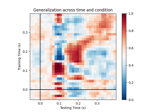
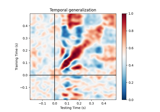
mne.decoding.GeneralizingEstimator¶
- class mne.decoding.GeneralizingEstimator(base_estimator, scoring=None, n_jobs=1, verbose=None)[source]¶
Generalization Light.
Fit a search-light along the last dimension and use them to apply a systematic cross-tasks generalization.
- Parameters
- base_estimatorobject
The base estimator to iteratively fit on a subset of the dataset.
- scoring
callable()|str|None Score function (or loss function) with signature
score_func(y, y_pred, **kwargs). Note that the predict_method is automatically identified if scoring is a string (e.g. scoring=”roc_auc” calls predict_proba) but is not automatically set if scoring is a callable (e.g. scoring=sklearn.metrics.roc_auc_score).- n_jobs
int The number of jobs to run in parallel (default 1). Requires the joblib package. The number of jobs to run in parallel for both
fitandpredict. If -1, then the number of jobs is set to the number of cores.- verbosebool,
str,int, orNone If not None, override default verbose level (see
mne.verbose()and Logging documentation for more). If used, it should be passed as a keyword-argument only.
- Attributes
- classes_
Methods
__hash__(/)Return hash(self).
Estimate distances of each data slice to all hyperplanes.
fit(X, y, **fit_params)Fit a series of independent estimators to the dataset.
fit_transform(X, y, **fit_params)Fit and transform a series of independent estimators to the dataset.
get_params([deep])Get parameters for this estimator.
predict(X)Predict each data slice with all possible estimators.
Estimate probabilistic estimates of each data slice with all possible estimators.
score(X, y)Score each of the estimators on the tested dimensions.
set_params(**params)Set the parameters of this estimator.
transform(X)Transform each data slice with all possible estimators.
- decision_function(X)[source]¶
Estimate distances of each data slice to all hyperplanes.
- Parameters
- X
array, shape (n_samples, nd_features, n_slices) The training input samples. Each estimator outputs the distance to its hyperplane, e.g.:
[estimators[ii].decision_function(X[..., ii]) for ii in range(n_estimators)]. The feature dimension can be multidimensional e.g.X.shape = (n_samples, n_features_1, n_features_2, n_estimators).
- X
- Returns
- y_pred
array, shape (n_samples, n_estimators, n_slices, n_classes * (n_classes-1) // 2) The predicted values for each estimator.
- y_pred
Notes
This requires base_estimator to have a
decision_functionmethod.
- fit(X, y, **fit_params)[source]¶
Fit a series of independent estimators to the dataset.
- Parameters
- X
array, shape (n_samples, nd_features, n_tasks) The training input samples. For each data slice, a clone estimator is fitted independently. The feature dimension can be multidimensional e.g. X.shape = (n_samples, n_features_1, n_features_2, n_tasks).
- y
array, shape (n_samples,) | (n_samples, n_targets) The target values.
- **fit_params
dictofstr-> object Parameters to pass to the fit method of the estimator.
- X
- Returns
- selfobject
Return self.
Examples using
fit:
- fit_transform(X, y, **fit_params)[source]¶
Fit and transform a series of independent estimators to the dataset.
- Parameters
- X
array, shape (n_samples, nd_features, n_tasks) The training input samples. For each task, a clone estimator is fitted independently. The feature dimension can be multidimensional, e.g.:
X.shape = (n_samples, n_features_1, n_features_2, n_estimators)
- y
array, shape (n_samples,) | (n_samples, n_targets) The target values.
- **fit_params
dictofstr-> object Parameters to pass to the fit method of the estimator.
- X
- Returns
- y_pred
array, shape (n_samples, n_tasks) | (n_samples, n_tasks, n_targets) The predicted values for each estimator.
- y_pred
- predict(X)[source]¶
Predict each data slice with all possible estimators.
- Parameters
- X
array, shape (n_samples, nd_features, n_slices) The training input samples. For each data slice, a fitted estimator predicts each slice of the data independently. The feature dimension can be multidimensional e.g. X.shape = (n_samples, n_features_1, n_features_2, n_estimators).
- X
- Returns
- y_pred
array, shape (n_samples, n_estimators, n_slices) | (n_samples, n_estimators, n_slices, n_targets) The predicted values for each estimator.
- y_pred
- predict_proba(X)[source]¶
Estimate probabilistic estimates of each data slice with all possible estimators.
- Parameters
- X
array, shape (n_samples, nd_features, n_slices) The training input samples. For each data slice, a fitted estimator predicts a slice of the data. The feature dimension can be multidimensional e.g.
X.shape = (n_samples, n_features_1, n_features_2, n_estimators).
- X
- Returns
- y_pred
array, shape (n_samples, n_estimators, n_slices, n_classes) The predicted values for each estimator.
- y_pred
Notes
This requires base_estimator to have a
predict_probamethod.
- score(X, y)[source]¶
Score each of the estimators on the tested dimensions.
- Parameters
- X
array, shape (n_samples, nd_features, n_slices) The input samples. For each data slice, the corresponding estimator scores the prediction, e.g.:
[estimators[ii].score(X[..., ii], y) for ii in range(n_slices)]. The feature dimension can be multidimensional e.g.X.shape = (n_samples, n_features_1, n_features_2, n_estimators).- y
array, shape (n_samples,) | (n_samples, n_targets) The target values.
- X
- Returns
- score
array, shape (n_samples, n_estimators, n_slices) Score for each estimator / data slice couple.
- score
Examples using
score:
- set_params(**params)[source]¶
Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as pipelines). The latter have parameters of the form
<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.- Parameters
- **params
dict Parameters.
- **params
- Returns
- instinstance
The object.
- transform(X)[source]¶
Transform each data slice with all possible estimators.
- Parameters
- X
array, shape (n_samples, nd_features, n_slices) The input samples. For estimator the corresponding data slice is used to make a transformation. The feature dimension can be multidimensional e.g. X.shape = (n_samples, n_features_1, n_features_2, n_estimators).
- X
- Returns
- Xt
array, shape (n_samples, n_estimators, n_slices) The transformed values generated by each estimator.
- Xt