mne.io.BaseRaw¶
-
class
mne.io.BaseRaw(info, preload=False, first_samps=(0, ), last_samps=None, filenames=(None, ), raw_extras=(None, ), orig_format='double', dtype=<class 'numpy.float64'>, buffer_size_sec=1.0, orig_units=None, verbose=None)[source]¶ Base class for Raw data.
- Parameters
- info
dict A dict passed from the subclass.
- preloadbool |
str|ndarray Preload data into memory for data manipulation and faster indexing. If True, the data will be preloaded into memory (fast, requires large amount of memory). If preload is a string, preload is the file name of a memory-mapped file which is used to store the data on the hard drive (slower, requires less memory). If preload is an ndarray, the data are taken from that array. If False, data are not read until save.
- first_sampsiterable
Iterable of the first sample number from each raw file. For unsplit raw files this should be a length-one list or tuple.
- last_sampsiterable |
None Iterable of the last sample number from each raw file. For unsplit raw files this should be a length-one list or tuple. If None, then preload must be an ndarray.
- filenames
tuple Tuple of length one (for unsplit raw files) or length > 1 (for split raw files).
- raw_extras
listofdict The data necessary for on-demand reads for the given reader format. Should be the same length as
filenames. Will have the entryraw_extras['orig_nchan']added to it for convenience.- orig_format
str The data format of the original raw file (e.g.,
'double').- dtypedtype |
None The dtype of the raw data. If preload is an ndarray, its dtype must match what is passed here.
- buffer_size_sec
float The buffer size in seconds that should be written by default using
mne.io.Raw.save().- orig_units
dict|None Dictionary mapping channel names to their units as specified in the header file. Example: {‘FC1’: ‘nV’}.
New in version 0.17.
- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only.
- info
See also
mne.io.RawDocumentation of attribute and methods.
Notes
This class is public to allow for stable type-checking in user code (i.e.,
isinstance(my_raw_object, BaseRaw)) but should not be used as a constructor forRawobjects (use instead one of the subclass constructors, or one of themne.io.read_raw_*functions).Subclasses must provide the following methods:
_read_segment_file(self, data, idx, fi, start, stop, cals, mult) (only needed for types that support on-demand disk reads)
- Attributes
annotationsAnnotationsfor marking segments of data.ch_namesChannel names.
compensation_gradeThe current gradient compensation grade.
filenamesThe filenames used.
first_sampThe first data sample.
first_timeThe first time point (including first_samp but not meas_date).
last_sampThe last data sample.
n_timesNumber of time points.
projWhether or not projections are active.
timesTime points.
Methods
__contains__(ch_type)Check channel type membership.
__getitem__(item)Get raw data and times.
__hash__()Hash the object.
__len__()Return the number of time points.
add_channels(add_list[, force_update_info])Append new channels to the instance.
add_events(events[, stim_channel, replace])Add events to stim channel.
add_proj(projs[, remove_existing, verbose])Add SSP projection vectors.
anonymize([daysback, keep_his, verbose])Anonymize measurement information in place.
append(raws[, preload])Concatenate raw instances as if they were continuous.
apply_function(fun[, picks, dtype, n_jobs, …])Apply a function to a subset of channels.
apply_gradient_compensation(grade[, verbose])Apply CTF gradient compensation.
apply_hilbert([picks, envelope, n_jobs, …])Compute analytic signal or envelope for a subset of channels.
apply_proj([verbose])Apply the signal space projection (SSP) operators to the data.
close()Clean up the object.
copy()Return copy of Raw instance.
crop([tmin, tmax, include_tmax])Crop raw data file.
del_proj([idx])Remove SSP projection vector.
drop_channels(ch_names)Drop channel(s).
filter(l_freq, h_freq[, picks, …])Filter a subset of channels.
get_channel_types([picks, unique, only_data_chs])Get a list of channel type for each channel.
get_data([picks, start, stop, …])Get data in the given range.
Get a DigMontage from instance.
interpolate_bads([reset_bads, mode, origin, …])Interpolate bad MEG and EEG channels.
load_bad_channels([bad_file, force])Mark channels as bad from a text file.
load_data([verbose])Load raw data.
notch_filter(freqs[, picks, filter_length, …])Notch filter a subset of channels.
pick(picks[, exclude])Pick a subset of channels.
pick_channels(ch_names[, ordered])Pick some channels.
pick_types([meg, eeg, stim, eog, ecg, emg, …])Pick some channels by type and names.
plot([events, duration, start, n_channels, …])Plot raw data.
plot_projs_topomap([ch_type, cmap, sensors, …])Plot SSP vector.
plot_psd([fmin, fmax, tmin, tmax, proj, …])Plot the power spectral density across channels.
plot_psd_topo([tmin, tmax, fmin, fmax, …])Plot channel-wise frequency spectra as topography.
plot_sensors([kind, ch_type, title, …])Plot sensor positions.
rename_channels(mapping)Rename channels.
reorder_channels(ch_names)Reorder channels.
resample(sfreq[, npad, window, stim_picks, …])Resample all channels.
save(fname[, picks, tmin, tmax, …])Save raw data to file.
savgol_filter(h_freq[, verbose])Filter the data using Savitzky-Golay polynomial method.
set_annotations(annotations[, emit_warning])Setter for annotations.
set_channel_types(mapping[, verbose])Define the sensor type of channels.
set_eeg_reference([ref_channels, …])Specify which reference to use for EEG data.
set_meas_date(meas_date)Set the measurement start date.
set_montage(montage[, match_case, …])Set EEG sensor configuration and head digitization.
time_as_index(times[, use_rounding, origin])Convert time to indices.
to_data_frame([picks, index, scalings, …])Export data in tabular structure as a pandas DataFrame.
-
__contains__(ch_type)[source]¶ Check channel type membership.
- Parameters
- ch_type
str Channel type to check for. Can be e.g. ‘meg’, ‘eeg’, ‘stim’, etc.
- ch_type
- Returns
- inbool
Whether or not the instance contains the given channel type.
Examples
Channel type membership can be tested as:
>>> 'meg' in inst True >>> 'seeg' in inst False
-
__getitem__(item)[source]¶ Get raw data and times.
- Parameters
- item
tupleor array_like See below for use cases.
- item
- Returns
Examples
Generally raw data is accessed as:
>>> data, times = raw[picks, time_slice]
To get all data, you can thus do either of:
>>> data, times = raw[:]
Which will be equivalent to:
>>> data, times = raw[:, :]
To get only the good MEG data from 10-20 seconds, you could do:
>>> picks = mne.pick_types(raw.info, meg=True, exclude='bads') >>> t_idx = raw.time_as_index([10., 20.]) >>> data, times = raw[picks, t_idx[0]:t_idx[1]]
-
__len__()[source]¶ Return the number of time points.
- Returns
- len
int The number of time points.
- len
Examples
This can be used as:
>>> len(raw) 1000
-
add_channels(add_list, force_update_info=False)[source]¶ Append new channels to the instance.
- Parameters
- add_list
list A list of objects to append to self. Must contain all the same type as the current object.
- force_update_infobool
If True, force the info for objects to be appended to match the values in
self. This should generally only be used when adding stim channels for which important metadata won’t be overwritten.New in version 0.12.
- add_list
- Returns
See also
Notes
If
selfis a Raw instance that has been preloaded into anumpy.memmapinstance, the memmap will be resized.Examples using
add_channels:
-
add_events(events, stim_channel=None, replace=False)[source]¶ Add events to stim channel.
- Parameters
- events
ndarray, shape (n_events, 3) Events to add. The first column specifies the sample number of each event, the second column is ignored, and the third column provides the event value. If events already exist in the Raw instance at the given sample numbers, the event values will be added together.
- stim_channel
str|None Name of the stim channel to add to. If None, the config variable ‘MNE_STIM_CHANNEL’ is used. If this is not found, it will default to ‘STI 014’.
- replacebool
If True the old events on the stim channel are removed before adding the new ones.
- events
Notes
Data must be preloaded in order to add events.
Examples using
add_events:
-
add_proj(projs, remove_existing=False, verbose=None)[source]¶ Add SSP projection vectors.
- Parameters
- projs
list List with projection vectors.
- remove_existingbool
Remove the projection vectors currently in the file.
- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only. Defaults to self.verbose.
- projs
- Returns
Examples using
add_proj:
-
property
annotations¶ Annotationsfor marking segments of data.
-
anonymize(daysback=None, keep_his=False, verbose=None)[source]¶ Anonymize measurement information in place.
- Parameters
- daysback
int|None Number of days to subtract from all dates. If
None(default), the acquisition date,info['meas_date'], will be set toJanuary 1ˢᵗ, 2000. This parameter is ignored ifinfo['meas_date']isNone(i.e., no acquisition date has been set).- keep_hisbool
If
True,his_idofsubject_infowill not be overwritten. Defaults toFalse.Warning
This could mean that
infois not fully anonymized. Use with caution.- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only.
