Note
Click here to download the full example code
Plotting with mne.viz.Brain#
In this example, we’ll show how to use mne.viz.Brain.
# Author: Alex Rockhill <aprockhill@mailbox.org>
#
# License: BSD-3-Clause
Load data#
In this example we use the sample data which is data from a subject
being presented auditory and visual stimuli to display the functionality
of mne.viz.Brain for plotting data on a brain.
import os.path as op
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
import mne
from mne.datasets import sample
print(__doc__)
data_path = sample.data_path()
subjects_dir = op.join(data_path, 'subjects')
sample_dir = op.join(data_path, 'MEG', 'sample')
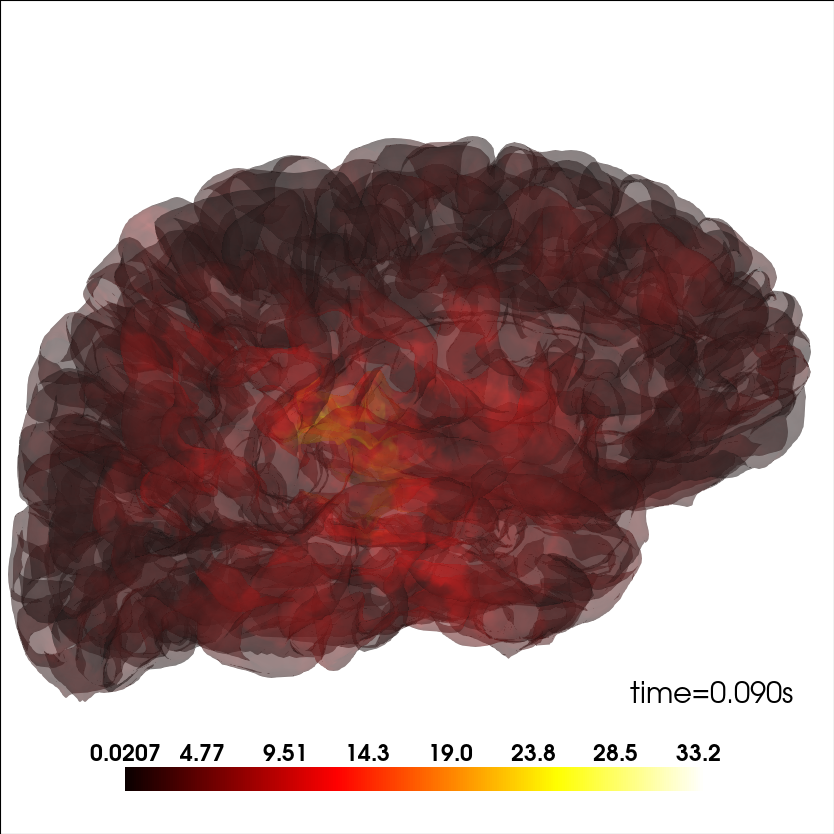
Add source information#
Plot source information.
