mne.io.read_raw_fif#
- mne.io.read_raw_fif(fname, allow_maxshield=False, preload=False, on_split_missing='raise', verbose=None)[source]#
Reader function for Raw FIF data.
- Parameters
- fname
str| file-like The raw filename to load. For files that have automatically been split, the split part will be automatically loaded. Filenames should end with raw.fif, raw.fif.gz, raw_sss.fif, raw_sss.fif.gz, raw_tsss.fif, raw_tsss.fif.gz, or _meg.fif. If a file-like object is provided, preloading must be used.
Changed in version 0.18: Support for file-like objects.
- allow_maxshieldbool |
str(defaultFalse) If True, allow loading of data that has been recorded with internal active compensation (MaxShield). Data recorded with MaxShield should generally not be loaded directly, but should first be processed using SSS/tSSS to remove the compensation signals that may also affect brain activity. Can also be “yes” to load without eliciting a warning.
- preloadbool or
str(defaultFalse) Preload data into memory for data manipulation and faster indexing. If True, the data will be preloaded into memory (fast, requires large amount of memory). If preload is a string, preload is the file name of a memory-mapped file which is used to store the data on the hard drive (slower, requires less memory).
- on_split_missing
str Can be
'raise'(default) to raise an error,'warn'to emit a warning, or'ignore'to ignore when split file is missing.New in version 0.22.
- verbosebool |
str|int|None Control verbosity of the logging output. If
None, use the default verbosity level. See the logging documentation andmne.verbose()for details. Should only be passed as a keyword argument.
- fname
- Returns
- rawinstance of
Raw A Raw object containing FIF data.
- rawinstance of
Notes
New in version 0.9.0.
When reading a FIF file, note that the first N seconds annotated
BAD_ACQ_SKIPare skipped. They are removed fromraw.timesandraw.n_timesparameters butraw.first_sampandraw.first_timeare updated accordingly.
Examples using mne.io.read_raw_fif#
Signal-space separation (SSS) and Maxwell filtering
EEG processing and Event Related Potentials (ERPs)
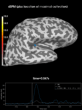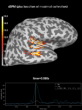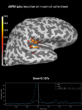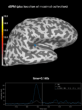
Source localization with MNE, dSPM, sLORETA, and eLORETA
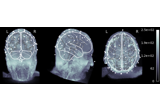
EEG source localization given electrode locations on an MRI
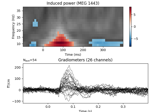
Non-parametric 1 sample cluster statistic on single trial power
Non-parametric between conditions cluster statistic on single trial power

Spatiotemporal permutation F-test on full sensor data
Permutation t-test on source data with spatio-temporal clustering
Repeated measures ANOVA on source data with spatio-temporal clustering
Mass-univariate twoway repeated measures ANOVA on single trial power
Cortical Signal Suppression (CSS) for removal of cortical signals
Define target events based on time lag, plot evoked response
Transform EEG data using current source density (CSD)
Plot sensor denoising using oversampled temporal projection
How to convert 3D electrode positions to a 2D image
Compute Power Spectral Density of inverse solution from single epochs
Compute power and phase lock in label of the source space
Compute source power spectral density (PSD) in a label
Compute source power spectral density (PSD) of VectorView and OPM data
Compute induced power in the source space with dSPM

Explore event-related dynamics for specific frequency bands
Permutation F-test on sensor data with 1D cluster level

Decoding sensor space data with generalization across time and conditions
Analysis of evoked response using ICA and PCA reduction techniques
Linear classifier on sensor data with plot patterns and filters
Compute MNE-dSPM inverse solution on single epochs
Compute evoked ERS source power using DICS, LCMV beamformer, and dSPM
Compute source power estimate by projecting the covariance with MNE
Compute iterative reweighted TF-MxNE with multiscale time-frequency dictionary






![Regression on continuous data (rER[P/F])](../_images/sphx_glr_linear_regression_raw_thumb.png)