- daysback
- Returns
Notes
Removes potentially identifying information if it exists in
info. Specifically for each of the following we use:- meas_date, file_id, meas_id
A default value, or as specified by
daysback.
- subject_info
Default values, except for ‘birthday’ which is adjusted to maintain the subject age.
- experimenter, proj_name, description
Default strings.
- utc_offset
None.
- proj_id
Zeros.
- proc_history
Dates use the
meas_datelogic, and experimenter a default string.
- helium_info, device_info
Dates use the
meas_datelogic, meta info uses defaults.
If
info['meas_date']isNone, it will remainNoneduring processing the above fields.Operates in place.
New in version 0.13.0.
-
append(raws, preload=None)[source]¶ Concatenate raw instances as if they were continuous.
Note
Boundaries of the raw files are annotated bad. If you wish to use the data as continuous recording, you can remove the boundary annotations after concatenation (see
mne.Annotations.delete()).- Parameters
- raws
list, orRawinstance List of Raw instances to concatenate to the current instance (in order), or a single raw instance to concatenate.
- preloadbool,
str, orNone(defaultNone) Preload data into memory for data manipulation and faster indexing. If True, the data will be preloaded into memory (fast, requires large amount of memory). If preload is a string, preload is the file name of a memory-mapped file which is used to store the data on the hard drive (slower, requires less memory). If preload is None, preload=True or False is inferred using the preload status of the instances passed in.
- raws
Examples using
append:
-
apply_function(fun, picks=None, dtype=None, n_jobs=1, channel_wise=True, verbose=None, *args, **kwargs)[source]¶ Apply a function to a subset of channels.
The function “fun” is applied to the channels defined in “picks”. The data of the Raw object is modified inplace. If the function returns a different data type (e.g. numpy.complex) it must be specified using the dtype parameter, which causes the data type used for representing the raw data to change.
The Raw object has to have the data loaded e.g. with
preload=Trueorself.load_data().Note
If n_jobs > 1, more memory is required as
len(picks) * n_timesadditional time points need to be temporaily stored in memory.Note
If the data type changes (dtype != None), more memory is required since the original and the converted data needs to be stored in memory.
- Parameters
- fun
callable() A function to be applied to the channels. The first argument of fun has to be a timeseries (numpy.ndarray). The function must operate on an array of shape
(n_times,)ifchannel_wise=Trueand(len(picks), n_times)otherwise. The function must return an ndarray shaped like its input.- picks
str|list|slice|None Channels to include. Slices and lists of integers will be interpreted as channel indices. In lists, channel type strings (e.g.,
['meg', 'eeg']) will pick channels of those types, channel name strings (e.g.,['MEG0111', 'MEG2623']will pick the given channels. Can also be the string values “all” to pick all channels, or “data” to pick data channels. None (default) will pick all data channels(excluding reference MEG channels).- dtype
numpy.dtype(default:None) Data type to use for raw data after applying the function. If None the data type is not modified.
- n_jobs
int(default: 1) Number of jobs to run in parallel. Ignored if
channel_wiseis False.- channel_wisebool (default:
True) Whether to apply the function to each channel individually. If False, the function will be applied to all channels at once.
New in version 0.18.
- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only. Defaults to self.verbose.- *args
list Additional positional arguments to pass to fun (first pos. argument of fun is the timeseries of a channel).
- **kwargs
dict Keyword arguments to pass to fun.
- fun
- Returns
- selfinstance of
Raw The raw object with transformed data.
- selfinstance of
Examples using
apply_function:
-
apply_gradient_compensation(grade, verbose=None)[source]¶ Apply CTF gradient compensation.
Warning
The compensation matrices are stored with single precision, so repeatedly switching between different of compensation (e.g., 0->1->3->2) can increase numerical noise, especially if data are saved to disk in between changing grades. It is thus best to only use a single gradient compensation level in final analyses.
- Parameters
- grade
int CTF gradient compensation level.
- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only. Defaults to self.verbose.
- grade
- Returns
- rawinstance of
Raw The modified Raw instance. Works in-place.
- rawinstance of
-
apply_hilbert(picks=None, envelope=False, n_jobs=1, n_fft='auto', verbose=None)[source]¶ Compute analytic signal or envelope for a subset of channels.
- Parameters
- picks
str|list|slice|None Channels to include. Slices and lists of integers will be interpreted as channel indices. In lists, channel type strings (e.g.,
['meg', 'eeg']) will pick channels of those types, channel name strings (e.g.,['MEG0111', 'MEG2623']will pick the given channels. Can also be the string values “all” to pick all channels, or “data” to pick data channels. None (default) will pick all data channels(excluding reference MEG channels).- envelopebool
Compute the envelope signal of each channel. Default False. See Notes.
- n_jobs
int The number of jobs to run in parallel (default 1). Requires the joblib package.
- n_fft
int|None|str Points to use in the FFT for Hilbert transformation. The signal will be padded with zeros before computing Hilbert, then cut back to original length. If None, n == self.n_times. If ‘auto’, the next highest fast FFT length will be use.
- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only. Defaults to self.verbose.
- picks
- Returns
Notes
Parameters
If
envelope=False, the analytic signal for the channels defined inpicksis computed and the data of the Raw object is converted to a complex representation (the analytic signal is complex valued).If
envelope=True, the absolute value of the analytic signal for the channels defined inpicksis computed, resulting in the envelope signal.If envelope=False, more memory is required since the original raw data as well as the analytic signal have temporarily to be stored in memory. If n_jobs > 1, more memory is required as
len(picks) * n_timesadditional time points need to be temporaily stored in memory.Also note that the
n_fftparameter will allow you to pad the signal with zeros before performing the Hilbert transform. This padding is cut off, but it may result in a slightly different result (particularly around the edges). Use at your own risk.Analytic signal
The analytic signal “x_a(t)” of “x(t)” is:
x_a = F^{-1}(F(x) 2U) = x + i y
where “F” is the Fourier transform, “U” the unit step function, and “y” the Hilbert transform of “x”. One usage of the analytic signal is the computation of the envelope signal, which is given by “e(t) = abs(x_a(t))”. Due to the linearity of Hilbert transform and the MNE inverse solution, the enevlope in source space can be obtained by computing the analytic signal in sensor space, applying the MNE inverse, and computing the envelope in source space.
Examples using
apply_hilbert:
-
apply_proj(verbose=None)[source]¶ Apply the signal space projection (SSP) operators to the data.
- Parameters
- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only. Defaults to self.verbose.
- verbosebool,
- Returns
Notes
Once the projectors have been applied, they can no longer be removed. It is usually not recommended to apply the projectors at too early stages, as they are applied automatically later on (e.g. when computing inverse solutions). Hint: using the copy method individual projection vectors can be tested without affecting the original data. With evoked data, consider the following example:
projs_a = mne.read_proj('proj_a.fif') projs_b = mne.read_proj('proj_b.fif') # add the first, copy, apply and see ... evoked.add_proj(a).copy().apply_proj().plot() # add the second, copy, apply and see ... evoked.add_proj(b).copy().apply_proj().plot() # drop the first and see again evoked.copy().del_proj(0).apply_proj().plot() evoked.apply_proj() # finally keep both
-
property
ch_names¶ Channel names.
-
close()[source]¶ Clean up the object.
Does nothing for objects that close their file descriptors. Things like RawFIF will override this method.
-
property
compensation_grade¶ The current gradient compensation grade.
-
copy()[source]¶ Return copy of Raw instance.
- Returns
- instinstance of
Raw A copy of the instance.
- instinstance of
Examples using
copy:
-
crop(tmin=0.0, tmax=None, include_tmax=True)[source]¶ Crop raw data file.
Limit the data from the raw file to go between specific times. Note that the new tmin is assumed to be t=0 for all subsequently called functions (e.g., time_as_index, or Epochs). New first_samp and last_samp are set accordingly.
Thus function operates in-place on the instance. Use
mne.io.Raw.copy()if operation on a copy is desired.- Parameters
- Returns
- rawinstance of
Raw The cropped raw object, modified in-place.
- rawinstance of
Examples using
crop:
-
del_proj(idx='all')[source]¶ Remove SSP projection vector.
Note
The projection vector can only be removed if it is inactive (has not been applied to the data).
- Parameters
- Returns
Examples using
del_proj:
-
drop_channels(ch_names)[source]¶ Drop channel(s).
- Parameters
- Returns
See also
Notes
New in version 0.9.0.
Examples using
drop_channels:
-
property
filenames¶ The filenames used.
-
filter(l_freq, h_freq, picks=None, filter_length='auto', l_trans_bandwidth='auto', h_trans_bandwidth='auto', n_jobs=1, method='fir', iir_params=None, phase='zero', fir_window='hamming', fir_design='firwin', skip_by_annotation=('edge', 'bad_acq_skip'), pad='reflect_limited', verbose=None)[source]¶ Filter a subset of channels.