brain_kwargs = dict(alpha=0.1, background='white', cortex='low_contrast')
brain = mne.viz.Brain('sample', subjects_dir=subjects_dir, **brain_kwargs)
stc = mne.read_source_estimate(op.join(sample_dir, 'sample_audvis-meg'))
stc.crop(0.09, 0.1)
kwargs = dict(fmin=stc.data.min(), fmax=stc.data.max(), alpha=0.25,
smoothing_steps='nearest', time=stc.times)
brain.add_data(stc.lh_data, hemi='lh', vertices=stc.lh_vertno, **kwargs)
brain.add_data(stc.rh_data, hemi='rh', vertices=stc.rh_vertno, **kwargs)
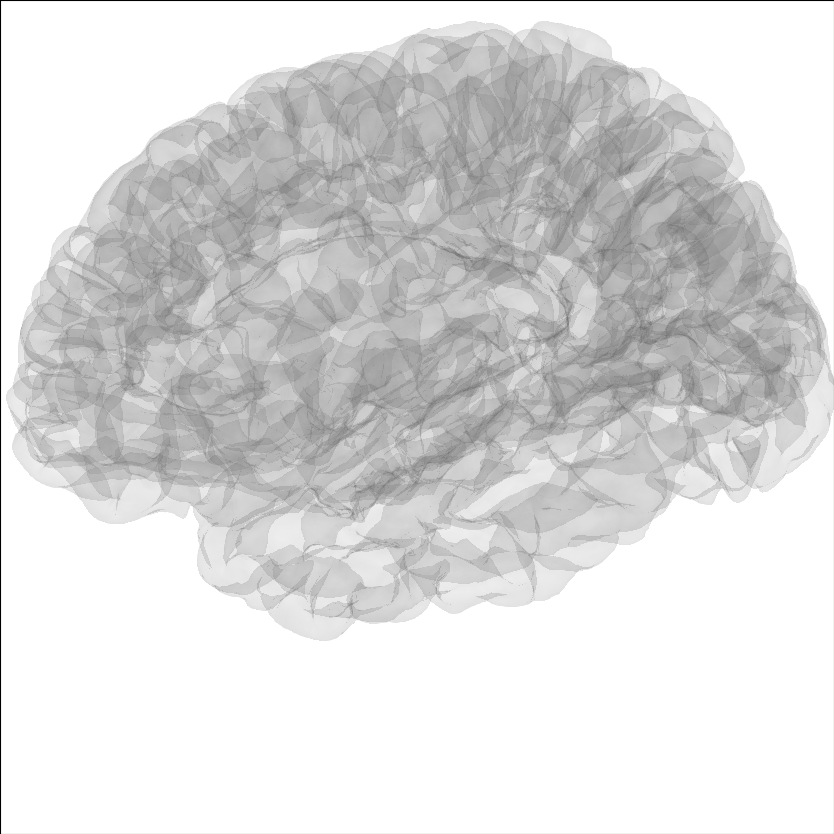
Modify the view of the brain#
You can adjust the view of the brain using show_view method.
brain = mne.viz.Brain('sample', subjects_dir=subjects_dir, **brain_kwargs)
brain.show_view(azimuth=190, elevation=70, distance=350, focalpoint=(0, 0, 20))
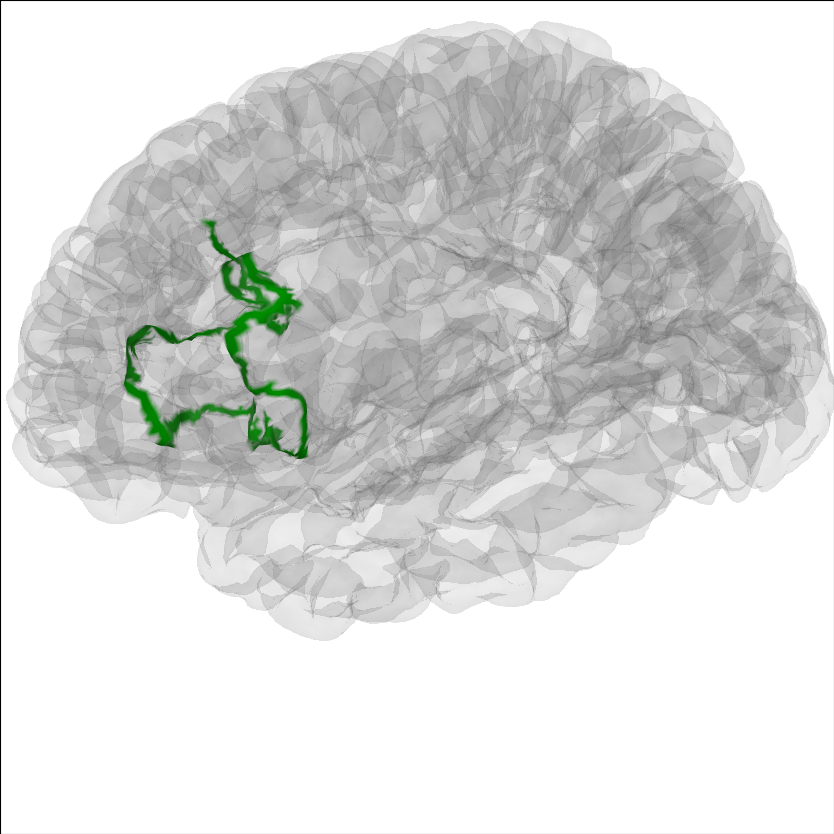
Highlight a region on the brain#
It can be useful to highlight a region of the brain for analyses.
