mne.preprocessing.create_eog_epochs#
- mne.preprocessing.create_eog_epochs(raw, ch_name=None, event_id=998, picks=None, tmin=-0.5, tmax=0.5, l_freq=1, h_freq=10, reject=None, flat=None, baseline=None, preload=True, reject_by_annotation=True, thresh=None, decim=1, verbose=None)[source]#
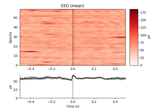
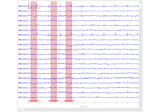
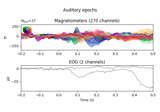
Conveniently generate epochs around EOG artifact events.
This function will:
Filter the EOG data channel.
Find the peaks of eyeblinks in the EOG data using
mne.preprocessing.find_eog_events().Create
Epochsaround the eyeblinks.
- Parameters:
- rawinstance of
Raw The raw data.
- ch_name
str|listofstr|None The name of the channel(s) to use for EOG peak detection. If a string, can be an arbitrary channel. This doesn’t have to be a channel of
eogtype; it could, for example, also be an ordinary EEG channel that was placed close to the eyes, likeFp1orFp2.Multiple channel names can be passed as a list of strings.
If
None(default), use the channel(s) inrawwith typeeog.- event_id
int The index to assign to found events.
- picks
str|list|slice|None Channels to include. Slices and lists of integers will be interpreted as channel indices. In lists, channel type strings (e.g.,
['meg', 'eeg']) will pick channels of those types, channel name strings (e.g.,['MEG0111', 'MEG2623']will pick the given channels. Can also be the string values “all” to pick all channels, or “data” to pick data channels. None (default) will pick all channels. Note that channels ininfo['bads']will be included if their names or indices are explicitly provided.- tmin
float Start time before event.
- tmax
float End time after event.
- l_freq
float Low pass frequency to apply to the EOG channel while finding events.
- h_freq
float High pass frequency to apply to the EOG channel while finding events.
- reject
dict|None Rejection parameters based on peak-to-peak amplitude. Valid keys are ‘grad’ | ‘mag’ | ‘eeg’ | ‘eog’ | ‘ecg’. If reject is None then no rejection is done. Example:
reject = dict(grad=4000e-13, # T / m (gradiometers) mag=4e-12, # T (magnetometers) eeg=40e-6, # V (EEG channels) eog=250e-6 # V (EOG channels) )
- flat
dict|None Rejection parameters based on flatness of signal. Valid keys are ‘grad’ | ‘mag’ | ‘eeg’ | ‘eog’ | ‘ecg’, and values are floats that set the minimum acceptable peak-to-peak amplitude. If flat is None then no rejection is done.
- baseline
tupleorlistof length 2, orNone The time interval to apply rescaling / baseline correction. If None do not apply it. If baseline is (a, b) the interval is between “a (s)” and “b (s)”. If a is None the beginning of the data is used and if b is None then b is set to the end of the interval. If baseline is equal to (None, None) all the time interval is used. If None, no correction is applied.
- preloadbool
Preload epochs or not.
- reject_by_annotationbool
Whether to reject based on annotations. If
True(default), epochs overlapping with segments whose description begins with'bad'are rejected. IfFalse, no rejection based on annotations is performed.New in version 0.14.0.
- thresh
float Threshold to trigger EOG event.
- decim
int Factor by which to subsample the data.
Warning
Low-pass filtering is not performed, this simply selects every Nth sample (where N is the value passed to
decim), i.e., it compresses the signal (see Notes). If the data are not properly filtered, aliasing artifacts may occur.New in version 0.21.0.
- verbosebool |
str|int|None Control verbosity of the logging output. If
None, use the default verbosity level. See the logging documentation andmne.verbose()for details. Should only be passed as a keyword argument.
- rawinstance of
- Returns:
- eog_epochsinstance of
Epochs Data epoched around EOG events.
- eog_epochsinstance of
See also
Notes
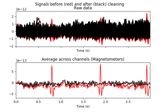
Filtering is only applied to the EOG channel while finding events. The resulting
eog_epochswill have no filtering applied (i.e., have the same filter properties as the inputrawinstance).