- Parameters
- l_freq
float|None For FIR filters, the lower pass-band edge; for IIR filters, the lower cutoff frequency. If None the data are only low-passed.
- h_freq
float|None For FIR filters, the upper pass-band edge; for IIR filters, the upper cutoff frequency. If None the data are only high-passed.
- picks
str|list|slice|None Channels to include. Slices and lists of integers will be interpreted as channel indices. In lists, channel type strings (e.g.,
['meg', 'eeg']) will pick channels of those types, channel name strings (e.g.,['MEG0111', 'MEG2623']will pick the given channels. Can also be the string values “all” to pick all channels, or “data” to pick data channels. None (default) will pick all data channels.- filter_length
str|int Length of the FIR filter to use (if applicable):
‘auto’ (default): The filter length is chosen based on the size of the transition regions (6.6 times the reciprocal of the shortest transition band for fir_window=’hamming’ and fir_design=”firwin2”, and half that for “firwin”).
str: A human-readable time in units of “s” or “ms” (e.g., “10s” or “5500ms”) will be converted to that number of samples if
phase="zero", or the shortest power-of-two length at least that duration forphase="zero-double".int: Specified length in samples. For fir_design=”firwin”, this should not be used.
- l_trans_bandwidth
float|str Width of the transition band at the low cut-off frequency in Hz (high pass or cutoff 1 in bandpass). Can be “auto” (default) to use a multiple of
l_freq:min(max(l_freq * 0.25, 2), l_freq)
Only used for
method='fir'.- h_trans_bandwidth
float|str Width of the transition band at the high cut-off frequency in Hz (low pass or cutoff 2 in bandpass). Can be “auto” (default in 0.14) to use a multiple of
h_freq:min(max(h_freq * 0.25, 2.), info['sfreq'] / 2. - h_freq)
Only used for
method='fir'.- n_jobs
int|str Number of jobs to run in parallel. Can be ‘cuda’ if
cupyis installed properly and method=’fir’.- method
str ‘fir’ will use overlap-add FIR filtering, ‘iir’ will use IIR forward-backward filtering (via filtfilt).
- iir_params
dict|None Dictionary of parameters to use for IIR filtering. If iir_params is None and method=”iir”, 4th order Butterworth will be used. For more information, see
mne.filter.construct_iir_filter().- phase
str Phase of the filter, only used if
method='fir'. Symmetric linear-phase FIR filters are constructed, and ifphase='zero'(default), the delay of this filter is compensated for, making it non-causal. Ifphase=='zero-double', then this filter is applied twice, once forward, and once backward (also making it non-causal). If ‘minimum’, then a minimum-phase filter will be constricted and applied, which is causal but has weaker stop-band suppression.New in version 0.13.
- fir_window
str The window to use in FIR design, can be “hamming” (default), “hann” (default in 0.13), or “blackman”.
New in version 0.15.
- fir_design
str Can be “firwin” (default) to use
scipy.signal.firwin(), or “firwin2” to usescipy.signal.firwin2(). “firwin” uses a time-domain design technique that generally gives improved attenuation using fewer samples than “firwin2”.New in version 0.15.
- skip_by_annotation
str|listofstr If a string (or list of str), any annotation segment that begins with the given string will not be included in filtering, and segments on either side of the given excluded annotated segment will be filtered separately (i.e., as independent signals). The default (
('edge', 'bad_acq_skip')will separately filter any segments that were concatenated bymne.concatenate_raws()ormne.io.Raw.append(), or separated during acquisition. To disable, provide an empty list. Only used ifinstis raw.New in version 0.16..
- pad
str The type of padding to use. Supports all
numpy.pad()modeoptions. Can also be “reflect_limited”, which pads with a reflected version of each vector mirrored on the first and last values of the vector, followed by zeros. Only used formethod='fir'.- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only. Defaults to self.verbose.
- l_freq
- Returns
See also
Notes
Applies a zero-phase low-pass, high-pass, band-pass, or band-stop filter to the channels selected by
picks. The data are modified inplace.The object has to have the data loaded e.g. with
preload=Trueorself.load_data().l_freqandh_freqare the frequencies below which and above which, respectively, to filter out of the data. Thus the uses are:l_freq < h_freq: band-pass filterl_freq > h_freq: band-stop filterl_freq is not None and h_freq is None: high-pass filterl_freq is None and h_freq is not None: low-pass filter
self.info['lowpass']andself.info['highpass']are only updated with picks=None.Note
If n_jobs > 1, more memory is required as
len(picks) * n_timesadditional time points need to be temporaily stored in memory.For more information, see the tutorials Background information on filtering and Filtering and resampling data and
mne.filter.create_filter().New in version 0.15.
Examples using
filter:
-
property
first_samp¶ The first data sample.
-
property
first_time¶ The first time point (including first_samp but not meas_date).
-
get_channel_types(picks=None, unique=False, only_data_chs=False)[source]¶ Get a list of channel type for each channel.
- Parameters
- picks
str|list|slice|None Channels to include. Slices and lists of integers will be interpreted as channel indices. In lists, channel type strings (e.g.,
['meg', 'eeg']) will pick channels of those types, channel name strings (e.g.,['MEG0111', 'MEG2623']will pick the given channels. Can also be the string values “all” to pick all channels, or “data” to pick data channels. None (default) will pick all channels.- uniquebool
Whether to return only unique channel types. Default is
False.- only_data_chsbool
Whether to ignore non-data channels. Default is
False.
- picks
- Returns
- channel_types
list The channel types.
- channel_types
Examples using
get_channel_types:
-
get_data(picks=None, start=0, stop=None, reject_by_annotation=None, return_times=False, verbose=None)[source]¶ Get data in the given range.
- Parameters
- picks
str|list|slice|None Channels to include. Slices and lists of integers will be interpreted as channel indices. In lists, channel type strings (e.g.,
['meg', 'eeg']) will pick channels of those types, channel name strings (e.g.,['MEG0111', 'MEG2623']will pick the given channels. Can also be the string values “all” to pick all channels, or “data” to pick data channels. None (default) will pick all channels.- start
int The first sample to include. Defaults to 0.
- stop
int|None End sample (first not to include). If None (default), the end of the data is used.
- reject_by_annotation
None| ‘omit’ | ‘NaN’ Whether to reject by annotation. If None (default), no rejection is done. If ‘omit’, segments annotated with description starting with ‘bad’ are omitted. If ‘NaN’, the bad samples are filled with NaNs.
- return_timesbool
Whether to return times as well. Defaults to False.
- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only. Defaults to self.verbose.
- picks
- Returns
Notes
New in version 0.14.0.
Examples using
get_data:
-
get_montage()[source]¶ Get a DigMontage from instance.
- Returns
- montage
None|str|DigMontage A montage containing channel positions. If str or DigMontage is specified, the channel info will be updated with the channel positions. Default is None. See also the documentation of
mne.channels.DigMontagefor more information.
- montage
-
interpolate_bads(reset_bads=True, mode='accurate', origin='auto', method=None, verbose=None)[source]¶ Interpolate bad MEG and EEG channels.
Operates in place.
- Parameters
- reset_badsbool
If True, remove the bads from info.
- mode
str Either
'accurate'or'fast', determines the quality of the Legendre polynomial expansion used for interpolation of channels using the minimum-norm method.- originarray_like, shape (3,) |
str Origin of the sphere in the head coordinate frame and in meters. Can be
'auto'(default), which means a head-digitization-based origin fit.New in version 0.17.
- method
dict Method to use for each channel type. Currently only the key “eeg” has multiple options:
"spline"(default)Use spherical spline interpolation.
"MNE"Use minimum-norm projection to a sphere and back. This is the method used for MEG channels.
The value for “meg” is “MNE”, and the value for “fnirs” is “nearest”. The default (None) is thus an alias for:
method=dict(meg="MNE", eeg="spline", fnirs="nearest")
New in version 0.21.
- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only. Defaults to self.verbose.
- Returns
Notes
New in version 0.9.0.
-
property
last_samp¶ The last data sample.
-
load_bad_channels(bad_file=None, force=False)[source]¶ Mark channels as bad from a text file.
This function operates mostly in the style of the C function
mne_mark_bad_channels. Each line in the text file will be interpreted as a name of a bad channel.- Parameters
- bad_file
str File name of the text file containing bad channels If bad_file = None, bad channels are cleared, but this is more easily done directly as raw.info[‘bads’] = [].
- forcebool
Whether or not to force bad channel marking (of those that exist) if channels are not found, instead of raising an error.
- bad_file
-
load_data(verbose=None)[source]¶ Load raw data.
- Parameters
- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only. Defaults to self.verbose.
- verbosebool,
- Returns
- rawinstance of
Raw The raw object with data.