To highlight a region on the brain you can use the add_label method.
Labels are stored in the Freesurfer label directory from the recon-all
for that subject. Labels can also be made following the
Freesurfer instructions
Here we will show Brodmann Area 44.
Note
The MNE sample dataset contains only a subselection of the
Freesurfer labels created during the recon-all.
brain = mne.viz.Brain('sample', subjects_dir=subjects_dir, **brain_kwargs)
brain.add_label('BA44', hemi='lh', color='green', borders=True)
brain.show_view(azimuth=190, elevation=70, distance=350, focalpoint=(0, 0, 20))
Include the head in the image#
Add a head image using the add_head method.
brain = mne.viz.Brain('sample', subjects_dir=subjects_dir, **brain_kwargs)
brain.add_head(alpha=0.5)
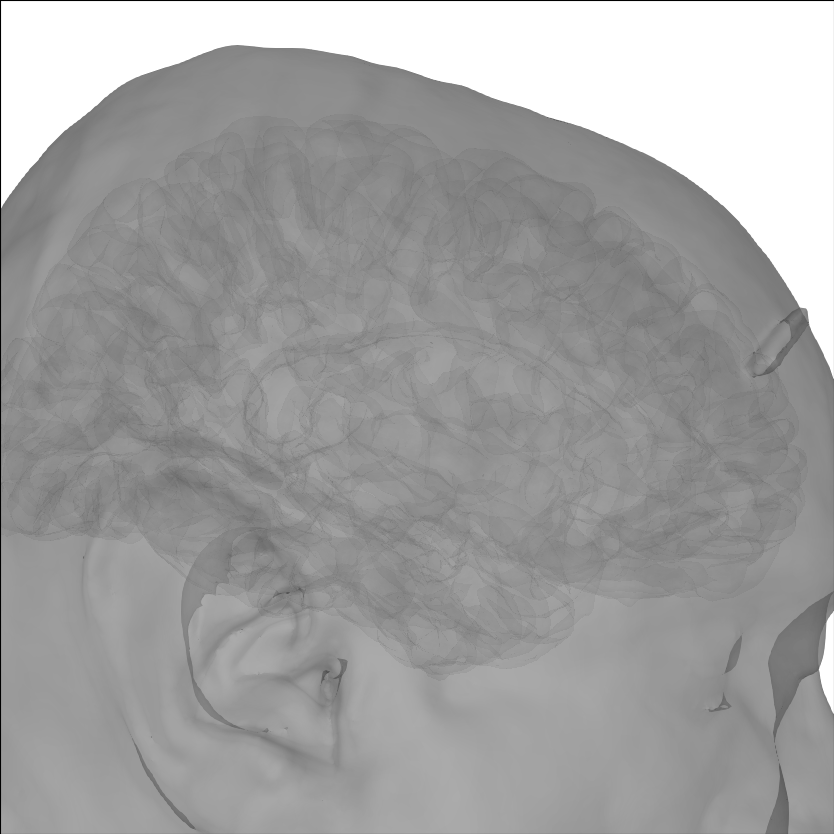
Using lh.seghead for head surface.
