mne.read_cov#
- mne.read_cov(fname, verbose=None)[source]#
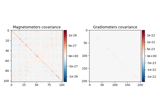
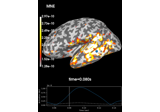
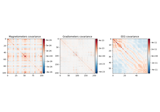
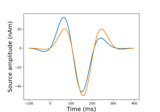
Read a noise covariance from a FIF file.
- Parameters:
- fname
str The name of file containing the covariance matrix. It should end with -cov.fif or -cov.fif.gz.
- verbosebool |
str|int|None Control verbosity of the logging output. If
None, use the default verbosity level. See the logging documentation andmne.verbose()for details. Should only be passed as a keyword argument.
- fname
- Returns:
- cov
Covariance The noise covariance matrix.
- cov
See also
Examples using mne.read_cov#
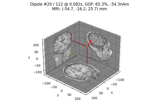
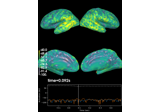
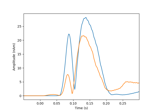
The role of dipole orientations in distributed source localization
Cortical Signal Suppression (CSS) for removal of cortical signals
Compute a sparse inverse solution using the Gamma-MAP empirical Bayesian method
Compute sparse inverse solution with mixed norm: MxNE and irMxNE
Compute MNE inverse solution on evoked data with a mixed source space
Computing source timecourses with an XFit-like multi-dipole model
Plot point-spread functions (PSFs) and cross-talk functions (CTFs)
Compute spatial resolution metrics in source space
Compute spatial resolution metrics to compare MEG with EEG+MEG