mne.SourceSpaces#
- class mne.SourceSpaces(source_spaces, info=None)[source]#
Represent a list of source space.
Currently implemented as a list of dictionaries containing the source space information
- Parameters
- Attributes
- info
dict Dictionary with information about the creation of the source space file. Has keys ‘working_dir’ and ‘command_line’.
- info
Methods
__add__(other)Combine source spaces.
__contains__(key, /)Return key in self.
__getitem__(*args, **kwargs)Get an item.
__iter__(/)Implement iter(self).
__len__(/)Return len(self).
__mul__(value, /)Return self*value.
append(object, /)Append object to the end of the list.
clear(/)Remove all items from list.
copy()Make a copy of the source spaces.
count(value, /)Return number of occurrences of value.
export_volume(fname[, include_surfaces, ...])Export source spaces to nifti or mgz file.
extend(iterable, /)Extend list by appending elements from the iterable.
index(value[, start, stop])Return first index of value.
insert(index, object, /)Insert object before index.
plot([head, brain, skull, subjects_dir, ...])Plot the source space.
pop([index])Remove and return item at index (default last).
remove(value, /)Remove first occurrence of value.
reverse(/)Reverse IN PLACE.
save(fname[, overwrite, verbose])Save the source spaces to a fif file.
sort(*[, key, reverse])Sort the list in ascending order and return None.
- __contains__(key, /)#
Return key in self.
- __iter__(/)#
Implement iter(self).
- __len__(/)#
Return len(self).
- __mul__(value, /)#
Return self*value.
- append(object, /)#
Append object to the end of the list.
- clear(/)#
Remove all items from list.
- copy()[source]#
Make a copy of the source spaces.
- Returns
- srcinstance of
SourceSpaces The copied source spaces.
- srcinstance of
- count(value, /)#
Return number of occurrences of value.
- export_volume(fname, include_surfaces=True, include_discrete=True, dest='mri', trans=None, mri_resolution=False, use_lut=True, overwrite=False, verbose=None)[source]#
Export source spaces to nifti or mgz file.
- Parameters
- fname
str Name of nifti or mgz file to write.
- include_surfacesbool
If True, include surface source spaces.
- include_discretebool
If True, include discrete source spaces.
- dest‘mri’ | ‘surf’
If ‘mri’ the volume is defined in the coordinate system of the original T1 image. If ‘surf’ the coordinate system of the FreeSurfer surface is used (Surface RAS).
- trans
dict,str, orNone Either a transformation filename (usually made using mne_analyze) or an info dict (usually opened using read_trans()). If string, an ending of
.fifor.fif.gzwill be assumed to be in FIF format, any other ending will be assumed to be a text file with a 4x4 transformation matrix (like the--transMNE-C option. Must be provided if source spaces are in head coordinates and include_surfaces and mri_resolution are True.- mri_resolutionbool |
str If True, the image is saved in MRI resolution (e.g. 256 x 256 x 256), and each source region (surface or segmentation volume) filled in completely. If “sparse”, only a single voxel in the high-resolution MRI is filled in for each source point.
Changed in version 0.21.0: Support for “sparse” was added.
- use_lutbool
If True, assigns a numeric value to each source space that corresponds to a color on the freesurfer lookup table.
- overwritebool
If True (default False), overwrite the destination file if it exists.
New in version 0.19.
- verbosebool |
str|int|None Control verbosity of the logging output. If
None, use the default verbosity level. See the logging documentation andmne.verbose()for details. Should only be passed as a keyword argument.
- fname
Notes
This method requires nibabel.
Examples using
export_volume:
Compute MNE inverse solution on evoked data with a mixed source space
Compute MNE inverse solution on evoked data with a mixed source space
- extend(iterable, /)#
Extend list by appending elements from the iterable.
- index(value, start=0, stop=sys.maxsize, /)#
Return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
- insert(index, object, /)#
Insert object before index.