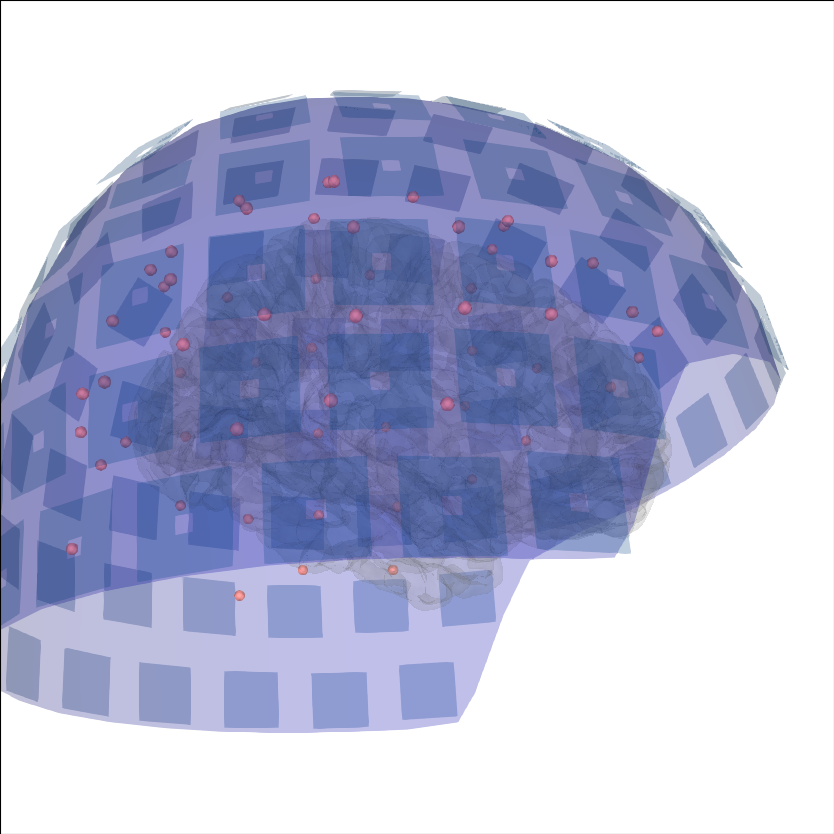
Add sensors positions#
To put into context the data that generated the source time course, the sensor positions can be displayed as well.
brain = mne.viz.Brain('sample', subjects_dir=subjects_dir, **brain_kwargs)
evoked = mne.read_evokeds(op.join(sample_dir, 'sample_audvis-ave.fif'))[0]
trans = mne.read_trans(op.join(sample_dir, 'sample_audvis_raw-trans.fif'))
brain.add_sensors(evoked.info, trans)
brain.show_view(distance=500) # move back to show sensors
Reading /home/circleci/mne_data/MNE-sample-data/MEG/sample/sample_audvis-ave.fif ...
Read a total of 4 projection items:
PCA-v1 (1 x 102) active
PCA-v2 (1 x 102) active
PCA-v3 (1 x 102) active
Average EEG reference (1 x 60) active
Found the data of interest:
t = -199.80 ... 499.49 ms (Left Auditory)
0 CTF compensation matrices available
nave = 55 - aspect type = 100
Projections have already been applied. Setting proj attribute to True.
No baseline correction applied
Read a total of 4 projection items:
PCA-v1 (1 x 102) active
PCA-v2 (1 x 102) active
PCA-v3 (1 x 102) active
Average EEG reference (1 x 60) active
Found the data of interest:
t = -199.80 ... 499.49 ms (Right Auditory)
0 CTF compensation matrices available
nave = 61 - aspect type = 100
Projections have already been applied. Setting proj attribute to True.
No baseline correction applied
Read a total of 4 projection items:
PCA-v1 (1 x 102) active
PCA-v2 (1 x 102) active
PCA-v3 (1 x 102) active
Average EEG reference (1 x 60) active
Found the data of interest:
t = -199.80 ... 499.49 ms (Left visual)
0 CTF compensation matrices available
nave = 67 - aspect type = 100
Projections have already been applied. Setting proj attribute to True.
No baseline correction applied
Read a total of 4 projection items:
PCA-v1 (1 x 102) active
PCA-v2 (1 x 102) active
PCA-v3 (1 x 102) active
Average EEG reference (1 x 60) active
Found the data of interest:
t = -199.80 ... 499.49 ms (Right visual)
0 CTF compensation matrices available
nave = 58 - aspect type = 100
Projections have already been applied. Setting proj attribute to True.