- rawinstance of
Notes
This function will load raw data if it was not already preloaded. If data were already preloaded, it will do nothing.
New in version 0.10.0.
Examples using
load_data:
-
property
n_times¶ Number of time points.
-
notch_filter(freqs, picks=None, filter_length='auto', notch_widths=None, trans_bandwidth=1.0, n_jobs=1, method='fir', iir_params=None, mt_bandwidth=None, p_value=0.05, phase='zero', fir_window='hamming', fir_design='firwin', pad='reflect_limited', verbose=None)[source]¶ Notch filter a subset of channels.
- Parameters
- freqs
float|arrayoffloat|None Specific frequencies to filter out from data, e.g., np.arange(60, 241, 60) in the US or np.arange(50, 251, 50) in Europe. None can only be used with the mode ‘spectrum_fit’, where an F test is used to find sinusoidal components.
- picks
str|list|slice|None Channels to include. Slices and lists of integers will be interpreted as channel indices. In lists, channel type strings (e.g.,
['meg', 'eeg']) will pick channels of those types, channel name strings (e.g.,['MEG0111', 'MEG2623']will pick the given channels. Can also be the string values “all” to pick all channels, or “data” to pick data channels. None (default) will pick all data channels.- filter_length
str|int Length of the FIR filter to use (if applicable):
‘auto’ (default): The filter length is chosen based on the size of the transition regions (6.6 times the reciprocal of the shortest transition band for fir_window=’hamming’ and fir_design=”firwin2”, and half that for “firwin”).
str: A human-readable time in units of “s” or “ms” (e.g., “10s” or “5500ms”) will be converted to that number of samples if
phase="zero", or the shortest power-of-two length at least that duration forphase="zero-double".int: Specified length in samples. For fir_design=”firwin”, this should not be used.
When
method=='spectrum_fit', this sets the effective window duration over which fits are computed. Seemne.filter.create_filter()for options. Longer window lengths will give more stable frequency estimates, but require (potentially much) more processing and are not able to adapt as well to non-stationarities.The default in 0.21 is None, but this will change to
'10s'in 0.22.- notch_widths
float|arrayoffloat|None Width of each stop band (centred at each freq in freqs) in Hz. If None, freqs / 200 is used.
- trans_bandwidth
float Width of the transition band in Hz. Only used for
method='fir'.- n_jobs
int|str Number of jobs to run in parallel. Can be ‘cuda’ if
cupyis installed properly and method=’fir’.- method
str ‘fir’ will use overlap-add FIR filtering, ‘iir’ will use IIR forward-backward filtering (via filtfilt).
- iir_params
dict|None Dictionary of parameters to use for IIR filtering. If iir_params is None and method=”iir”, 4th order Butterworth will be used. For more information, see
mne.filter.construct_iir_filter().- mt_bandwidth
float|None The bandwidth of the multitaper windowing function in Hz. Only used in ‘spectrum_fit’ mode.
- p_value
float P-value to use in F-test thresholding to determine significant sinusoidal components to remove when method=’spectrum_fit’ and freqs=None. Note that this will be Bonferroni corrected for the number of frequencies, so large p-values may be justified.
- phase
str Phase of the filter, only used if
method='fir'. Symmetric linear-phase FIR filters are constructed, and ifphase='zero'(default), the delay of this filter is compensated for, making it non-causal. Ifphase=='zero-double', then this filter is applied twice, once forward, and once backward (also making it non-causal). If ‘minimum’, then a minimum-phase filter will be constricted and applied, which is causal but has weaker stop-band suppression.New in version 0.13.
- fir_window
str The window to use in FIR design, can be “hamming” (default), “hann” (default in 0.13), or “blackman”.
New in version 0.15.
- fir_design
str Can be “firwin” (default) to use
scipy.signal.firwin(), or “firwin2” to usescipy.signal.firwin2(). “firwin” uses a time-domain design technique that generally gives improved attenuation using fewer samples than “firwin2”.New in version 0.15.
- pad
str The type of padding to use. Supports all
numpy.pad()modeoptions. Can also be “reflect_limited”, which pads with a reflected version of each vector mirrored on the first and last values of the vector, followed by zeros. Only used formethod='fir'. The default is'reflect_limited'.New in version 0.15.
- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only. Defaults to self.verbose.
- freqs
- Returns
- rawinstance of
Raw The raw instance with filtered data.
- rawinstance of
See also
Notes
Applies a zero-phase notch filter to the channels selected by “picks”. By default the data of the Raw object is modified inplace.
The Raw object has to have the data loaded e.g. with
preload=Trueorself.load_data().Note
If n_jobs > 1, more memory is required as
len(picks) * n_timesadditional time points need to be temporaily stored in memory.For details, see
mne.filter.notch_filter().Examples using
notch_filter:
-
pick(picks, exclude=())[source]¶ Pick a subset of channels.
- Parameters
- picks
str|list|slice|None Channels to include. Slices and lists of integers will be interpreted as channel indices. In lists, channel type strings (e.g.,
['meg', 'eeg']) will pick channels of those types, channel name strings (e.g.,['MEG0111', 'MEG2623']will pick the given channels. Can also be the string values “all” to pick all channels, or “data” to pick data channels. None (default) will pick all channels.- exclude
list|str Set of channels to exclude, only used when picking based on types (e.g., exclude=”bads” when picks=”meg”).
- picks
- Returns
Examples using
pick:
-
pick_channels(ch_names, ordered=False)[source]¶ Pick some channels.
- Parameters
- Returns
See also
Notes
The channel names given are assumed to be a set, i.e. the order does not matter. The original order of the channels is preserved. You can use
reorder_channelsto set channel order if necessary.New in version 0.9.0.
Examples using
pick_channels:
-
pick_types(meg=None, eeg=False, stim=False, eog=False, ecg=False, emg=False, ref_meg='auto', misc=False, resp=False, chpi=False, exci=False, ias=False, syst=False, seeg=False, dipole=False, gof=False, bio=False, ecog=False, fnirs=False, csd=False, include=(), exclude='bads', selection=None, verbose=None)[source]¶ Pick some channels by type and names.
- Parameters
- megbool |
str If True include MEG channels. If string it can be ‘mag’, ‘grad’, ‘planar1’ or ‘planar2’ to select only magnetometers, all gradiometers, or a specific type of gradiometer.
- eegbool
If True include EEG channels.
- stimbool
If True include stimulus channels.
- eogbool
If True include EOG channels.
- ecgbool
If True include ECG channels.
- emgbool
If True include EMG channels.
- ref_megbool |
str If True include CTF / 4D reference channels. If ‘auto’, reference channels are included if compensations are present and
megis not False. Can also be the string options for themegparameter.- miscbool
If True include miscellaneous analog channels.
- respbool
If True include response-trigger channel. For some MEG systems this is separate from the stim channel.
- chpibool
If True include continuous HPI coil channels.
- excibool
Flux excitation channel used to be a stimulus channel.
- iasbool
Internal Active Shielding data (maybe on Triux only).
- systbool
System status channel information (on Triux systems only).
- seegbool
Stereotactic EEG channels.
- dipolebool
Dipole time course channels.
- gofbool
Dipole goodness of fit channels.
- biobool
Bio channels.
- ecogbool
Electrocorticography channels.
- fnirsbool |
str Functional near-infrared spectroscopy channels. If True include all fNIRS channels. If False (default) include none. If string it can be ‘hbo’ (to include channels measuring oxyhemoglobin) or ‘hbr’ (to include channels measuring deoxyhemoglobin).
- csdbool
EEG-CSD channels.
- include
listofstr List of additional channels to include. If empty do not include any.
- exclude
listofstr|str List of channels to exclude. If ‘bads’ (default), exclude channels in
info['bads'].- selection
listofstr Restrict sensor channels (MEG, EEG) to this list of channel names.
- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only. Defaults to self.verbose.
- megbool |
- Returns
See also
Notes
New in version 0.9.0.
Examples using
pick_types:
-
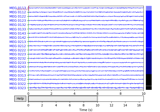
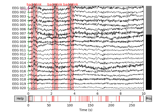
plot(events=None, duration=10.0, start=0.0, n_channels=20, bgcolor='w', color=None, bad_color=(0.8, 0.8, 0.8), event_color='cyan', scalings=None, remove_dc=True, order=None, show_options=False, title=None, show=True, block=False, highpass=None, lowpass=None, filtorder=4, clipping=3.0, show_first_samp=False, proj=True, group_by='type', butterfly=False, decim='auto', noise_cov=None, event_id=None, show_scrollbars=True, show_scalebars=True, verbose=None)[source]¶ Plot raw data.
- Parameters
- events
array|None Events to show with vertical bars.
- duration
float Time window (s) to plot. The lesser of this value and the duration of the raw file will be used.