- plot(head=False, brain=None, skull=None, subjects_dir=None, trans=None, verbose=None)[source]#
Plot the source space.
- Parameters
- headbool
If True, show head surface.
- brainbool |
str If True, show the brain surfaces. Can also be a str for surface type (e.g., ‘pial’, same as True). Default is None, which means ‘white’ for surface source spaces and False otherwise.
- skullbool |
str|listofstr|listofdict|None Whether to plot skull surface. If string, common choices would be ‘inner_skull’, or ‘outer_skull’. Can also be a list to plot multiple skull surfaces. If a list of dicts, each dict must contain the complete surface info (such as you get from
mne.make_bem_model()). True is an alias of ‘outer_skull’. The subjects bem and bem/flash folders are searched for the ‘surf’ files. Defaults to None, which is False for surface source spaces, and True otherwise.- subjects_dir
str|None Path to SUBJECTS_DIR if it is not set in the environment.
- trans
str| ‘auto’ |dict|None The full path to the head<->MRI transform
*-trans.fiffile produced during coregistration. If trans is None, an identity matrix is assumed. This is only needed when the source space is in head coordinates.- verbosebool |
str|int|None Control verbosity of the logging output. If
None, use the default verbosity level. See the logging documentation andmne.verbose()for details. Should only be passed as a keyword argument.
- Returns
- figinstance of
Figure3D The figure.
- figinstance of
Examples using
plot:
Compute MNE inverse solution on evoked data with a mixed source space
Compute MNE inverse solution on evoked data with a mixed source space
- pop(index=- 1, /)#
Remove and return item at index (default last).
Raises IndexError if list is empty or index is out of range.
- remove(value, /)#
Remove first occurrence of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
- reverse(/)#
Reverse IN PLACE.
- save(fname, overwrite=False, *, verbose=None)[source]#
Save the source spaces to a fif file.
- Parameters
- fname
str File to write.
- overwritebool
If True (default False), overwrite the destination file if it exists.
- verbosebool |
str|int|None Control verbosity of the logging output. If
None, use the default verbosity level. See the logging documentation andmne.verbose()for details. Should only be passed as a keyword argument.
- fname
- sort(*, key=None, reverse=False)#
Sort the list in ascending order and return None.
The sort is in-place (i.e. the list itself is modified) and stable (i.e. the order of two equal elements is maintained).
If a key function is given, apply it once to each list item and sort them, ascending or descending, according to their function values.
The reverse flag can be set to sort in descending order.
Examples using mne.SourceSpaces#
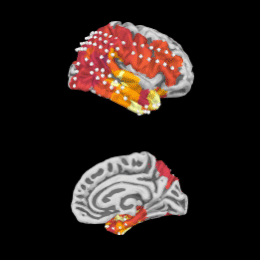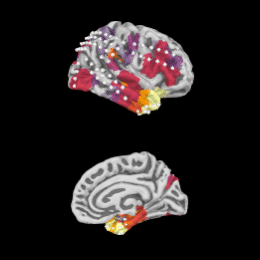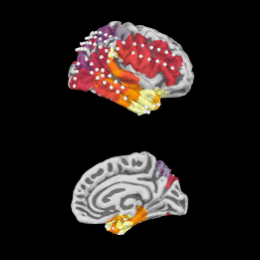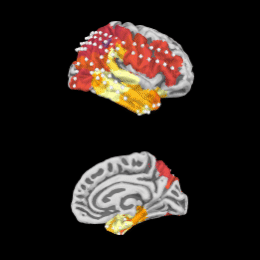
Permutation t-test on source data with spatio-temporal clustering
2 samples permutation test on source data with spatio-temporal clustering
Repeated measures ANOVA on source data with spatio-temporal clustering
Compute MNE-dSPM inverse solution on evoked data in volume source space

Extracting the time series of activations in a label
Compute sparse inverse solution with mixed norm: MxNE and irMxNE

Compute MNE inverse solution on evoked data with a mixed source space
Visualize source leakage among labels using a circular graph