometry. In other words, coordinates from a volume-based analysis in MNI space can be displayed on an inflated average surface by finding the closest vertex on the white surface and mapping to that vertex on the inflated mesh.
- Parameters
- coords
ndarray, shape (n_coords, 3) Coordinates in stereotaxic space (default) or array of vertex ids (with
coord_as_verts=True).- coords_as_vertsbool
Whether the coords parameter should be interpreted as vertex ids.
- map_surface
None Surface to map coordinates through, or None to use raw coords.
- scale_factor
float Controls the size of the foci spheres (relative to 1cm).
- colormatplotlib color
code HTML name, RBG tuple, or hex code.
- alpha
floatin [0, 1] Opacity of focus gylphs.
- name
str Internal name to use.
- hemi
str|None If None, it is assumed to belong to the hemipshere being shown. If two hemispheres are being shown, an error will be thrown.
- resolution
int The resolution of the spheres.
- coords
Examples using
add_foci:
- add_head(dense=True, color='gray', alpha=0.5)[source]¶
Add a mesh to render the outer head surface.
- Parameters
Notes
New in version 0.24.
Examples using
add_head:
- add_label(label, color=None, alpha=1, scalar_thresh=None, borders=False, hemi=None, subdir=None, reset_camera=True)[source]¶
Add an ROI label to the image.
- Parameters
- label
str| instance ofLabel Label filepath or name. Can also be an instance of an object with attributes “hemi”, “vertices”, “name”, and optionally “color” and “values” (if scalar_thresh is not None).
- colormatplotlib-style color |
None Anything matplotlib accepts: string, RGB, hex, etc. (default “crimson”).
- alpha
floatin [0, 1] Alpha level to control opacity.
- scalar_thresh
None|float Threshold the label ids using this value in the label file’s scalar field (i.e. label only vertices with scalar >= thresh).
- bordersbool |
int Show only label borders. If int, specify the number of steps (away from the true border) along the cortical mesh to include as part of the border definition.
- hemi
str|None If None, it is assumed to belong to the hemipshere being shown.
- subdir
None|str If a label is specified as name, subdir can be used to indicate that the label file is in a sub-directory of the subject’s label directory rather than in the label directory itself (e.g. for
$SUBJECTS_DIR/$SUBJECT/label/aparc/lh.cuneus.labelbrain.add_label('cuneus', subdir='aparc')).- reset_camerabool
If True, reset the camera view after adding the label. Defaults to True.
- label
Notes
To remove previously added labels, run Brain.remove_labels().
Examples using
add_label:
- add_sensors(info, trans, meg=None, eeg='original', fnirs=True, ecog=True, seeg=True, dbs=True, verbose=None)[source]¶
Add mesh objects to represent sensor positions.
- Parameters
- info
mne.Info The
mne.Infoobject with information about the sensors and methods of measurement.- trans
str|dict| instance ofTransform If str, the path to the head<->MRI transform
*-trans.fiffile produced during coregistration. Can also be'fsaverage'to use the built-in fsaverage transformation.- meg
str|list| bool |None Can be “helmet”, “sensors” or “ref” to show the MEG helmet, sensors or reference sensors respectively, or a combination like
('helmet', 'sensors')(same as None, default). True translates to('helmet', 'sensors', 'ref').- eegbool |
str|list String options are:
- “original” (default; equivalent to
True) Shows EEG sensors using their digitized locations (after transformation to the chosen
coord_frame)
- “original” (default; equivalent to
- “projected”
The EEG locations projected onto the scalp, as is done in forward modeling
Can also be a list of these options, or an empty list (
[], equivalent ofFalse).- fnirs
str|list| bool |None Can be “channels”, “pairs”, “detectors”, and/or “sources” to show the fNIRS channel locations, optode locations, or line between source-detector pairs, or a combination like
('pairs', 'channels'). True translates to('pairs',).- ecogbool
If True (default), show ECoG sensors.
- seegbool
If True (default), show sEEG electrodes.
- dbsbool
If True (default), show DBS (deep brain stimulation) electrodes.
- verbosebool |
str|int|None Control verbosity of the logging output. If
None, use the default verbosity level. See the logging documentation andmne.verbose()for details. Should only be passed as a keyword argument.
- info
Notes
New in version 0.24.
Examples using
add_sensors:
- add_skull(outer=True, color='gray', alpha=0.5)[source]¶
Add a mesh to render the skull surface.
- Parameters
Notes
New in version 0.24.
- add_text(x, y, text, name=None, color=None, opacity=1.0, row=0, col=0, font_size=None, justification=None)[source]¶
Add a text to the visualization.
- Parameters
- x
float X coordinate.
- y
float Y coordinate.
- text
str Text to add.
- name
str Name of the text (text label can be updated using update_text()).
- color
tuple Color of the text. Default is the foreground color set during initialization (default is black or white depending on the background color).
- opacity
float Opacity of the text (default 1.0).
- row
int|None Row index of which brain to use. Default is the top row.
- col
int|None Column index of which brain to use. Default is the left-most column.
- font_size
float|None The font size to use.
- justification
str|None The text justification.
- x
Examples using
add_text:
- add_volume_labels(aseg='aparc+aseg', labels=None, colors=None, alpha=0.5, smooth=0.9, legend=None)[source]¶
Add labels to the rendering from an anatomical segmentation.