- start
float Initial time to show (can be changed dynamically once plotted). If show_first_samp is True, then it is taken relative to
raw.first_samp.- n_channels
int Number of channels to plot at once. Defaults to 20. The lesser of
n_channelsandlen(raw.ch_names)will be shown. Has no effect iforderis ‘position’, ‘selection’ or ‘butterfly’.- bgcolorcolor object
Color of the background.
- color
dict| color object |None Color for the data traces. If None, defaults to:
dict(mag='darkblue', grad='b', eeg='k', eog='k', ecg='m', emg='k', ref_meg='steelblue', misc='k', stim='k', resp='k', chpi='k')
- bad_colorcolor object
Color to make bad channels.
- event_colorcolor object |
dict Color to use for events. Can also be a dict with
{event_number: color}pairings. Useevent_number==-1for any event numbers in the events list that are not in the dictionary.- scalings
dict|None Scaling factors for the traces. If any fields in scalings are ‘auto’, the scaling factor is set to match the 99.5th percentile of a subset of the corresponding data. If scalings == ‘auto’, all scalings fields are set to ‘auto’. If any fields are ‘auto’ and data is not preloaded, a subset of times up to 100mb will be loaded. If None, defaults to:
dict(mag=1e-12, grad=4e-11, eeg=20e-6, eog=150e-6, ecg=5e-4, emg=1e-3, ref_meg=1e-12, misc=1e-3, stim=1, resp=1, chpi=1e-4, whitened=1e2)
- remove_dcbool
If True remove DC component when plotting data.
- order
arrayofint|None Order in which to plot data. If the array is shorter than the number of channels, only the given channels are plotted. If None (default), all channels are plotted. If
group_byis'position'or'selection', theorderparameter is used only for selecting the channels to be plotted.- show_optionsbool
If True, a dialog for options related to projection is shown.
- title
str|None The title of the window. If None, and either the filename of the raw object or ‘<unknown>’ will be displayed as title.
- showbool
Show figure if True.
- blockbool
Whether to halt program execution until the figure is closed. Useful for setting bad channels on the fly by clicking on a line. May not work on all systems / platforms.
- highpass
float|None Highpass to apply when displaying data.
- lowpass
float|None Lowpass to apply when displaying data. If highpass > lowpass, a bandstop rather than bandpass filter will be applied.
- filtorder
int Filtering order. 0 will use FIR filtering with MNE defaults. Other values will construct an IIR filter of the given order and apply it with
filtfilt()(making the effective order twicefiltorder). Filtering may produce some edge artifacts (at the left and right edges) of the signals during display.Changed in version 0.18: Support for
filtorder=0to use FIR filtering.- clipping
str|float|None If None, channels are allowed to exceed their designated bounds in the plot. If “clamp”, then values are clamped to the appropriate range for display, creating step-like artifacts. If “transparent”, then excessive values are not shown, creating gaps in the traces. If float, clipping occurs for values beyond the
clippingmultiple of their dedicated range, soclipping=1.is an alias forclipping='transparent'.Changed in version 0.21: Support for float, and default changed from None to 1.5.
- show_first_sampbool
If True, show time axis relative to the
raw.first_samp.- projbool
Whether to apply projectors prior to plotting (default is
True). Individual projectors can be enabled/disabled interactively (see Notes). This argument only affects the plot; useraw.apply_proj()to modify the data stored in the Raw object.- group_by
str How to group channels.
'type'groups by channel type,'original'plots in the order of ch_names,'selection'uses Elekta’s channel groupings (only works for Neuromag data),'position'groups the channels by the positions of the sensors.'selection'and'position'modes allow custom selections by using lasso selector on the topomap. Pressingctrlkey while selecting allows appending to the current selection. Channels marked as bad appear with red edges on the topomap.'type'and'original'groups the channels by type in butterfly mode whereas'selection'and'position'use regional grouping.'type'and'original'modes are overridden withorderkeyword.- butterflybool
Whether to start in butterfly mode. Defaults to False.
- decim
int| ‘auto’ Amount to decimate the data during display for speed purposes. You should only decimate if the data are sufficiently low-passed, otherwise aliasing can occur. The ‘auto’ mode (default) uses the decimation that results in a sampling rate least three times larger than
min(info['lowpass'], lowpass)(e.g., a 40 Hz lowpass will result in at least a 120 Hz displayed sample rate).- noise_covinstance of
Covariance|str|None Noise covariance used to whiten the data while plotting. Whitened data channels are scaled by
scalings['whitened'], and their channel names are shown in italic. Can be a string to load a covariance from disk. See alsomne.Evoked.plot_white()for additional inspection of noise covariance properties when whitening evoked data. For data processed with SSS, the effective dependence between magnetometers and gradiometers may introduce differences in scaling, consider usingmne.Evoked.plot_white().New in version 0.16.0.
- event_id
dict|None Event IDs used to show at event markers (default None shows the event numbers).
New in version 0.16.0.
- show_scrollbarsbool
Whether to show scrollbars when the plot is initialized. Can be toggled after initialization by pressing z (“zen mode”) while the plot window is focused. Default is
True.New in version 0.19.0.
- show_scalebarsbool
Whether or not to show the scale bars. Defaults to True.
New in version 0.20.0.
- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only.
- events
- Returns
- figinstance of
matplotlib.figure.Figure Raw traces.
- figinstance of
Notes
The arrow keys (up/down/left/right) can typically be used to navigate between channels and time ranges, but this depends on the backend matplotlib is configured to use (e.g., mpl.use(‘TkAgg’) should work). The left/right arrows will scroll by 25% of
duration, whereas shift+left/shift+right will scroll by 100% ofduration. The scaling can be adjusted with - and + (or =) keys. The viewport dimensions can be adjusted with page up/page down and home/end keys. Full screen mode can be toggled with the F11 key. To mark or un-mark a channel as bad, click on a channel label or a channel trace. The changes will be reflected immediately in the raw object’sraw.info['bads']entry.If projectors are present, a button labelled “Proj” in the lower right corner of the plot window opens a secondary control window, which allows enabling/disabling specific projectors individually. This provides a means of interactively observing how each projector would affect the raw data if it were applied.
Annotation mode is toggled by pressing ‘a’, butterfly mode by pressing ‘b’, and whitening mode (when
noise_cov is not None) by pressing ‘w’. By default, the channel means are removed whenremove_dcis set toTrue. This flag can be toggled by pressing ‘d’.Examples using
plot:
-
plot_projs_topomap(ch_type=None, cmap=None, sensors=True, colorbar=False, res=64, size=1, show=True, outlines='head', contours=6, image_interp='bilinear', axes=None, vlim=(None, None), sphere=None, extrapolate='auto', border='mean')[source]¶ Plot SSP vector.
- Parameters
- ch_type‘mag’ | ‘grad’ | ‘planar1’ | ‘planar2’ | ‘eeg’ |
None|list The channel type to plot. For ‘grad’, the gradiometers are collec- ted in pairs and the RMS for each pair is plotted. If None (default), it will return all channel types present. If a list of ch_types is provided, it will return multiple figures.
- cmapmatplotlib colormap | (colormap, bool) | ‘interactive’ |
None Colormap to use. If tuple, the first value indicates the colormap to use and the second value is a boolean defining interactivity. In interactive mode (only works if
colorbar=True) the colors are adjustable by clicking and dragging the colorbar with left and right mouse button. Left mouse button moves the scale up and down and right mouse button adjusts the range. Hitting space bar resets the range. Up and down arrows can be used to change the colormap. If None (default), ‘Reds’ is used for all positive data, otherwise defaults to ‘RdBu_r’. If ‘interactive’, translates to (None, True).- sensorsbool |
str Add markers for sensor locations to the plot. Accepts matplotlib plot format string (e.g., ‘r+’ for red plusses). If True, a circle will be used (via .add_artist). Defaults to True.
- colorbarbool
Plot a colorbar.
- res
int The resolution of the topomap image (n pixels along each side).
- sizescalar
Side length of the topomaps in inches (only applies when plotting multiple topomaps at a time).
- showbool
Show figure if True.
- outlines‘head’ | ‘skirt’ |
dict|None The outlines to be drawn. If ‘head’, the default head scheme will be drawn. If ‘skirt’ the head scheme will be drawn, but sensors are allowed to be plotted outside of the head circle. If dict, each key refers to a tuple of x and y positions, the values in ‘mask_pos’ will serve as image mask. Alternatively, a matplotlib patch object can be passed for advanced masking options, either directly or as a function that returns patches (required for multi-axis plots). If None, nothing will be drawn. Defaults to ‘head’.
- contours
int|arrayoffloat The number of contour lines to draw. If 0, no contours will be drawn. When an integer, matplotlib ticker locator is used to find suitable values for the contour thresholds (may sometimes be inaccurate, use array for accuracy). If an array, the values represent the levels for the contours. Defaults to 6.
- image_interp
str The image interpolation to be used. All matplotlib options are accepted.