No baseline correction applied
Channel types:: grad: 203, mag: 102, eeg: 59
Getting helmet for system 306m
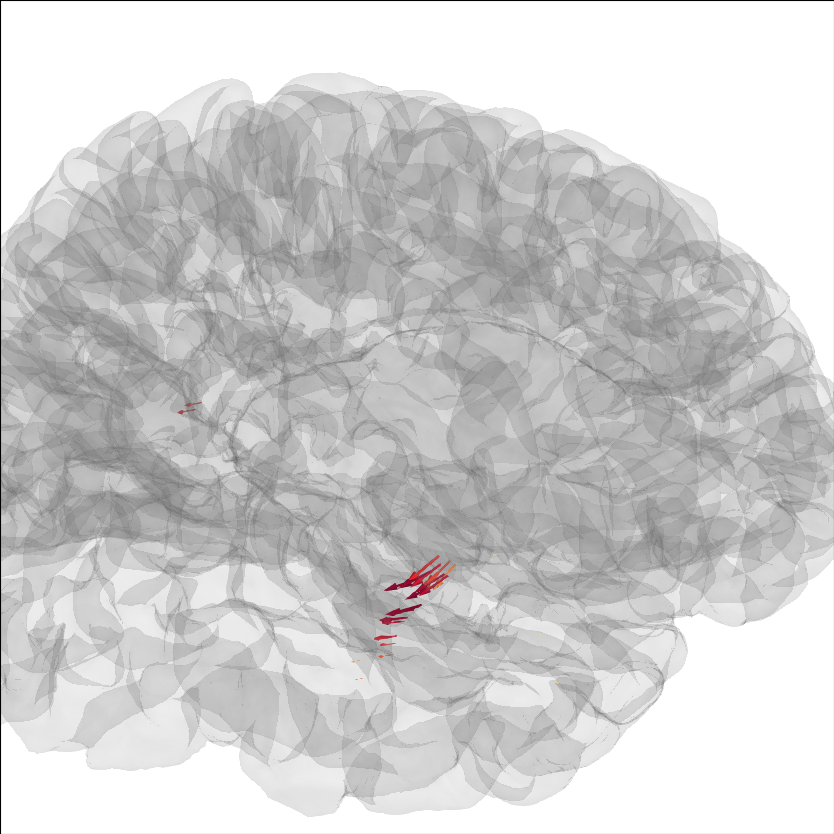
Add current dipoles#
Dipole modeling as in The role of dipole orientations in distributed source localization can be plotted on the brain as well.
brain = mne.viz.Brain('sample', subjects_dir=subjects_dir, **brain_kwargs)
dip = mne.read_dipole(op.join(sample_dir, 'sample_audvis_set1.dip'))
cmap = plt.get_cmap('YlOrRd')
colors = [cmap(gof / dip.gof.max()) for gof in dip.gof]
brain.add_dipole(dip, trans, colors=colors, scales=list(dip.amplitude * 1e8))
brain.show_view(azimuth=-20, elevation=60, distance=300)
img = brain.screenshot() # for next section
34 dipole(s) found
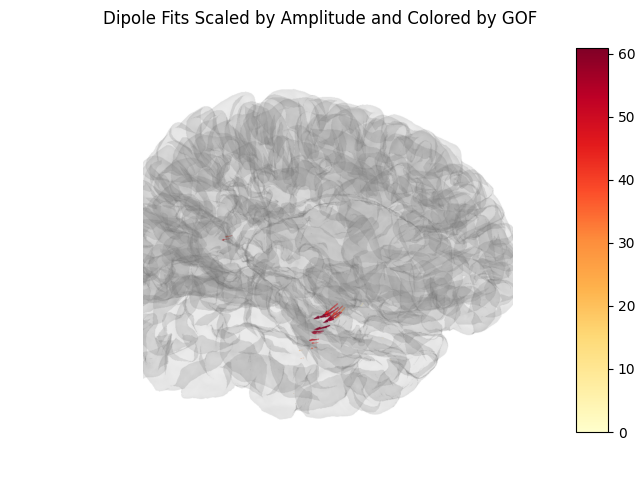
Create a screenshot for exporting the brain image#
Also, we can a static image of the brain using screenshot (above),
which will allow us to add a colorbar. This is useful for figures in
publications.
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.imshow(img)
ax.axis('off')
cax = fig.add_axes([0.9, 0.1, 0.05, 0.8])
fig.colorbar(mpl.cm.ScalarMappable(
norm=mpl.colors.Normalize(vmin=0, vmax=dip.gof.max()), cmap=cmap), cax=cax)
fig.suptitle('Dipole Fits Scaled by Amplitude and Colored by GOF')
Total running time of the script: ( 1 minutes 24.395 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 210 MB