mne.filter.resample#
- mne.filter.resample(x, up=1.0, down=1.0, npad=100, axis=-1, window='boxcar', n_jobs=None, pad='reflect_limited', *, verbose=None)[source]#
Resample an array.
Operates along the last dimension of the array.
- Parameters:
- x
ndarray Signal to resample.
- up
float Factor to upsample by.
- down
float Factor to downsample by.
- npad
int|str Amount to pad the start and end of the data. Can also be “auto” to use a padding that will result in a power-of-two size (can be much faster).
- axis
int Axis along which to resample (default is the last axis).
- window
str|tuple Frequency-domain window to use in resampling. See
scipy.signal.resample().- n_jobs
int|str Number of jobs to run in parallel. Can be ‘cuda’ if
cupyis installed properly.- pad
str The type of padding to use. Supports all
numpy.pad()modeoptions. Can also be"reflect_limited", which pads with a reflected version of each vector mirrored on the first and last values of the vector, followed by zeros. The default is'reflect_limited'.New in version 0.15.
- verbosebool |
str|int|None Control verbosity of the logging output. If
None, use the default verbosity level. See the logging documentation andmne.verbose()for details. Should only be passed as a keyword argument.
- x
- Returns:
- y
array The x array resampled.
- y
Notes
This uses (hopefully) intelligent edge padding and frequency-domain windowing improve scipy.signal.resample’s resampling method, which we have adapted for our use here. Choices of npad and window have important consequences, and the default choices should work well for most natural signals.
Resampling arguments are broken into “up” and “down” components for future compatibility in case we decide to use an upfirdn implementation. The current implementation is functionally equivalent to passing up=up/down and down=1.
Examples using mne.filter.resample#
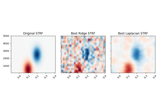
Spectro-temporal receptive field (STRF) estimation on continuous data