- axesinstance of
Axes|list|None The axes to plot to. If list, the list must be a list of Axes of the same length as the number of projectors. If instance of Axes, there must be only one projector. Defaults to None.
- vlim
tupleof length 2 | ‘joint’ Colormap limits to use. If
tuple, specifies the lower and upper bounds of the colormap (in that order); providingNonefor either of these will set the corresponding boundary at the min/max of the data (separately for each projector). The keyword value'joint'will compute the colormap limits jointly across all provided projectors of the same channel type, using the min/max of the projector data. If vlim is'joint',infomust not beNone. Defaults to(None, None).- sphere
float| array_like |str|None The sphere parameters to use for the cartoon head. Can be array-like of shape (4,) to give the X/Y/Z origin and radius in meters, or a single float to give the radius (origin assumed 0, 0, 0). Can also be a spherical ConductorModel, which will use the origin and radius. Can be “auto” to use a digitization-based fit. Can also be None (default) to use ‘auto’ when enough extra digitization points are available, and 0.095 otherwise. Currently the head radius does not affect plotting.
New in version 0.20.
- extrapolate
str Options:
'box'Extrapolate to four points placed to form a square encompassing all data points, where each side of the square is three times the range of the data in the respective dimension.
'local'(default)Extrapolate only to nearby points (approximately to points closer than median inter-electrode distance). This will also set the mask to be polygonal based on the convex hull of the sensors.
'head'Extrapolate out to the edges of the clipping circle. This will be on the head circle when the sensors are contained within the head circle, but it can extend beyond the head when sensors are plotted outside the head circle.
-
Changed in version 0.21:
The default was changed to
'local''local'was changed to use a convex hull mask'head'was changed to extrapolate out to the clipping circle.
New in version 0.20.
- border
float| ‘mean’ Value to extrapolate to on the topomap borders. If
'mean'(default), then each extrapolated point has the average value of its neighbours.New in version 0.20.
- ch_type‘mag’ | ‘grad’ | ‘planar1’ | ‘planar2’ | ‘eeg’ |
- Returns
- figinstance of
Figure Figure distributing one image per channel across sensor topography.
- figinstance of
Examples using
plot_projs_topomap:
-
plot_psd(fmin=0, fmax=inf, tmin=None, tmax=None, proj=False, n_fft=None, n_overlap=0, reject_by_annotation=True, picks=None, ax=None, color='black', xscale='linear', area_mode='std', area_alpha=0.33, dB=True, estimate='auto', show=True, n_jobs=1, average=False, line_alpha=None, spatial_colors=True, sphere=None, verbose=None)[source]¶ Plot the power spectral density across channels.
Different channel types are drawn in sub-plots. When the data have been processed with a bandpass, lowpass or highpass filter, dashed lines indicate the boundaries of the filter (–). The line noise frequency is also indicated with a dashed line (-.).
- Parameters
- fmin
float Start frequency to consider.
- fmax
float End frequency to consider.
- tmin
float|None Start time to consider.
- tmax
float|None End time to consider.
- projbool
Apply projection.
- n_fft
int|None Number of points to use in Welch FFT calculations. Default is None, which uses the minimum of 2048 and the number of time points.
- n_overlap
int The number of points of overlap between blocks. The default value is 0 (no overlap).
- reject_by_annotationbool
Whether to omit bad segments from the data before fitting. If
True(default), annotated segments whose description begins with'bad'are omitted. IfFalse, no rejection based on annotations is performed.Has no effect if
instis not amne.io.Rawobject.- picks
str|list|slice|None Channels to include. Slices and lists of integers will be interpreted as channel indices. In lists, channel type strings (e.g.,
['meg', 'eeg']) will pick channels of those types, channel name strings (e.g.,['MEG0111', 'MEG2623']will pick the given channels. Can also be the string values “all” to pick all channels, or “data” to pick data channels. None (default) will pick good data channels Cannot be None ifaxis supplied.If bothpicksandaxare None separate subplots will be created for each standard channel type (mag,grad, andeeg).- axinstance of
Axes|None Axes to plot into. If None, axes will be created.
- color
str|tuple A matplotlib-compatible color to use. Has no effect when spatial_colors=True.
- xscale
str Can be ‘linear’ (default) or ‘log’.
- area_mode
str|None Mode for plotting area. If ‘std’, the mean +/- 1 STD (across channels) will be plotted. If ‘range’, the min and max (across channels) will be plotted. Bad channels will be excluded from these calculations. If None, no area will be plotted. If average=False, no area is plotted.
- area_alpha
float Alpha for the area.
- dBbool
Plot Power Spectral Density (PSD), in units (amplitude**2/Hz (dB)) if
dB=True, andestimate='power'orestimate='auto'. Plot PSD in units (amplitude**2/Hz) ifdB=Falseand,estimate='power'. Plot Amplitude Spectral Density (ASD), in units (amplitude/sqrt(Hz)), ifdB=Falseandestimate='amplitude'orestimate='auto'. Plot ASD, in units (amplitude/sqrt(Hz) (db)), ifdB=Trueandestimate='amplitude'.- estimate
str, {‘auto’, ‘power’, ‘amplitude’} Can be “power” for power spectral density (PSD), “amplitude” for amplitude spectrum density (ASD), or “auto” (default), which uses “power” when dB is True and “amplitude” otherwise.
- showbool
Show figure if True.
- n_jobs
int The number of jobs to run in parallel (default 1). Requires the joblib package.
- averagebool
If False, the PSDs of all channels is displayed. No averaging is done and parameters area_mode and area_alpha are ignored. When False, it is possible to paint an area (hold left mouse button and drag) to plot a topomap.
- line_alpha
float|None Alpha for the PSD line. Can be None (default) to use 1.0 when
average=Trueand 0.1 whenaverage=False.- spatial_colorsbool
Whether to use spatial colors. Only used when
average=False.- sphere
float| array_like |str|None The sphere parameters to use for the cartoon head. Can be array-like of shape (4,) to give the X/Y/Z origin and radius in meters, or a single float to give the radius (origin assumed 0, 0, 0). Can also be a spherical ConductorModel, which will use the origin and radius. Can be “auto” to use a digitization-based fit. Can also be None (default) to use ‘auto’ when enough extra digitization points are available, and 0.095 otherwise. Currently the head radius does not affect plotting.
New in version 0.20.
- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only.
- fmin
- Returns
- figinstance of
Figure Figure with frequency spectra of the data channels.
- figinstance of
Examples using
plot_psd:
-
plot_psd_topo(tmin=0.0, tmax=None, fmin=0, fmax=100, proj=False, n_fft=2048, n_overlap=0, layout=None, color='w', fig_facecolor='k', axis_facecolor='k', dB=True, show=True, block=False, n_jobs=1, axes=None, verbose=None)[source]¶ Plot channel-wise frequency spectra as topography.
- Parameters
- tmin
float Start time for calculations. Defaults to zero.
- tmax
float|None End time for calculations. If None (default), the end of data is used.
- fmin
float Start frequency to consider. Defaults to zero.
- fmax
float End frequency to consider. Defaults to 100.
- projbool
Apply projection. Defaults to False.
- n_fft
int Number of points to use in Welch FFT calculations. Defaults to 2048.
- n_overlap
int The number of points of overlap between blocks. Defaults to 0 (no overlap).
- layoutinstance of
Layout|None Layout instance specifying sensor positions (does not need to be specified for Neuromag data). If None (default), the correct layout is inferred from the data.
- color
str|tuple A matplotlib-compatible color to use for the curves. Defaults to white.
- fig_facecolor
str|tuple A matplotlib-compatible color to use for the figure background. Defaults to black.
- axis_facecolor
str|tuple A matplotlib-compatible color to use for the axis background. Defaults to black.
- dBbool
If True, transform data to decibels. Defaults to True.
- showbool
Show figure if True. Defaults to True.
- blockbool
Whether to halt program execution until the figure is closed. May not work on all systems / platforms. Defaults to False.
- n_jobs
int The number of jobs to run in parallel (default 1). Requires the joblib package.
- axesinstance of matplotlib
Axes|None Axes to plot into. If None, axes will be created.
- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only.
- tmin
- Returns
- figinstance of
matplotlib.figure.Figure Figure distributing one image per channel across sensor topography.
- figinstance of
Examples using
plot_psd_topo:
-
plot_sensors(kind='topomap', ch_type=None, title=None, show_names=False, ch_groups=None, to_sphere=True, axes=None, block=False, show=True, sphere=None, verbose=None)[source]¶ Plot sensor positions.
- Parameters
- kind
str Whether to plot the sensors as 3d, topomap or as an interactive sensor selection dialog. Available options ‘topomap’, ‘3d’, ‘select’. If ‘select’, a set of channels can be selected interactively by using lasso selector or clicking while holding control key. The selected channels are returned along with the figure instance. Defaults to ‘topomap’.
