mne.preprocessing.find_eog_events#
- mne.preprocessing.find_eog_events(raw, event_id=998, l_freq=1, h_freq=10, filter_length='10s', ch_name=None, tstart=0, reject_by_annotation=False, thresh=None, verbose=None)[source]#
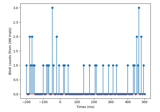
Locate EOG artifacts.
Note
To control true-positive and true-negative detection rates, you may adjust the
threshparameter.- Parameters:
- rawinstance of
Raw The raw data.
- event_id
int The index to assign to found events.
- l_freq
float Low cut-off frequency to apply to the EOG channel in Hz.
- h_freq
float High cut-off frequency to apply to the EOG channel in Hz.
- filter_length
str|int|None Number of taps to use for filtering.
- ch_name
str|listofstr|None The name of the channel(s) to use for EOG peak detection. If a string, can be an arbitrary channel. This doesn’t have to be a channel of
eogtype; it could, for example, also be an ordinary EEG channel that was placed close to the eyes, likeFp1orFp2.Multiple channel names can be passed as a list of strings.
If
None(default), use the channel(s) inrawwith typeeog.- tstart
float Start detection after tstart seconds.
- reject_by_annotationbool
Whether to omit data that is annotated as bad.
- thresh
float|None Threshold to trigger the detection of an EOG event. This controls the thresholding of the underlying peak-finding algorithm. Larger values mean that fewer peaks (i.e., fewer EOG events) will be detected. If
None, use the default of(max(eog) - min(eog)) / 4, witheogbeing the filtered EOG signal.- verbosebool |
str|int|None Control verbosity of the logging output. If
None, use the default verbosity level. See the logging documentation andmne.verbose()for details. Should only be passed as a keyword argument.
- rawinstance of
- Returns:
- eog_events
array Events.
- eog_events
See also