- Parameters
- aseg
str The anatomical segmentation file. Default
aparc+aseg. This may be any anatomical segmentation file in the mri subdirectory of the Freesurfer subject directory.- labels
list Labeled regions of interest to plot. See
mne.get_montage_volume_labels()for one way to determine regions of interest. Regions can also be chosen from the FreeSurfer LUT.- colors
list| matplotlib-style color |None A list of anything matplotlib accepts: string, RGB, hex, etc. (default FreeSurfer LUT colors).
- alpha
floatin [0, 1] Alpha level to control opacity.
- smooth
floatin [0, 1) The smoothing factor to be applied. Default 0 is no smoothing.
- legendbool |
None|dict Add a legend displaying the names of the
labels. Default (None) isTrueif the number oflabelsis 10 or fewer. Can also be a dict ofkwargsto pass topyvista.Plotter.add_legend().
- aseg
Notes
New in version 0.24.
Examples using
add_volume_labels:
- property data¶
Data used by time viewer and color bar widgets.
- property interaction¶
The interaction style.
- plot_time_line(update=True)[source]¶
Add the time line to the MPL widget.
- Parameters
- updatebool
Force an update of the plot. Defaults to True.
- save_image(filename=None, mode='rgb')[source]¶
Save view from all panels to disk.
Examples using
save_image:
- save_movie(filename=None, time_dilation=4.0, tmin=None, tmax=None, framerate=24, interpolation=None, codec=None, bitrate=None, callback=None, time_viewer=False, **kwargs)[source]¶
Save a movie (for data with a time axis).
The movie is created through the
imageiomodule. The format is determined by the extension, and additional options can be specified through keyword arguments that depend on the format, see imageio’s format page.Warning
This method assumes that time is specified in seconds when adding data. If time is specified in milliseconds this will result in movies 1000 times longer than expected.
- Parameters
- filename
str Path at which to save the movie. The extension determines the format (e.g.,
'*.mov','*.gif', …; see theimageiodocumentation for available formats).- time_dilation
float Factor by which to stretch time (default 4). For example, an epoch from -100 to 600 ms lasts 700 ms. With
time_dilation=4this would result in a 2.8 s long movie.- tmin
float First time point to include (default: all data).
- tmax
float Last time point to include (default: all data).
- framerate
float Framerate of the movie (frames per second, default 24).
- interpolation
str|None Interpolation method (
scipy.interpolate.interp1dparameter). Must be one of ‘linear’, ‘nearest’, ‘zero’, ‘slinear’, ‘quadratic’, or ‘cubic’. If None, it uses the currentbrain.interpolation, which defaults to'nearest'. Defaults to None.- codec
str|None The codec to use.
- bitrate
float|None The bitrate to use.
- callback
callable()|None A function to call on each iteration. Useful for status message updates. It will be passed keyword arguments
frameandn_frames.- time_viewerbool
If True, include time viewer traces. Only used if
time_viewer=Trueandseparate_canvas=False.- **kwargs
dict Specify additional options for
imageio.
- filename
- screenshot(mode='rgb', time_viewer=False)[source]¶
Generate a screenshot of current view.
- Parameters
- Returns
- screenshot
array Image pixel values.
- screenshot
Examples using
screenshot:
- set_data_smoothing(n_steps)[source]¶
Set the number of smoothing steps.
- Parameters
- n_steps
int Number of smoothing steps.
- n_steps
- set_playback_speed(speed)[source]¶
Set the time playback speed.
- Parameters
- speed
float The speed of the playback.
- speed
- set_time(time)[source]¶
Set the time to display (in seconds).
- Parameters
- time
float The time to show, in seconds.
- time
- set_time_interpolation(interpolation)[source]¶
Set the interpolation mode.
- Parameters
- interpolation
str|None Interpolation method (
scipy.interpolate.interp1dparameter). Must be one of ‘linear’, ‘nearest’, ‘zero’, ‘slinear’, ‘quadratic’, or ‘cubic’.
- interpolation
- setup_time_viewer(time_viewer=True, show_traces=True)[source]¶
Configure the time viewer parameters.
- Parameters
Notes
The keyboard shortcuts are the following:
‘?’: Display help window ‘i’: Toggle interface ‘s’: Apply auto-scaling ‘r’: Restore original clim ‘c’: Clear all traces ‘n’: Shift the time forward by the playback speed ‘b’: Shift the time backward by the playback speed ‘Space’: Start/Pause playback ‘Up’: Decrease camera elevation angle ‘Down’: Increase camera elevation angle ‘Left’: Decrease camera azimuth angle ‘Right’: Increase camera azimuth angle
- show_view(view=None, roll=None, distance=None, row='deprecated', col='deprecated', hemi=None, align=True, azimuth=None, elevation=None, focalpoint=None)[source]¶
Orient camera to display view.
- Parameters
- view
str The name of the view to show (e.g. “lateral”). Other arguments take precedence and modify the camera starting from the
view.- roll
float|None The roll of the camera rendering the view in degrees.
- distance
float|None The distance from the camera rendering the view to the focalpoint in plot units (either m or mm).
- row
int|None The row to set. Default all rows.
- col
int|None The column to set. Default all columns.
- hemi
str|None Which hemi to use for view lookup (when in “both” mode).
- alignbool
If True, consider view arguments relative to canonical MRI directions (closest to MNI for the subject) rather than native MRI space. This helps when MRIs are not in standard orientation (e.g., have large rotations).
- azimuth
float The azimuthal angle of the camera rendering the view in degrees.
- elevation
float The The zenith angle of the camera rendering the view in degrees.
- focalpoint
tuple, shape (3,) |None The focal point of the camera rendering the view: (x, y, z) in plot units (either m or mm).
- view
Examples using
show_view:
- property time_interpolation¶
The interpolation mode.