- ch_type
None|str The channel type to plot. Available options ‘mag’, ‘grad’, ‘eeg’, ‘seeg’, ‘ecog’, ‘all’. If
'all', all the available mag, grad, eeg, seeg and ecog channels are plotted. If None (default), then channels are chosen in the order given above.- title
str|None Title for the figure. If None (default), equals to
'Sensor positions (%s)' % ch_type.- show_namesbool |
arrayofstr Whether to display all channel names. If an array, only the channel names in the array are shown. Defaults to False.
- ch_groups‘position’ |
arrayof shape (n_ch_groups, n_picks) |None Channel groups for coloring the sensors. If None (default), default coloring scheme is used. If ‘position’, the sensors are divided into 8 regions. See
orderkwarg ofmne.viz.plot_raw(). If array, the channels are divided by picks given in the array.New in version 0.13.0.
- to_spherebool
Whether to project the 3d locations to a sphere. When False, the sensor array appears similar as to looking downwards straight above the subject’s head. Has no effect when kind=’3d’. Defaults to True.
New in version 0.14.0.
- axesinstance of
Axes| instance ofAxes3D|None Axes to draw the sensors to. If
kind='3d', axes must be an instance of Axes3D. If None (default), a new axes will be created.New in version 0.13.0.
- blockbool
Whether to halt program execution until the figure is closed. Defaults to False.
New in version 0.13.0.
- showbool
Show figure if True. Defaults to True.
- sphere
float| array_like |str|None The sphere parameters to use for the cartoon head. Can be array-like of shape (4,) to give the X/Y/Z origin and radius in meters, or a single float to give the radius (origin assumed 0, 0, 0). Can also be a spherical ConductorModel, which will use the origin and radius. Can be “auto” to use a digitization-based fit. Can also be None (default) to use ‘auto’ when enough extra digitization points are available, and 0.095 otherwise. Currently the head radius does not affect plotting.
New in version 0.20.
- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only. Defaults to self.verbose.
- kind
- Returns
See also
Notes
This function plots the sensor locations from the info structure using matplotlib. For drawing the sensors using mayavi see
mne.viz.plot_alignment().New in version 0.12.0.
Examples using
plot_sensors:
-
property
proj¶ Whether or not projections are active.
-
rename_channels(mapping)[source]¶ Rename channels.
- Parameters
- mapping
dict|callable() A dictionary mapping the old channel to a new channel name e.g. {‘EEG061’ : ‘EEG161’}. Can also be a callable function that takes and returns a string.
Changed in version 0.10.0: Support for a callable function.
- mapping
- Returns
Notes
New in version 0.9.0.
Examples using
rename_channels:
-
reorder_channels(ch_names)[source]¶ Reorder channels.
- Parameters
- ch_names
list The desired channel order.
- ch_names
- Returns
See also
Notes
Channel names must be unique. Channels that are not in
ch_namesare dropped.New in version 0.16.0.
-
resample(sfreq, npad='auto', window='boxcar', stim_picks=None, n_jobs=1, events=None, pad='reflect_limited', verbose=None)[source]¶ Resample all channels.
Warning
The intended purpose of this function is primarily to speed up computations (e.g., projection calculation) when precise timing of events is not required, as downsampling raw data effectively jitters trigger timings. It is generally recommended not to epoch downsampled data, but instead epoch and then downsample, as epoching downsampled data jitters triggers. For more, see this illustrative gist.
If resampling the continuous data is desired, it is recommended to construct events using the original data. The event onsets can be jointly resampled with the raw data using the ‘events’ parameter (a resampled copy is returned).
- Parameters
- sfreq
float New sample rate to use.
- npad
int|str Amount to pad the start and end of the data. Can also be “auto” to use a padding that will result in a power-of-two size (can be much faster).
- window
str|tuple Frequency-domain window to use in resampling. See
scipy.signal.resample().- stim_picks
listofint|None Stim channels. These channels are simply subsampled or supersampled (without applying any filtering). This reduces resampling artifacts in stim channels, but may lead to missing triggers. If None, stim channels are automatically chosen using
mne.pick_types().- n_jobs
int|str Number of jobs to run in parallel. Can be ‘cuda’ if
cupyis installed properly.- events2D
array, shape (n_events, 3) |None An optional event matrix. When specified, the onsets of the events are resampled jointly with the data. NB: The input events are not modified, but a new array is returned with the raw instead.
- pad
str The type of padding to use. Supports all
numpy.pad()modeoptions. Can also be “reflect_limited”, which pads with a reflected version of each vector mirrored on the first and last values of the vector, followed by zeros. Only used formethod='fir'. The default is'reflect_limited'.New in version 0.15.
- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only. Defaults to self.verbose.
- sfreq
- Returns
See also
Notes
For some data, it may be more accurate to use
npad=0to reduce artifacts. This is dataset dependent – check your data!For optimum performance and to make use of
n_jobs > 1, the raw object has to have the data loaded e.g. withpreload=Trueorself.load_data(), but this increases memory requirements. The resulting raw object will have the data loaded into memory.Examples using
resample:
-
save(fname, picks=None, tmin=0, tmax=None, buffer_size_sec=None, drop_small_buffer=False, proj=False, fmt='single', overwrite=False, split_size='2GB', split_naming='neuromag', verbose=None)[source]¶ Save raw data to file.
- Parameters
- fname
str File name of the new dataset. This has to be a new filename unless data have been preloaded. Filenames should end with raw.fif, raw.fif.gz, raw_sss.fif, raw_sss.fif.gz, raw_tsss.fif, raw_tsss.fif.gz, or _meg.fif.
- picks
str|list|slice|None Channels to include. Slices and lists of integers will be interpreted as channel indices. In lists, channel type strings (e.g.,
['meg', 'eeg']) will pick channels of those types, channel name strings (e.g.,['MEG0111', 'MEG2623']will pick the given channels. Can also be the string values “all” to pick all channels, or “data” to pick data channels. None (default) will pick all channels.- tmin
float Start time of the raw data to use in seconds (must be >= 0).
- tmax
float End time of the raw data to use in seconds (cannot exceed data duration).
- buffer_size_sec
float|None Size of data chunks in seconds. If None (default), the buffer size of the original file is used.
- drop_small_bufferbool
Drop or not the last buffer. It is required by maxfilter (SSS) that only accepts raw files with buffers of the same size.
- projbool
If True the data is saved with the projections applied (active).
Note
If
apply_proj()was used to apply the projections, the projectons will be active even ifprojis False.- fmt‘single’ | ‘double’ | ‘int’ | ‘short’
Format to use to save raw data. Valid options are ‘double’, ‘single’, ‘int’, and ‘short’ for 64- or 32-bit float, or 32- or 16-bit integers, respectively. It is strongly recommended to use ‘single’, as this is backward-compatible, and is standard for maintaining precision. Note that using ‘short’ or ‘int’ may result in loss of precision, complex data cannot be saved as ‘short’, and neither complex data types nor real data stored as ‘double’ can be loaded with the MNE command-line tools. See raw.orig_format to determine the format the original data were stored in.
- overwritebool
If True, the destination file (if it exists) will be overwritten. If False (default), an error will be raised if the file exists. To overwrite original file (the same one that was loaded), data must be preloaded upon reading.
- split_size
str|int Large raw files are automatically split into multiple pieces. This parameter specifies the maximum size of each piece. If the parameter is an integer, it specifies the size in Bytes. It is also possible to pass a human-readable string, e.g., 100MB.
Note
Due to FIFF file limitations, the maximum split size is 2GB.
- split_naming{‘neuromag’ | ‘bids’}
Add the filename partition with the appropriate naming schema.
New in version 0.17.
- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only. Defaults to self.verbose.
- fname
Notes
If Raw is a concatenation of several raw files, be warned that only the measurement information from the first raw file is stored. This likely means that certain operations with external tools may not work properly on a saved concatenated file (e.g., probably some or all forms of SSS). It is recommended not to concatenate and then save raw files for this reason.
Examples using
save:
-
savgol_filter(h_freq, verbose=None)[source]¶ Filter the data using Savitzky-Golay polynomial method.
- Parameters
- h_freq
float Approximate high cut-off frequency in Hz. Note that this is not an exact cutoff, since Savitzky-Golay filtering 1 is done using polynomial fits instead of FIR/IIR filtering. This parameter is thus used to determine the length of the window over which a 5th-order polynomial smoothing is used.
- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only. Defaults to self.verbose.
- h_freq
- Returns
See also
Notes
For Savitzky-Golay low-pass approximation, see:
New in version 0.9.0.
References
- 1
Abraham Savitzky and Marcel J. E. Golay. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Analytical Chemistry, 36(8):1627–1639, 1964. doi:10.1021/ac60214a047.
Examples
>>> import mne >>> from os import path as op >>> evoked_fname = op.join(mne.datasets.sample.data_path(), 'MEG', 'sample', 'sample_audvis-ave.fif') >>> evoked = mne.read_evokeds(evoked_fname, baseline=(None, 0))[0] >>> evoked.savgol_filter(10.) # low-pass at around 10 Hz >>> evoked.plot()
-
set_annotations(annotations, emit_warning=True)[source]¶ Setter for annotations.
This setter checks if they are inside the data range.
- Parameters
- annotationsinstance of
mne.Annotations|None Annotations to set. If None, the annotations is defined but empty.
- emit_warningbool
Whether to emit warnings when limiting or omitting annotations.
- annotationsinstance of
- Returns
- selfinstance of
Raw The raw object with annotations.
- selfinstance of
Examples using
set_annotations:
-
set_channel_types(mapping, verbose=None)[source]¶ Define the sensor type of channels.
- Parameters
- mapping
dict A dictionary mapping a channel to a sensor type (str), e.g.,
{'EEG061': 'eog'}.- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only. Defaults to self.verbose.
- mapping
- Returns
Notes
The following sensor types are accepted:
ecg, eeg, emg, eog, exci, ias, misc, resp, seeg, stim, syst, ecog, hbo, hbr, fnirs_cw_amplitude, fnirs_od
New in version 0.9.0.
Examples using
set_channel_types:
-
set_eeg_reference(ref_channels='average', projection=False, ch_type='auto', forward=None, verbose=None)[source]¶ Specify which reference to use for EEG data.
Use this function to explicitly specify the desired reference for EEG. This can be either an existing electrode or a new virtual channel. This function will re-reference the data according to the desired reference.
- Parameters
- ref_channels
listofstr|str Can be:
The name(s) of the channel(s) used to construct the reference.
'average'to apply an average reference (default)'REST'to use the Reference Electrode Standardization Technique infinity reference 2.An empty list, in which case MNE will not attempt any re-referencing of the data
- projectionbool
If
ref_channels='average'this argument specifies if the average reference should be computed as a projection (True) or not (False; default). Ifprojection=True, the average reference is added as a projection and is not applied to the data (it can be applied afterwards with theapply_projmethod). Ifprojection=False, the average reference is directly applied to the data. Ifref_channelsis not'average',projectionmust be set toFalse(the default in this case).- ch_type‘auto’ | ‘eeg’ | ‘ecog’ | ‘seeg’
The name of the channel type to apply the reference to. If ‘auto’, the first channel type of eeg, ecog or seeg that is found (in that order) will be selected.
New in version 0.19.
- forwardinstance of
Forward|None Forward solution to use. Only used with
ref_channels='REST'.New in version 0.21.
- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only. Defaults to self.verbose.
- ref_channels
- Returns
See also
mne.set_bipolar_referenceConvenience function for creating bipolar references.
Notes
Some common referencing schemes and the corresponding value for the
ref_channelsparameter:- Average reference:
A new virtual reference electrode is created by averaging the current EEG signal by setting
ref_channels='average'. Bad EEG channels are automatically excluded if they are properly set ininfo['bads'].
- A single electrode:
Set
ref_channelsto a list containing the name of the channel that will act as the new reference, for exampleref_channels=['Cz'].
- The mean of multiple electrodes:
A new virtual reference electrode is created by computing the average of the current EEG signal recorded from two or more selected channels. Set
ref_channelsto a list of channel names, indicating which channels to use. For example, to apply an average mastoid reference, when using the 10-20 naming scheme, setref_channels=['M1', 'M2'].
- REST
The given EEG electrodes are referenced to a point at infinity using the lead fields in
forward, which helps standardize the signals.
If a reference is requested that is not the average reference, this function removes any pre-existing average reference projections.
During source localization, the EEG signal should have an average reference.
In order to apply a reference, the data must be preloaded. This is not necessary if
ref_channels='average'andprojection=True.For an average or REST reference, bad EEG channels are automatically excluded if they are properly set in
info['bads'].
New in version 0.9.0.
References
- 2
D. Yao. A method to standardize a reference of scalp EEG recordings to a point at infinity. Physiological Measurement, 22(4):693–711, November 2001. doi:10.1088/0967-3334/22/4/305.
Examples using
set_eeg_reference:
-
set_meas_date(meas_date)[source]¶ Set the measurement start date.
- Parameters
- meas_date
datetime|float|tuple|None The new measurement date. If datetime object, it must be timezone-aware and in UTC. A tuple of (seconds, microseconds) or float (alias for
(meas_date, 0)) can also be passed and a datetime object will be automatically created. If None, will remove the time reference.
- meas_date
- Returns
See also
Notes
If you want to remove all time references in the file, call
mne.io.anonymize_info(inst.info)after callinginst.set_meas_date(None).New in version 0.20.
-
set_montage(montage, match_case=True, on_missing='raise', verbose=None)[source]¶ Set EEG sensor configuration and head digitization.
- Parameters
- montage
None|str|DigMontage A montage containing channel positions. If str or DigMontage is specified, the channel info will be updated with the channel positions. Default is None. See also the documentation of
mne.channels.DigMontagefor more information.- match_casebool
If True (default), channel name matching will be case sensitive.
New in version 0.20.
- on_missing
str Can be
'raise'(default) to raise an error,'warn'to emit a warning, or'ignore'to ignore when channels have missing coordinates.New in version 0.20.1.
- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only. Defaults to self.verbose.
- montage
- Returns
Notes
Operates in place.
Examples using
set_montage:
-
time_as_index(times, use_rounding=False, origin=None)[source]¶ Convert time to indices.
- Parameters
- timeslist-like |
float|int List of numbers or a number representing points in time.
- use_roundingbool
If True, use rounding (instead of truncation) when converting times to indices. This can help avoid non-unique indices.
- origin
datetime|float|int|None Time reference for times. If None,
timesare assumed to be relative tofirst_samp.New in version 0.17.0.
- timeslist-like |
- Returns
- index
ndarray Indices relative to
first_sampcorresponding to the times supplied.
- index
Examples using
time_as_index:
-
property
times¶ Time points.
-
to_data_frame(picks=None, index=None, scalings=None, copy=True, start=None, stop=None, long_format=False, time_format='ms')[source]¶ Export data in tabular structure as a pandas DataFrame.
Channels are converted to columns in the DataFrame. By default, an additional column “time” is added, unless
indexis notNone(in which case time values form the DataFrame’s index).- Parameters
- picks
str|list|slice|None Channels to include. Slices and lists of integers will be interpreted as channel indices. In lists, channel type strings (e.g.,
['meg', 'eeg']) will pick channels of those types, channel name strings (e.g.,['MEG0111', 'MEG2623']will pick the given channels. Can also be the string values “all” to pick all channels, or “data” to pick data channels. None (default) will pick all channels.- index‘time’ |
None Kind of index to use for the DataFrame. If
None, a sequential integer index (pandas.RangeIndex) will be used. If'time', apandas.Float64Index,pandas.Int64Index,pandas.DatetimeIndex, orpandas.TimedeltaIndexwill be used (depending on the value oftime_format). Defaults toNone.- scalings
dict|None Scaling factor applied to the channels picked. If
None, defaults todict(eeg=1e6, mag=1e15, grad=1e13)— i.e., converts EEG to µV, magnetometers to fT, and gradiometers to fT/cm.- copybool
If
True, data will be copied. Otherwise data may be modified in place. Defaults toTrue.- start
int|None Starting sample index for creating the DataFrame from a temporal span of the Raw object.
None(the default) uses the first sample.- stop
int|None Ending sample index for creating the DataFrame from a temporal span of the Raw object.
None(the default) uses the last sample.- long_formatbool
If True, the DataFrame is returned in long format where each row is one observation of the signal at a unique combination of time point and channel. For convenience, a
ch_typecolumn is added to facilitate subsetting the resulting DataFrame. Defaults toFalse.- time_format
str|None Desired time format. If
None, no conversion is applied, and time values remain as float values in seconds. If'ms', time values will be rounded to the nearest millisecond and converted to integers. If'timedelta', time values will be converted topandas.Timedeltavalues. If'datetime', time values will be converted topandas.Timestampvalues, relative toraw.info['meas_date']and offset byraw.first_samp. Defaults to'ms'.New in version 0.20.
- picks
- Returns
- dfinstance of
pandas.DataFrame A dataframe suitable for usage with other statistical/plotting/analysis packages.
- dfinstance of
Examples using
to_data_frame:
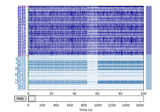
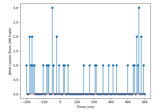
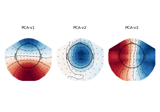
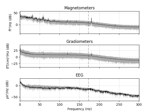



![Regression on continuous data (rER[P/F])](../_images/sphx_glr_plot_linear_regression_raw_thumb.png)